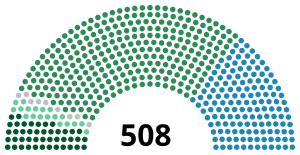
General elections were held in Italy on 26 October 1913, with a second round of voting on 2 November. The Liberals narrowly retained an absolute majority in the Chamber of Deputies, while the Radical Party emerged as the largest opposition bloc. Both groupings did particularly well in Southern Italy, while the Italian Socialist Party gained eight seats and was the largest party in Emilia-Romagna. However, the election marked the beginning of the decline of Liberal establishment.

A legislative election to elect the members of the 11th Imperial Council were held in Cisleithania, the northern and western ("Austrian") crown lands of Austria-Hungary, on 14 and 23 May 1907. They were the first elections held under universal male suffrage, after an electoral reform abolishing tax paying requirements for voters had been adopted by the Council and was endorsed by Emperor Franz Joseph earlier in the year. However, seat allocations were based on tax revenues from the States.

General elections were held in Italy on 27 January 1861, with a second round on 3 February. The newly elected Parliament first convened in Turin on 4 March 1861, where, thirteen days later, it declared the unification of the country as the Kingdom of Italy.

General elections were held in Italy on 22 October 1865, with a second round of voting on 29 October. It was the second one in the history of Italy.

Bettino Ricasoli resigned as Prime Minister of Italy on 10 April 1867, due to a recalcitrant Italian Chamber. The chamber disapproved of his agreements with the Vatican regarding the repatriation of certain religious properties. Subsequent to his resignation, general elections were held in Italy on 10 March 1867; with the second round of voting on 17 March 1867. These snap elections resulted in Urbano Rattazzi being elected once again to office.

General elections were held in Italy on 20 November 1870, with a second round of voting on 27 November. They were a snap election, called by Prime Minister Giovanni Lanza to take advantage by the Capture of Rome and to give parliamentary representation to the future capital of Italy.

The 1874 Italian general election was held in Italy on 8 November, with a second round of voting on 15 November. They were a snap election, called by Prime Minister Marco Minghetti to strengthen his majority.

The Italian general election of 1876 was held in Italy on 5 November, with a second round of voting on 12 November.

General elections were held in Italy on 16 May 1880, with a second round of voting on 23 May.

General elections were held in Italy on 23 May 1886, with a second round of voting on 30 May. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc emerged as the largest in Parliament, winning 292 of the 508 seats. As in 1882, the election was held using small multi-member constituencies with between two and five seats.

General elections were held in Italy on 23 November 1890, with a second round of voting on 30 November. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc emerged as the largest in Parliament, winning 401 of the 508 seats. As in 1886, the election was held using small multi-member constituencies with between two and five seats.

General elections were held in Italy on 6 November 1892, with a second round of voting on 13 November. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc emerged as the largest in Parliament, winning 323 of the 508 seats. The electoral system reverted to the pre-1882 method of using single-member constituencies with second round run-offs.

General elections were held in Italy on 3 June 1900, with a second round of voting on 10 June. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc remained the largest in Parliament, winning 296 of the 508 seats.

General elections were held in Italy on 6 November 1904, with a second round of voting on 13 November. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc remained the largest in Parliament, winning 339 of the 508 seats. The papal ban on Catholics voting was relaxed for the first time, and three Catholics were elected.

General elections were held in Italy on 7 March 1909, with a second round of voting on 14 March. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc remained the largest in Parliament, winning 329 of the 508 seats.

General elections were held in Liechtenstein on 11 March 1918, with a second round on 18 March. They were the first elections held in the country contested by political parties, as the Christian-Social People's Party and Progressive Citizens' Party had been founded that year. The Progressive Citizens' Party emerged as the largest in the Landtag, winning seven of the 12 elected seats.
The Dissident Left, commonly named The Pentarchy like its five leaders, was a progressive and radical parliamentary group active in Italy during the last decades of the 19th century.

The Liberal Union, simply and collectively called Liberals, was a political alliance formed in the first years of the 20th century by the Italian Prime Minister and leader of the Historical Left Giovanni Giolitti. The alliance was formed when the Left and the Right merged in a single centrist and liberal coalition which largely dominated the Italian Parliament.
See also: 1903 in Italy, other events of 1904, 1905 in Italy.