
Bulgaria elects on national level a head of state - the president - and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term directly by the people. The National Assembly has 240 members, elected for a four-year term by proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies with a 4% threshold. Bulgaria has a multi-party system, in which no one party often has a chance of gaining power alone, and parties must work with each to form governments.

Parliamentary elections were held in Macedonia on 18 October 1998, with a second round on 1 November. VMRO-DPMNE emerged as the largest party, winning 49 of the 120 seats, and later formed a coalition government with Democratic Alternative and the Democratic Party of Albanians.

Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 9 April 2006, with a second round of voting in 110 of the 176 single-member constituencies on 23 April. The Hungarian Socialist Party emerged as the largest party in the National Assembly with 186 of the 386 seats, and continued the coalition government with the Alliance of Free Democrats. It marked the first time a government had been re-elected since the end of Communist rule.

Folketing elections were held in Denmark on 22 April 1918, the first in which women could vote. The result was a victory for Venstre, which won 45 of the 180 seats in the Folketing, which had been expanded from 114 to 140 seats. Voter turnout was 75.5%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Russia on 12 December 1993. They included the last elections to the Federation Council of Russia.

Early parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 25 and 26 October 1959. Following the electoral reforms made after the June elections, the Independence Party won 16 of the 40 seats in the Lower House of the Althing.
The Third Amendment of the Constitution Bill 1958 was a proposal to amend the Constitution of Ireland to alter the electoral system from proportional representation under the single transferable vote (PR-STV) to first-past-the-post (FPTP). The proposal was rejected in a referendum held on 17 June 1959. This was the same date as the presidential election in which Taoiseach Éamon de Valera was elected as president.
Electoral reform is change in electoral systems to improve how public desires are expressed in election results. That can include reforms of:
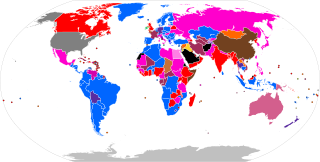
An electoral system is a set of rules that determine how elections and referendums are conducted and how their results are determined. Political electoral systems are organized by governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations.

Full general elections were held in Belgium on 14 October 1894, with run-off elections held on 21 October 1894.

General elections were held in Italy on 29 October 1882, with a second round of voting on 5 November. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc emerged as the largest in Parliament, winning 289 of the 508 seats.

A referendum on the electoral system was held in Slovenia on 8 December 1996. Voters were given three options to approve or not; a compensatory system, a two-round majority system and a proportional representation system at a national level. Due to the low turnout of 37.9%, none of the proposals crossed the legal threshold and the results were invalidated. However, in 1998 the results were revisited by the Constitutional Court, who found that the two round majority system had been approved.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 27 October 1923. Voters elected all 28 seats in the Lower House of the Althing and eight of the fourteen seats in Upper House. The Citizens' Party, a loose collection of conservatives, emerged as the largest party in the Lower House, winning 16 of the 28 seats.

A referendum on the electoral system was held in Liechtenstein on 30 May 1935. Voters were asked whether they approved of introducing a system using proportional representation. The proposal was rejected by 52.7% of voters. Nevertheless, a proportional system was later adopted in 1939.

Constituent Assembly elections were held in Portugal on 28 May 1911, following a coup in October 1910. The result was a victory for the Portuguese Republican Party, which won 229 of the 234 seats.
A referendum on the electoral system was held in Switzerland on 23 October 1910. Voters were asked whether they approved of introducing proportional representation for National Council elections. Although the proposal was approved by a majority of cantons, it was rejected by 52.5% of voters. This was the second such referendum, after the one in 1900 also failed. However, a third referendum on the same issue was held in 1918, and passed with 66.8% in favour.

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 26 October 1902. The Free Democratic Party retained its majority in the National Council.

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 29 October 1911. The Free Democratic Party retained its majority in the National Council.

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 28 October 1917. The Free Democratic Party retained its majority in the National Council. They were the last elections held under the majoritarian system; following a referendum in 1918 in which two-thirds of voters voted for the introduction of proportional representation, the electoral system was changed and early elections held in 1919.















