The Alawite State, initially named the Territory of the Alawites, after the locally-dominant Alawites from its inception until its integration to the Syrian Federation in 1922, was a French mandate territory on the coast of present-day Syria after World War I. The French Mandate from the League of Nations lasted from 1920 to 1946.

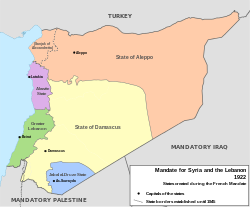
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon was a League of Nations mandate founded in the aftermath of the First World War and the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire, concerning Syria and Lebanon. The mandate system was supposed to differ from colonialism, with the governing country intended to act as a trustee until the inhabitants were considered eligible for self-government. At that point, the mandate would terminate and a sovereign state would be born.

The Great Syrian Revolt, also known as the Revolt of 1925, was a general uprising across the State of Syria and Greater Lebanon during the period of 1925 to 1927. The leading rebel forces initially comprised fighters of the Jabal Druze State in southern Syria, and were later joined by Sunni, Druze and Shiite and factions all over Syria. The common goal was to end French occupation in the newly mandated regions, which passed from Turkish to French administration following World War I.

Salkhad is a Syrian city in the As-Suwayda Governorate, southern Syria. It is the capital of Salkhad District, one of the governorate's three districts. It has a population of 15,000 inhabitants.
The al-Atrash, also known as Bani al-Atrash, is a Druze clan based in Jabal Hauran in southwestern Syria. The family's name al-atrash is Arabic for "the deaf" and derives from one the family's deaf patriarchs. The al-Atrash clan migrated to Jabal Hauran in the early 19th century, and under the leadership of their sheikh (chieftain) Ismail al-Atrash became the paramount ruling Druze family of Jabal Hauran in the mid-19th century, taking over from Al Hamdan. Through his battlefield reputation and his political intrigues with other Druze clans, Bedouin tribes, Ottoman authorities and European consuls, Ismail consolidated al-Atrash power. By the early 1880s, the family controlled eighteen villages, chief among which were as-Suwayda, Salkhad, al-Qurayya, 'Ira and Urman.

Sultan al-Atrash was a Syrian nationalist revolutionary who led the Great Syrian Revolt against the French colonial administration in Syria.

Abd al-Rahman Shahbandar was a prominent Syrian nationalist during the French Mandate of Syria and a leading opponent of compromise with French authority. His devotion to Arab nationalism dated to the days of the Committee of Union and Progress and its "Turkification" policies. He supported the Arab Revolt during World War I and briefly headed the foreign ministry under Emir Faisal.

The State of Aleppo was one of the six states that were established by the French High Commissioner of the Levant, General Henri Gouraud, in the French Mandate of Syria which followed the San Remo conference and the collapse of King Faisal I's short-lived Arab monarchy in Syria.

The Battle of al-Mazra'a was one of the major battles of the Great Syrian Revolt, that led to the spread of the rebellion throughout the French Mandate of Syria. It was fought on 2–3 August 1925 between Druze and Bedouin rebels led by Sultan Pasha al-Atrash and a heavily armed French force of the Army of the Levant near the town of al-Mazraa, around 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) northwest of the city of al-Suwayda.

The Hauran Druze Rebellion was a violent Druze uprising against Ottoman authority in the Syrian province, which erupted in 1909. The rebellion was led by the al-Atrash family, in an aim to gain independence, but ended in brutal suppression of the Druze, significant depopulation of the Hauran region and execution of the Druze leaders.

The State of Syria was a French Mandate state created by decree of 5 December 1924, with effect from 1 January 1925, from the union of the State of Aleppo and the State of Damascus. It was the successor of the Syrian Federation (1922–1924) which had been created by providing a central assembly for the State of Aleppo, the State of Damascus and the Alawite State. The Alawite State did not join the State of Syria.

Mansur al-Atrash was a Syrian politician and journalist. Together with fellow university students, Atrash became a founding member of the Ba'ath Party and its Syrian regional branch in 1947. During the presidency of Adib Shishakli (1951–54), he became an anti-government activist and was imprisoned twice, only to be released in an unsuccessful attempt by Shishakli to gain the support of Atrash's father, Sultan. In the year Shishakli was overthrown, Atrash was elected to parliament and turned down an offer to serve in Said al-Ghazzi's government. During the period of the United Arab Republic (1958–61), Atrash became a strong supporter of Egyptian president and pan-Arab leader Gamal Abdel Nasser. He opposed Syria's secession from the UAR and turned down offers to serve in successive separatist governments in protest.
Al-Qurayya is a town in southern Syria, administratively part of the al-Suwayda Governorate, located south of al-Suwayda. Nearby localities include Bosra to the southwest, Hout to the south, Salkhad to the southeast, al-Kafr, Hibran and Sahwat al-Khudr to the northeast, Sahwat Bilata and Rasas to the north and 'Ara and al-Mujaymer to the northwest. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), al-Qurayya had a population of 6,789 in the 2004 census. The town is also the administrative center of the al-Qurayya nahiyah which consists of four towns with a combined population of 9,892.

The Battle of al-Musayfirah was one of the major military engagements between Druze rebels and the French Army on 17 September 1925, during the early stage of the Great Syrian Revolt, which continued on until 1927. After initial rebel victories against French forces at al-Kafr and then al-Mazraa, an advance guard of the French Army, then under the leadership of General Maurice Gamelin, was dispatched to the village of al-Musayfirah on 15 September. After clearing the village of its inhabitants, they set up fortifications in preparation for an assault on al-Suwayda.
The capture of Salkhad refers to the clash between the Druze rebel forces of Sultan Pasha al-Atrash and a unit of the French Mandate based in Salkhad on 20 July 1925. It would become the first confrontation of the Great Syrian Revolt. Preceding the battle, on 19 July, al-Atrash's forces shot down a French reconnaissance plane, the first shots of the revolt, and captured its injured pilots. The next day, rebels captured Salkhad and its French garrison without facing significant resistance.
The 1925 Hama uprising was one of the major events of the Great Syrian Revolt. It involved a rebel assault led by Fawzi al-Qawuqji against Mandatory French security installations in Hama and a subsequent uprising by residents sympathetic to the rebel cause. Heavy French bombardment of the city and the dispatch of reinforcements followed. The hostilities began on 4 October 1925 and negotiations between a delegation of Hama's leading families and the French authorities resulted in the rebels' withdrawal on 5 October.

Sa'id al-'As was a Syrian nationalist, a former officer in the Ottoman army and a high-ranking commander of rebel forces during the Great Syrian Revolt against French rule in Syria and the 1936 revolt against British rule in Palestine. He was killed in action near Jerusalem during the latter uprising.

Nasib al-Bakri was a Syrian politician and nationalist leader in the first half of the 20th century. He played a major role in establishing al-Fatat, an underground organization which sought the independence and unity of the Ottoman Empire's Arab territories. As the chief envoy between al-Fatat and the Hejaz-based Hashemites, al-Bakri became a close aide to Emir Faisal when the latter became King of Syria following the success of the 1916 Arab Revolt. Al-Bakri opposed the establishment of the French Mandate of Syria and became one of the chief commanders of the Great Syrian Revolt, leading the rebels' brief capture of Damascus. He escaped a death warrant in Syria in 1927, but returned the following year after being amnestied.
The Battle of al-Kafr was a military engagement between a French Army column commanded by Captain Gabriel Normand and the local Druze and Bedouin forces of Sultan al-Atrash on 22 July 1925. It occurred at Normand's encampment at the village of al-Kafr, in the southern Syrian region of Jabal al-Druze. The battle was a rout for the French, who were ambushed by Sultan's forces. Sultan's victory prompted an upswing of support for him by the Druze and by the end of July, his forces controlled Jabal al-Druze. The battle precipitated the countrywide Great Syrian Revolt.