Related Research Articles

Plesetsk Cosmodrome is a Russian spaceport located in Mirny, Arkhangelsk Oblast, about 800 km north of Moscow and approximately 200 km south of Arkhangelsk. As of 2024, it is Europe's only operational orbital spaceport and the northernmost spaceport in the world. Originally developed as an ICBM site for the R-7 missile, it also served for numerous satellite launches using the R-7 and other rockets. Its high latitude makes it useful only for certain types of launches, especially the Molniya orbits, so for much of the site's history it functioned as a secondary location, with most orbital launches taking place from Baikonur, in the Kazakh SSR. With the end of the Soviet Union, Baikonur became a foreign territory, and Kazakhstan charged $115 million usage fees annually. Consequently, Plesetsk has seen considerably more activity since the 2000s.
Kosmos is a designation given to many satellites operated by the Soviet Union and subsequently Russia. Kosmos 1, the first spacecraft to be given a Kosmos designation, was launched on 16 March 1962.
Kosmos 140, Soyuz 7K-OK No.3, was an uncrewed flight of the Soyuz spacecraft. It was the third attempted test flight of the Soyuz 7K-OK model, after orbital and launch failures of the first two Soyuz spacecraft.

Kosmos 690 or Bion 2(in Russian: Бион 2, Космос 690), was a Bion satellite launched by the Soviet Union in late 1974.

Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188 were two uncrewed Soviet Union spacecraft that incorporated a Soyuz programme descent module for landing scientific instruments and test objects.
Meridian 2, also known as Meridian No.12L, was a Russian communications satellite. It was the second satellite of the Meridian system, which replaced the older Molniya series. It followed on from Meridian 1, which was launched in December 2006.

Kosmos 4, also known as Zenit-2 No.2 and occasionally in the West as Sputnik 14 was the first Soviet reconnaissance satellite to successfully reach orbit.

Kosmos 9, also known as Zenit-2 No.5, was a Soviet reconnaissance satellite launched in 1962. It was the ninth satellite to be designated under the Kosmos system, and the third successful launch of a Soviet reconnaissance satellite, following Kosmos 4 and Kosmos 7.

Kosmos 10, also known as Zenit-2 No.6, was a Soviet reconnaissance satellite launched in 1962. It was the tenth satellite to be designated under the Kosmos system, and the fourth successful launch of a Soviet reconnaissance satellite, following Kosmos 4, Kosmos 7 and Kosmos 9.
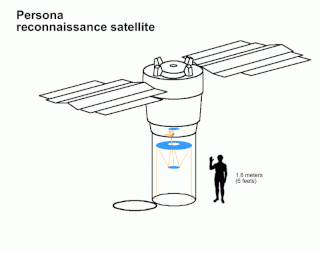
Kosmos 2441, also known as Persona No.1, was a Russian optical reconnaissance satellite launched in 2008. The first Persona satellite, it failed a few months into its mission, which was scheduled to have lasted three to five years. It was the first Russian reconnaissance satellite to be placed into a Sun-synchronous orbit.
Kosmos 2471, also known as Glonass-K1 No. 11L or Glonass-K No. 701, was a Russian navigation satellite which was launched in 2011. The first Glonass-K satellite to be launched, it was one of two Glonass-K1 spacecraft which served as prototypes for the operational Glonass-K2 spacecraft.
EKSKupol is a developing programme of Russian early warning satellites as a replacement for the US-KMO and US-K satellites of the Oko programme. The satellites are designed to identify any possible future ballistic missile launches, from outer space, and complement early warning radars such as the Voronezh. This gives advance notice of a nuclear attack and would provide information to the A-135 missile defence system which protects Moscow, as well as other Russian missile defense and counterattack resources. Six satellites are planned to be initially orbited. The first of these was launched on 17 November 2015 and as of November 2022, all six of them are in service.
Kosmos 2478 is a Russian military satellite launched in 2011 as part of the GLONASS satellite navigation system.

Kosmos 2501, also known as Glonass-K1 No.12L is a Russian navigation satellite which was launched in 2014. The second Glonass-K satellite to be launched, it is the second of two Glonass-K1 spacecraft which will serve as prototypes for the operational Glonass-K2 spacecraft.

Kosmos 2514 is a Russian military satellite launched in 2016 as part of the GLONASS satellite navigation system.

Kosmos 2516 is a Russian military satellite launched in 2016 as part of the GLONASS satellite navigation system.

Kosmos 2522 is a Russian military satellite launched in 2017 as part of the GLONASS satellite navigation system.

Kosmos 2527 is a Russian military satellite launched in 2018 as part of the GLONASS satellite navigation system.

Kosmos 2529 is a Russian military satellite launched in 2018 as part of the GLONASS satellite navigation system.
References
- 1 2 3 "Technical details for satellite COSMOS 2524". N2YO.com - Real Time Satellite Tracking and Predictions. Retrieved 2021-12-10.
- 1 2 3 "Lotos-S1 (14F145)". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2021-12-10.
- ↑ Hyl, Philip; s (2017-12-04). "Russia launches electronic intelligence satellite Cosmos 2524 in quick Soyuz 2 operational return". Seradata. Retrieved 2021-12-10.