Related Research Articles

FalconSAT is the United States Air Force Academy's (USAFA) small satellite engineering program. Satellites are designed, built, tested, and operated by Academy cadets. The project is administered by the USAFA Space Systems Research Center under the direction of the Department of Astronautics. Most of the cadets who work on the project are pursuing a bachelor of science degree in astronautical engineering, although students from other disciplines join the project.

Soyuz-2 is a modernised version of the Soviet Soyuz rocket. In its basic form, it is a three-stage launch vehicle for placing payloads into low Earth orbit. Compared to the previous versions of the Soyuz, the first-stage boosters and two core stages feature uprated engines with improved injection systems. Digital flight control and telemetry systems allow the rocket to be launched from a fixed launch platform, whereas the launch platforms for earlier Soyuz rockets had to be rotated as the rocket could not perform a roll to change its heading in flight.

GeoEye Inc. was an American commercial satellite imagery company based in Herndon, Virginia. GeoEye was merged into the DigitalGlobe corporation on January 29, 2013.

This comparison of orbital launch systems lists the attributes of all individual rocket configurations designed to reach orbit. A first list contains rockets that are operational or in development as of 2023; a second list includes all upcoming rockets and a third list includes all retired rockets. For the simple list of all conventional launcher families, see: Comparison of orbital launchers families. For the list of predominantly solid-fueled orbital launch systems, see: Comparison of solid-fueled orbital launch systems.

The year 2011 saw a number of significant events in spaceflight, including the retirement of NASA's Space Shuttle after its final flight in July 2011, and the launch of China's first space station module, Tiangong-1, in September. A total of 84 orbital launches were conducted over the course of the year, of which 78 were successful. Russia, China and the United States conducted the majority of the year's orbital launches, with 35, 19 and 18 launches respectively; 2011 marked the first year that China conducted more successful launches than the United States. Seven crewed missions were launched into orbit during 2011, carrying a total of 28 astronauts to the International Space Station. Additionally, the Zenit-3F and Long March 2F/G carrier rockets made their maiden flights in 2011, while the Delta II Heavy made its last.

In 2015, the maiden spaceflights of the Chinese Long March 6 and Long March 11 launch vehicles took place.

Several new rockets and spaceports began operations in 2016.

This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2019.

Notable spaceflight activities in 2017 included the maiden orbital flight of India's Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III on 5 June and the first suborbital test of Rocket Lab's Electron rocket, inaugurating the Mahia spaceport in New Zealand. The rocket is named for its innovative Rutherford engine which feeds propellants via battery-powered electric motors instead of the usual gas generator and turbopumps.

This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2018. For the first time since 1990, more than 100 orbital launches were performed globally.

Planet Labs PBC is a publicly trading American Earth imaging company based in San Francisco, California. Their goal is to image the entirety of the Earth daily to monitor changes and pinpoint trends.
Progress MS-06, identified by NASA as Progress 67P, was a Progress spaceflight operated by Roscosmos to resupply the International Space Station (ISS). It was launched on 14 June 2017.
Cartosat-2E is an Earth observation satellite developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), and is the seventh in the Cartosat series. It is designed to collect high-resolution, large-scale imagery for use in urban planning, infrastructure development, utilities planning, and traffic management.

PSLV-C37 was the 39th mission of the Indian Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) program and its 16th mission in the XL configuration undertaken by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Launched on 15 February 2017 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, the rocket successfully carried and deployed a record number of 104 satellites in Sun-synchronous orbits in a single mission, breaking the earlier record of launching 37 satellites by a Russian Dnepr rocket on 19 June 2014. This record was held until the launch of the Transporter-1 mission by SpaceX on 24 January 2021 which launched 143 satellites.

This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2020.
ICEYE Ltd. is a Finnish microsatellite manufacturer. ICEYE was founded in 2014 as a spin-off of Aalto University's University Radio Technology Department, and is based in Espoo.
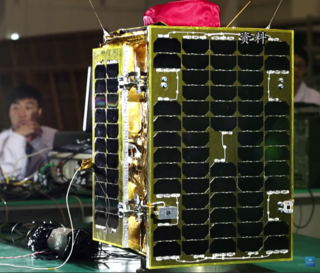
Jilin-1 is China's first self-developed commercial remote sensing satellite system. The satellites are operated by Chang Guang Satellite Technology Corporation and named after Jilin Province where the company is headquartered. The first set of satellites were launched by Long March 2D in Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center on 7 October 2015, at 04:13 UTC. All launched Jilin-1 satellites are in Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO).

Kanopus-V-IK is a Russian Earth observation satellite developed by the All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Electromechanics and operated by Roscosmos. It was launched on July 14, 2017, designed for monitoring the environment over a large swath of land, and has an expected service life of 5 years.
References
- ↑ "Astro Digital Landmapper Constellation Orbital Debris Assessment Report". 8 April 2017. Retrieved 20 October 2018.
- ↑ Krebs, Gunter. "Landmapper-BC 1, ..., 12 (Corvus-BC 1, ..., 12)". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 20 October 2018.
- ↑ "Landmapper-BC 1, ..., 12 (Corvus-BC 1, ..., 12)".
- ↑ "Landmapper-HD 1, ..., 20 (Corvus-HD 1, ..., 20)".
- ↑ "Vector micro-rocket launch w/ Astro Digital". 3 August 2017.