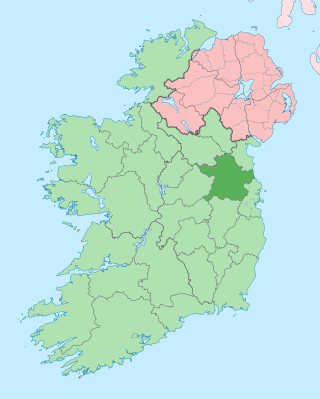
County Meath is a county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Ireland, within the province of Leinster. It is bordered by County Dublin to the southeast, Louth to the northeast, Kildare to the south, Offaly to the southwest, Westmeath to the west, Cavan to the northwest, and Monaghan to the north. To the east, Meath also borders the Irish Sea along a narrow strip between the rivers Boyne and Delvin, giving it the second shortest coastline of any county. Meath County Council is the local authority for the county.

Clondalkin is a suburban town in County Dublin, 10 km (6 mi) west of Dublin city centre, Ireland, under the administrative jurisdiction of South Dublin. It features an 8th-century round tower that acts as a focal point for the area.

Julianstown is a village in County Meath, Ireland. It is located near Drogheda on the R132 regional road. In 1641, the Battle of Julianstown was fought here during the Irish Rebellion of 1641.

Laytown railway station serves Laytown and Bettystown in County Meath, Ireland.

Kingscourt, historically known as Dunaree, is a town in County Cavan, Ireland. It is located near the Cavan–Meath border. The town was founded near the site of the old village of Cabra, by Mervyn Pratt, towards the end of the 18th century, and was completed by his brother, the Reverend Joseph Pratt. As of the 2022 census, the population was 2,955.

The Diocese of Meath is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church that is located in the middle part of Ireland. It is one of eight suffragan dioceses of the ecclesiastical province of Armagh. Thomas Deenihan has been bishop of the diocese since 2 September 2018.

Bettystown, previously known as Betaghstown and transliterated to Beattystown/Bettystown, is a village in County Meath, Ireland. Together with the neighbouring villages of Laytown, Mornington and Donacarney, it comprises the urban area of Laytown–Bettystown–Mornington–Donacarney with a combined population of 15,642 at the 2022 census. During the Celtic Tiger, with increasing property prices in Dublin, Bettystown expanded to cater for large numbers of commuters to Dublin. The area was well known before that as a spot for Dublin summer holiday visitors, with a number of caravan parks and seaside amusements.

Mornington is a coastal village on the estuary of the River Boyne in County Meath, Ireland approximately 5 km downriver from the centre of Drogheda. Together with the neighbouring villages of Laytown, Bettystown and Donacarney, it comprises the urban area of Laytown–Bettystown–Mornington–Donacarney with a combined population of 15,642 at the 2022 census.

Laytown–Bettystown–Mornington–Donacarney is a built up area in County Meath, Ireland, comprising the adjoining villages of Laytown, Bettystown, Mornington and Donacarney. Prior to 2016, it was listed as Laytown–Bettystown–Mornington.

Kentstown is a village in County Meath in Ireland at the junction of the R153 and R150 regional roads. The village is in a townland and civil parish of the same name.

Donacarney is a village in County Meath, Ireland, close to Drogheda and the border with County Louth. It contains one church, two estates, two schools, and one pub. Although it includes the townlands of Donacarney Great and Donacarney Little, most locals would never use those terms in describing Donacarney. The remains of a late-medieval tower house are sited close to Donacarney Cross. It is described in the Down Survey (1654–56) as "an ould Castle". It appears in this state on a map of 1771. Blackhills Crescent, Donacarney, takes its name from the area known as the Black Hills or Black Hill Lands north of the crossroads and the castle, the old name of which was Croc a' Searra in Irish.

The River Nanny, also called the Nanny Water, is a river that flows from Kentstown into the Irish Sea at Laytown. The river is known for its trout fishing, and its estuary on the Irish sea provides a haven for wintering birds.

The R150 road is a regional road in Ireland. It runs from Drogheda to the Meath coast and back inland across east County Meath.
Catholic Education, an Irish Schools Trust (CEIST) is the trustee body for 107 Catholic Voluntary Secondary Schools in Ireland. CEIST provides the moral and legal framework that enable its schools to offer second level Catholic education in Ireland. Its role is built on the vision of its five founding congregations Daughters of Charity, Presentation Sisters, Sisters of the Christian Retreat, Sisters of Mercy and Missionaries of the Sacred Heart. These religious congregations established CEIST in 2007 to ensure the viability of Catholic Education at post-primary level in Ireland into the future.
Clinton Liberty is an Irish actor and dancer of Nigerian and Jamaican descent. He is known for his roles in the ITV miniseries Holding (2022) and the HBO series House of the Dragon (2024–).
Coláiste na hInse, colloquially referred to by locals as The Coláiste, is a co-educational secondary school in Bettystown, County Meath, Ireland. Whilst English is the Coláiste's primary language of instruction, it places an emphasis on the use of Irish on a day to day basis.

Mornington Lifeboat Station is a former Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI) station in the village of Mornington, on the south side of the River Boyne estuary, near Drogheda in County Meath, Ireland.


















