Related Research Articles

A fructan is a polymer of fructose molecules. Fructans with a short chain length are known as fructooligosaccharides. Fructans can be found in over 12% of the angiosperms including both monocots and dicots such as agave, artichokes, asparagus, leeks, garlic, onions, yacón, jícama, barley and wheat.
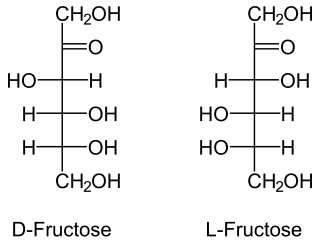
Fructosides are glycosides where the glycone group is fructose.
Serine dehydratase or L-serine ammonia lyase (SDH) is in the β-family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent (PLP) enzymes. SDH is found widely in nature, but its structural and properties vary among species. SDH is found in yeast, bacteria, and the cytoplasm of mammalian hepatocytes. SDH catalyzes is the deamination of L-serine to yield pyruvate, with the release of ammonia.
The enzyme 3-ketovalidoxylamine C-N-lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme diaminopimelate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.20) catalyzes the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds in meso 2,6 diaminoheptanedioate to produce CO2 and L-lysine, the essential amino acid. It employs the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate, also known as PLP, which participates in numerous enzymatic transamination, decarboxylation and deamination reactions.
The enzyme glucuronan lyase catalyzes the following process:
The enzyme inulin fructotransferase (DFA-I-forming) catalyzes the following process:
The enzyme inulin fructotransferase (DFA-III-forming) catalyzes the following process:
The enzyme fructose-2,6-bisphosphate 6-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.54) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a difructose-anhydride synthase (EC 3.2.1.134) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,1-fructan:2,1-fructan 1-fructosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 6G-fructosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inulosucrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Levansucrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
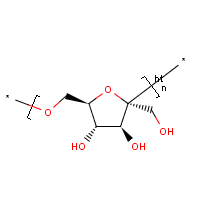
Levan is a naturally occurring fructan present in many plants and microorganisms. This polymer is made up of fructose, a monosaccharide sugar, connected by 2,6 beta glycosidic linkages. Levan can have both branched and linear structures of relatively low molecular weight. Branched levan forms a very small, sphere-like structure with basal chains 9 units long. The 2,1 branching allows methyl ethers to form and create a spherical shape. The ends of levan also tend to contain a glucosyl residue. Branched levan tends to be more stable than the linear structure. However, the amount of branching and length of polymerization tends to vary among different species. The shortest levan is 6-kestose, a chain of two fructose molecules and a terminal glucose molecule.
2,6-β-Fructan 6-levanbiohydrolase is an enzyme with systematic name (2→6)-β-D-fructofuranan 6-(β-D-fructosyl)-D-fructose-hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Levanase is an enzyme with systematic name (2→6)-β-D-fructan fructanohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Fructan β-fructosidase is an enzyme with systematic name β-D-fructan fructohydrolase. It catalyses the hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (2→1)- and (2→6)-linked β-D-fructofuranose residues in fructans.
Fructan beta-(2,6)-fructosidase is an enzyme with systematic name (2->6)-beta-D-fructan fructohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Kestose is a class of sugars that belongs to a group of fructooligosaccharides.
References
- Song KB, Bae KS, Lee YB, Lee KY, Rhee SK (2000). "Characteristics of levan fructotransferase from Arthrobacter ureafaciens K2032 and difructose anhydride IV formation from levan". Enzyme and Microbial Technology. 27 (3–5): 212–218. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(00)00135-6.
- Rhee SK; Ryu, EJ; Park, BS; Song, KB; Kang, SA; Kim, CH; Uhm, TB; Park, YI; Rhee, SK (2003). "Levan fructotransferase from Arthrobacter oxydans J17-21 catalyzes the formation of the di-D-fructose dianhydride IV from levan". J. Agric. Food Chem. 51 (9): 2632–6. doi:10.1021/jf026207o. PMID 12696949.
- Saito K, Tomita F (2000). "Difructose anhydrides: their mass-production and physiological functions". Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 64 (7): 1321–7. doi: 10.1271/bbb.64.1321 . PMID 10945246.