Rhodes is an Inner West suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Rhodes is located 12 kilometres west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Canada Bay. It was formerly part of Concord Municipality until a merger with Drummoyne Council to form Canada Bay in December 2000.

The Inner West of Sydney is an area directly west of the Sydney central business district, New South Wales, Australia. The suburbs that make up the Inner West are predominantly located along the southern shore of Port Jackson, stretching south to the shores of the Cooks River. The western boundary of the Inner West is approximately the A3 arterial road, which divides the Inner West from the Greater Western Sydney region. The Inner West is much larger than the Inner West Council local government area. The Inner West roughly corresponds with the Parish of Petersham and Parish of Concord, two cadastral divisions used for land titles.

Summer Hill is a suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Summer Hill is located 7 kilometres west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the Inner West Council.

Haberfield is a suburb in the Inner West of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Haberfield is located 6.5 kilometres west of the Sydney central business district in the local government area of the Inner West Council.

Strathfield is a suburb in the Inner West of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is located 12 kilometres west of the Sydney central business district and is the administrative centre of the Municipality of Strathfield. A small section of the suburb north of the railway line lies within the City of Canada Bay, while the area east of The Boulevard lies within the Municipality of Burwood. North Strathfield and Strathfield South are separate suburbs to the north and south, respectively.

Marrickville is a suburb in the Inner West of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Marrickville is located 7 kilometres south-west of the Sydney central business district and is the largest suburb in the Inner West Council local government area.

The Wangal people are a clan of the Dharug Aboriginal people whose heirs are custodians of the lands and waters of what is now the Inner West of Sydney, New South Wales, centred around the Municipality of Strathfield, Municipality of Burwood, City of Canada Bay and former Ashfield Council and extending west into the City of Parramatta.

Petersham is a suburb in the Inner West of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Petersham is located 6 kilometres south-west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of Inner West Council. Petersham is known for its extensive Portuguese commercial offerings, with many Portuguese businesses and restaurants, although only 156 (1.9%) of the population was actually born in Portugal.

Stanmore is a suburb in the Inner West of Sydney, in New South Wales, Australia 3 kilometres south west of the Sydney central business district. It is part of the local government area of the Inner West Council. It is known for its long strip of shops running along Parramatta Road.

Croydon is a suburb in the Inner West of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is located 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) west of the Sydney central business district. Croydon is split between the two local government areas of Municipality of Burwood and the Inner West Council.

Burwood is a suburb in the Inner West of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) west of the Sydney central business district and is the administrative centre for the local government area of Municipality of Burwood.

Rozelle is a suburb in the inner west of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is located 4 kilometres west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the Inner West Council.
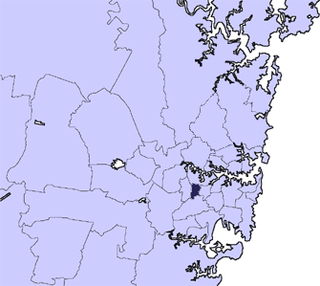
The Municipality of Burwood is a local government area in the inner-west of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. The mayor of the Municipality is Cr. John Faker, a member of the Labor Party. The municipality is 7 km2, making it the second smallest Local Government Area in New South Wales, being larger than only Hunter's Hill.

The Municipality of Leichhardt was a local government area in the inner-west region of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. It is about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) west of the Sydney central business district. On 12 May 2016, Leichhardt merged with Marrickville Council and the Municipality of Ashfield to form the Inner West Council.

St Peters is a suburb in the Inner West of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is 7 kilometres south of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of Inner West Council, with a small section in the southeast in the City of Sydney.
The Gadigal, also spelled as Cadigal and Caddiegal, are a group of Aboriginal people whose traditional lands are located in Gadi, on Eora country, the location of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. However, since the colonisation of Australia, most Gadigal people have been displaced from their traditional lands.

Lewisham Sewage Aqueduct is a heritage-listed sewage aqueduct in Gadigal Reserve, adjacent to 5 Grosvenor Crescent, Summer Hill, Inner West Council, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Sewerage Construction Branch and Department of Public Works and built in 1900. The property is owned by Sydney Water. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 18 November 1999.

Lewisham Sewer Vent is a heritage-listed sewer vent shaft at The Boulevarde, Lewisham, Inner West Council, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by NSW South Wales Public Works Department and built from 1909 to 1909. It is also known as The Boulevarde Sewer Vent. The property is owned by Sydney Water. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 15 November 2002.

The Long Cove Creek railway viaducts are heritage-listed railway viaducts which carry the Main Suburban railway line over Long Cove Creek between the suburbs of Lewisham and Summer Hill in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The viaducts were designed and built by the New South Wales Government Railways. The property is owned by Transport Asset Holding Entity, an agency of the Government of New South Wales. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.
New South Wales Aboriginal Education Consultative Group Office, abbreviated as NSW Aboriginal Education Consultative Group Office, is a heritage-listed former Aboriginal land, farm and house and now education centre and teacher-training facility at 37 Cavendish Street, Stanmore, Inner West Council, New South Wales, Australia. It was built from 1887 to 1888. It is also known as NSW Aboriginal Education Consultative Group Office and Records and NSW AECG Office. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 19 January 2018.