
Giza is the third-largest city in Egypt by area after Cairo and Alexandria; and fourth-largest city in Africa by population after Kinshasa, Lagos, and Cairo. It is the capital of Giza Governorate with a total population of 4,872,448 in the 2017 census. It is located on the west bank of the Nile opposite central Cairo, and is a part of the Greater Cairo metropolis. Giza lies less than 30 km (18.64 mi) north of Memphis, which was the capital city of the unified Egyptian state during the reign of pharaoh Narmer, roughly 3100 BC.

Medinet Habu is an archaeological locality situated near the foot of the Theban Hills on the West Bank of the River Nile opposite the modern city of Luxor, Egypt. Although other structures are located within the area and important discoveries have also been made at these sites, the location is today associated almost synonymously with the largest and best preserved site, the Mortuary Temple of Ramesses III.
El Araba El Madfuna is a town in Egypt. It is located south of Sohag.

Kafr El Sheikh is an Egyptian city and the capital of Kafr El Sheikh Governorate, Egypt, about 134 km north of Cairo, in the Nile Delta of lower Egypt. As of November 2006, the town had a population of around 500,000.
Belqas is a town located in the north-western corner of the Dakahlia Governorate in Egypt.
Hebenu or Alabastron was a city in ancient Egypt. It was located in Middle Egypt, or the Heptanomy, and belonged to the Hare nome (𓉆. It was the early capital of the Oryx nome (𓉇. The modern village of Zawiyat al-Amwat is built on the site where the ancient city stood.

Abu Tig is a city in the Asyut Governorate of Egypt. Located on the west bank of the Nile, it has a population of 70,969 inhabitants (2006).

Medinet Madi, also known simply as Madi or Maadi (ماضي) in Arabic, is a site in the southwestern Faiyum region of Egypt with the remains of a Greco-Roman town where a temple of the cobra-goddess Renenutet was founded during the reigns of Amenemhat III and Amenemhat IV. It was later expanded and embellished during the Greco-Roman period. In the Middle Kingdom the town was called Dja, later the town was known as Narmouti, Narmouthis and Narmuda.
Hurbayt is a town in Sharqia Governorate of Egypt.
Mit Okba or Mit Akaba is a former village, that was incorporated in the 1950s as two shiakhas in the Agouza district of Giza, Egypt, as the real estate development of Madinat al-Awqaf was built on its fileds. Many of the original houses, and much of the narrow street fabric remains today.

Biba is a city in Beni Suef Governorate, Egypt. It contains a cathedral that dates back to the sixth century, although the building that stands today was built in the 19th century.

Damanhur is a city in Lower Egypt, and the capital of the Beheira Governorate. It is located 160 km (99 mi) northwest of Cairo, and 70 km (43 mi) E.S.E. of Alexandria, in the middle of the western Nile Delta. Damanhur is a historic city, which history can be dated back to the Old Kingdom of Egypt. The modern city has also absorbed the ancient villages Shubra al-Jadida, Tāmus, Askanida and Chortaso.

Fuwwah is a city in the Kafr El Sheikh Governorate, Egypt.
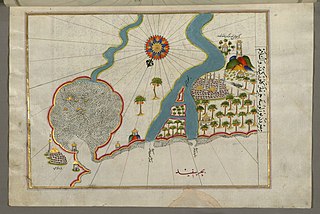
Bashmur was a region in the Nile Delta in Egypt. In the early Middle Ages, it was inhabited by Copts (Egyptians) and was the scene of a series of revolts against Arab occupation in the 8th and 9th centuries.
Agnou was an ancient city and bishopric in Egypt. It was located on the strip of land between the lake Burullus and the Mediterranean Sea, near the modern village al-Hanafi al-Kubra.
Zawyat Razin, formerly Shubra al-Laun and Ibshāda known in Antiquity as Nikiû, Nikiou or Nikious, is a city in the Monufia Governorate, Egypt.
Kafr El Battikh is a city in the Damietta Governorate, Egypt. Its population was estimated at 44,700 people in 2018.
Idfa is a village in Sohag Governorate in Upper Egypt located 6.4 km (4.0 mi) from the nearby city of Sohag. In antiquity, it was known by the ancient Egyptians as Iteb, then it was named by the Greeks as Itos.
Mahallat Menouf is a village in the Gharbia Governorate of Egypt.

Coptic names refer to the personal names used by the Copts, the indigenous Christian inhabitants of Egypt. They reflect the intersection of Egyptian, Greek, Arab and Christian influences in the region and encompass a diverse range of naming practices, which have evolved over centuries.










