| History of Georgia |
|---|
 |
This is an incomplete list of states that have existed on the present-day territory of Georgia since ancient times. It includes de facto independent entities like the major medieval Duchies (saeristavo).
| History of Georgia |
|---|
 |
This is an incomplete list of states that have existed on the present-day territory of Georgia since ancient times. It includes de facto independent entities like the major medieval Duchies (saeristavo).

The flag of Georgia, also known as the five-cross flag, is one of the national symbols of Georgia. Originally a banner of the medieval Kingdom of Georgia, it was repopularised in the late 20th and early 21st centuries during the Georgian national revival.
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlinked, such as by sharing some limited governmental institutions. Unlike the personal union, in a federation and a unitary state, a central (federal) government spanning all member states exists, with the degree of self-governance distinguishing the two. The ruler in a personal union does not need to be a hereditary monarch.

Kakheti is a region (mkhare) formed in the 1990s in eastern Georgia from the historical province of Kakheti and the small, mountainous province of Tusheti. Telavi is its capital. The region comprises eight administrative districts: Telavi, Gurjaani, Qvareli, Sagarejo, Dedoplistsqaro, Signagi, Lagodekhi and Akhmeta. Kakheti is bordered by the Russian Federation with the adjcented subdivisions, the country of Azerbaijan to the southeast, and among with Mtskheta-Mtianeti and Kvemo Kartli to the west. Kakheti has a strong linguistic and cultural identity, since its ethnographic subgroup of Kakhetians speak the Kakhetian dialect of Georgian.

Bagrat III, of the Georgian Bagrationi dynasty, was King of Abkhazia from 978 on and King of Georgia from 1008 on. He united these two titles by dynastic inheritance and, through conquest and diplomacy, added more lands to his realm, effectively becoming the first king of the Kingdom of Georgia. Before Bagrat was crowned as king, he had also reigned in Kartli as co-ruler with his father Gurgen from 976 to 978.
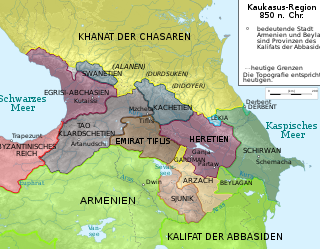
The Kingdom of Hereti was a medieval monarchy which emerged in Caucasus on the Iberian-Albanian frontier. Nowadays it roughly corresponds to the southeastern corner of Georgia's Kakheti region and a portion of Azerbaijan's northwestern districts.

Kakhetians are an ethnographic subgroup of Georgians who speak Kakhetian dialect of Georgian language. Kakhetians are indigenous population of Kakheti, historical region in eastern Georgia, a fertile valley which produces much of the country's wine. Today they are mainly followers of Georgian Orthodox Church.
The Kingdom of Abkhazia, also known as Abasgia or Egrisi-Abkhazia, was a medieval feudal state in the Caucasus which was established in the 780s. Through dynastic succession, it was united in 1008 with the Kingdom of the Iberians, forming the Kingdom of Georgia.

The Bagrationi dynasty is a royal dynasty which reigned in Georgia from the Middle Ages until the early 19th century, being among the oldest extant Christian ruling dynasties in the world. In modern usage, the name of the dynasty is sometimes Hellenized and referred to as the Georgian Bagratids, also known in English as the Bagrations.

The history of the Caucasus region may be divided by geography into the history of the North Caucasus (Ciscaucasia), historically in the sphere of influence of Scythia and of Southern Russia, and that of the South Caucasus in the sphere of influence of Persia, Anatolia, and Assyria.

The nation of Georgia was first unified as a kingdom under the Bagrationi dynasty by the King Bagrat III of Georgia in the early 11th century, arising from a number of predecessor states of the ancient kingdoms of Colchis and Iberia. The Kingdom of Georgia flourished during the 10th to 12th centuries under King David IV the Builder and King Tamar the Great, and fell to the Mongol invasion by 1243, and after a brief reunion under George V the Brilliant to the Timurid Empire. By 1490, Georgia was fragmented into a number of petty kingdoms and principalities, which throughout the Early Modern period struggled to maintain their autonomy against Ottoman and Iranian domination until Georgia was finally annexed by the Russian Empire in the 19th century. After a brief bid for independence with the Democratic Republic of Georgia of 1918–1921, Georgia was part of the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic from 1922 to 1936, and then formed the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic until the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Constantine III was King of the Abkhazia from c. 894 to 923 AD. He was the son and successor of Bagrat I of the Anchabadze dynasty.

This article lists Georgian monarchs, and includes monarchs of various Georgian kingdoms, principalities and duchies.
sadrosho was an administrative division in medieval and early modern Georgia which supplied men for a subdivision of the army marked by its own banner. A tactical unit furnished by this territorial unit was also known as sadrosho, each under the command of a military official, sardali.
The Kingdom of Kakheti-Hereti or just the First Kingdom of Kakheti was an early Medieval monarchy in eastern Georgia, centered at the province of Kakheti, with its capital first at Telavi. It emerged in c. 1014 AD, under the leadership of energetic ruler of principality of Kakheti, Kvirike III the Great that finally defeated the ruler of Hereti and crowned himself as a king of the unified realms of Kakheti and Hereti. From this time on, until 1104, the kingdom was an independent and separated state from the united Kingdom of Georgia. The kingdom included territories from riv. Ksani to Alijanchay river and from Didoeti to southwards along the river of Mtkvari.
The Kingdom of Iberia was a Georgian monarchy from 302 BC to AD 580.

The triarchy and collapse of the Kingdom of Georgia was a dynastic triumvirate military conflict of the Bagrationi monarchs and war of succession in the united Georgian kingdom during the second half of the 15th century. Beginning under the reign of King George VIII, it continued under Bagrat VI and Constantine II and included the entire country, with clashes all around the realm.

The unification of the Georgian realm was the 10th-century political movement that resulted in the consolidation of various Georgian Crowns into a single realm with centralized government in 1008, the Kingdom of Georgia, or Sakartvelo. Originally initiated by the powerful local aristocracy of the eristavs, due to centuries-long power struggles and aggressive wars of succession between the Georgian monarchs, arising from their independant ruling traditions of classical antiquity and its Hellenistic-era monarchical establishments in Colchis and Iberia. The initiative was supported by David III the Great of the Bagrationi dynasty, the most powerful ruler in the Caucasus at the time, who would put prince royal Bagrat, his kin and foster-son, on Iberian throne, who would eventually be crowned as a King of all-Georgia. David's Bagratid successors would become the champions of national unification, just like the Rurikids or the Capetians, but despite their enthusiasm, some of the Georgian polities that had been targeted for unification did not join the unification freely and would actively fight against it throughout this process, mostly seeking help and support from the Byzantine Empire and the Abbasid Caliphate. Even though, 1008 unification of the realm would unite most of western and central Georgian lands, the process will continue to the east, and eventually, would reach its total completion under King David IV the Builder. This unprecedented political unification of lands and the meteoric rise of Bagrationi power would inaugurate the Georgian Golden Age and creation of the only medieval pan-Caucasian empire attaining its greatest geographical extent, that would dominate entire Caucasus in the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries. The centralizing power of the crown started to weaken in the 14th century, and even though the tide turned back under King George V the Brilliant, the reunification came up to be short-lived; unified realm would evaporate after invasions of Mongols and Timur that would result in its total collapse in the 15th century.