You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Cebuano. (July 2021)Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Little Anegada is an island of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean.
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Cebuano. (July 2021)Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Little Anegada is an island of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean.

Hudson Strait in Nunavut links the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley, on the border between Newfoundland and Labrador Nunavut, and Resolution Island off Baffin Island. The strait is about 750 km (470 mi) long with an average width of 125 km (78 mi), varying from 70 km (43 mi) at the eastern entrance to 240 km (150 mi) at Deception Bay.

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

Dinguiraye is a small town in northern Guinea, known for its large mosque which until recently was thatched. As of 2014 it had a population of 47,250 people.

Santa Clara La Laguna is a municipality in the Sololá department of Guatemala.

The Molucca Sea is located in the western Pacific Ocean, around the vicinity of Indonesia, specifically bordered by the Indonesian Islands of Celebes (Sulawesi) to the west, Halmahera to the east, and the Sula Islands to the south. The Molucca Sea has a total surface area of 77,000 square miles. The Molucca Sea is rich in coral and has many diving sites due to the deepness of its waters. The deepness of the water explains the reasoning behind dividing the sea into three zones, which functions to transport water from the Pacific Ocean to the shallower seas surrounding it. The deepest hollow in the Molucca Sea is the 15,780-foot (4,810-meter) Batjan basin. This region is known for its periodic experiences of earthquakes, which stems from the sea itself being a micro plate, in which the Molucca Sea is being subducted in two opposite directions: one in the direction of the Eurasian Plate to the west and the other in the direction of the Philippine Sea Plate to the east.

Eilean Dubh Mòr is an uninhabited island in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. It lies at the mouth of the Firth of Lorn, between the islands of Lunga and Garbh Eileach. The area of the island has been measured variously—at 50 hectares by Livingstone and 65 hectares by Haswell-Smith, the latter including the nearby islet of Eilean Dubh Beag, which is joined to Eilean Dubh Mòr at low tide.
Kailuka is a village in Saaremaa Parish, Saare County, on the island of Saaremaa, Estonia. In 2011 there were 64 inhabitants, including 34 men and 30 women. Of these, 62 were Estonians. In 2000 the population was 75, including 35 men and 40 women. There were 74 permanent residents. Of these, 73 were Estonians.
Gunna is an island in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland.
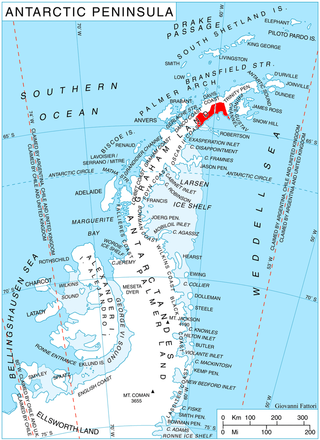
Drygalski Glacier is a broad glacier, 18 nautical miles long and 15 miles (24 km) wide at its head, which flows from Herbert Plateau southeast between Ruth Ridge and Kyustendil Ridge, and enters Solari Bay immediately north of Sentinel Nunatak on Nordenskjöld Coast, the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered in 1902 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, under Otto Nordenskiöld, and named "Drygalski Bay" after Professor Erich von Drygalski. The feature was determined to be a glacier by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1947.
The Kugaryuak River is located in the Canadian Arctic territory of Nunavut in the southwest Kitikmeot Region. It forks into two entities, the Western Kugaryuak and the Eastern Kugaryuak and flows into Coronation Gulf.

Médina Yoro Foulah Department is one of the 45 departments of Senegal, located in the Kolda Region. It was created in 2008.
Nuup Kangerlua is a 160 km (99.4 mi) long fjord in the Sermersooq municipality in southwestern Greenland. It was formerly known by its colonial name as Godthaab Fjord, Gilbert Sound and Baal's River.
William Glacier is a glacier flowing south from the interior highlands of Anvers Island to the head of Börgen Bay on the southeast coast of the island, in the Palmer Archipelago. Discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1897–99, under Gerlache, and charted by them simply as a "grand glacier." The name William Glacier first appears on a chart based upon a 1927 survey by DI personnel on the Discovery. Gateway Ridge separates William Glacier from Hooper Glacier.

Cape Monaco is a cape which forms the southwest tip of Anvers Island, in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. Gossler Islands and Chukovezer Island are lying respectively 3 km west and 7.2 km north of the cape.
Tidzi is a small town and rural commune in Essaouira Province of the Marrakech-Tensift-Al Haouz region of Morocco. At the time of the 2004 census, the commune had a total population of 4769 people living in 866 households.
Fortune Cove is a settlement in Prince Edward Island.
18°43′N64°18′W / 18.717°N 64.300°W