Saint Croix is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincorporated territory of the United States.

Wreck diving is recreational diving where the wreckage of ships, aircraft and other artificial structures are explored. The term is used mainly by recreational and technical divers. Professional divers, when diving on a shipwreck, generally refer to the specific task, such as salvage work, accident investigation or archaeological survey. Although most wreck dive sites are at shipwrecks, there is an increasing trend to scuttle retired ships to create artificial reef sites. Diving to crashed aircraft can also be considered wreck diving. The recreation of wreck diving makes no distinction as to how the vessel ended up on the bottom.

Norman Island is an island at the southern tip of the British Virgin Islands archipelago. It is one of a number of islands reputed to be the inspiration for Robert Louis Stevenson's pirate novel Treasure Island.

A dive boat is a boat that recreational divers or professional scuba divers use to reach a dive site which they could not conveniently reach by swimming from the shore. Dive boats may be propelled by wind or muscle power, but are usually powered by internal combustion engines. Some features, like convenient access from the water, are common to all dive boats, while others depend on the specific application or region where they are used. The vessel may be extensively modified to make it fit for purpose, or may be used without much adaptation if it is already usable.

RMS Rhone was a UK Royal Mail Ship owned by the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company (RMSP). She was wrecked off the coast of Salt Island in the British Virgin Islands on 29 October 1867 in a hurricane, killing 123 people. She is now a popular Caribbean wreck dive site.

Salinas is a coastal city located in the Province of Santa Elena, Ecuador. It is the seat of the canton that bears its name. The westernmost city on mainland Ecuador, Salinas is an important tourist center. Salinas, Ecuador's largest coastal resort, offers one of the country's best real estate investment markets and most popular and most upscale beach lifestyle. It was the site of the ISA World Junior Surfing Games Ecuador in 2009. There are two major yacht clubs in Salinas, the first is Salinas Yacht Club, which is smaller than the Puerto Lucia Yacht Club, in Santa Elena, in an area known as 'La Libertad' which, in Spanish means 'The Freedom Town'. Puerto Lucia boasts a hotel, several restaurants, a private beach and apartment buildings, as well as the large marina and port.
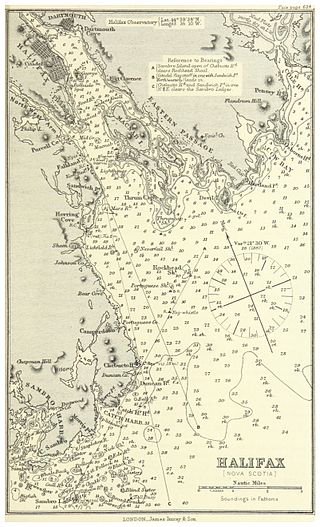
Halifax Harbour is a large natural harbour on the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia, Canada, located in the Halifax Regional Municipality. Halifax largely owes its existence to the harbour, being one of the largest and deepest ice-free natural harbours in the world. Before Confederation it was one of the most important commercial ports on the Atlantic seaboard. In 1917, it was the site of the world's largest man-made accidental explosion, when the SS Mont-Blanc blew up in the Halifax Explosion on December 6.

Carriacou is an island of the Grenadine Islands. It is a part of the nation of Grenada and is located in the south-eastern Caribbean Sea, northeast of the island of Grenada and the north coast of South America. The name is derived from the Carib language Kayryouacou.

Ċirkewwa is a harbour situated at the northernmost point of Malta.

Salt Island is one of the islands of the archipelago of the British Virgin Islands located about 4.7 miles south east of Road Town, the main town on Tortola. It is named after its salt ponds, which were once an important resource.

Eustatia Island is a 30-acre island of the British Virgin Islands (BVI) in the Caribbean. The word "Eustatia" is a Greek derived word meaning, "good place to stay." The entire island, and a small neighboring island, Saba Rock, are under the same long term lease. The island is regularly featured and photographed for several publications and was listed as one of the top 20 most beautiful islands in the world in the December 2004 issue of Islands magazine.

Saba Rock is a small island of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean, approximately an acre and a half in size. The island contains a small hotel, restaurant, bar, and gift shop. A dock is available for day visitors and a large mooring field accommodates yachts staying overnight. The resort operates a boat shuttle from Saba Rock to Bitter End Yacht Club and Leverick Bay Marina.

The Indians are an uninhabited small archipelago of islets in the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean. They are west of the small British Pelican Island and east of the small US Flanagan Island.
Wreck Alley is an area a few miles off the coast of Mission Beach, San Diego, California with several ships intentionally sunk as artificial reefs and as Scuba diving attractions for wreck divers.
Save Ontario Shipwrecks (SOS) is a Provincial Heritage Organization in Ontario, Canada. SOS is a public charitable organization which operates through Local Chapter Committees supported by a Provincial Board of Directors and Provincial Executive.

The Frederiksted Pier is the 1,526-foot, deep water, cruise ship pier located in Frederiksted, U.S. Virgin Islands. It is located at the west end of Saint Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands and accommodate two Eagle-class vessels, of a maximum of 142,000 gross tons each with drafts up to 29 feet and two mini-cruise vessels with drafts of 18 feet. Anchorage is also available in the outer harbor for larger ships. The platform of the pier is equipped with a fendering system that is designed for submarines.
The following index is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Wikipedia's articles on recreational dive sites. The level of coverage may vary:

Recreational dive sites are specific places that recreational scuba divers go to enjoy the underwater environment or for training purposes. They include technical diving sites beyond the range generally accepted for recreational diving. In this context all diving done for recreational purposes is included. Professional diving tends to be done where the job is, and with the exception of diver training and leading groups of recreational divers, does not generally occur at specific sites chosen for their easy access, pleasant conditions or interesting features.

Gunilda was a steel-hulled Scottish-built steam yacht in service between her construction in 1897 and her sinking in Lake Superior in 1911. Built in 1897 in Leith, Scotland by Ramage & Ferguson for J. M. or A. R. & J. M. Sladen, and became owned by F. W. Sykes in 1898; her first and second owners were all from England. In 1901, Gunilda was chartered by a member of the New York Yacht Club, sailing across the Atlantic Ocean with a complement of 25 crewmen. In 1903, she was purchased by oil baron William L. Harkness of Cleveland, Ohio, a member of the New York Yacht Club; she ended up becoming the club's flagship. Under Harkness' ownership, Gunilda visited many parts of the world, including the Caribbean, and beginning in 1910, the Great Lakes.


















