
The Virgin Islands are an archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. They are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles, While the British Virgin Islands are officially designated as “The Virgin Islands”, the name is most often used to refer to the entire international grouping of the British and United States Virgin Islands together with the Spanish Virgin Islands, which, contrary to their name are in fact officially part of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, itself an unincorporated territory of the United States. Geographically, the northern islands lie along the Puerto Rico Trench. St. Croix is a displaced part of that same geologic structure. Politically, the British Virgin Islands have been governed as the western island group of the Leeward Islands, which are the northern part of the Lesser Antilles, and form the border between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The archipelago is separated from the true Lesser Antilles by the Anegada Passage and from the main island of Puerto Rico by the Virgin Passage.
Saint Croix is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincorporated territory of the United States.

The Puerto Rico Trench is located on the boundary between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, parallel to and north of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands. The oceanic trench, the deepest in the Atlantic, is associated with a complex transition between the Lesser Antilles subduction zone to the south and the major transform fault zone or plate boundary, which extends west between Cuba and Hispaniola through the Cayman Trough to the coast of Central America.

The culture of Puerto Rico is the result of a number of internal and indigenous influences, both past and present. Modern cultural manifestations showcase the island's rich history and help create an identity that is uniquely Puerto Rican - Taíno, Spanish, African, and North American.

Green Cay is an uninhabited island of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean. It sits between the eastern tip of Little Jost Van Dyke and Tortola. It is 14 acres (6 ha) in area.

The fauna of Puerto Rico is similar to other island archipelago faunas, with high endemism, and low, skewed taxonomic diversity. Bats are the only extant native terrestrial mammals in Puerto Rico. All other terrestrial mammals in the area were introduced by humans, and include species such as cats, goats, sheep, the small Indian mongoose, and escaped monkeys. Marine mammals include dolphins, manatees, and whales. Of the 349 bird species, about 120 breed in the archipelago, and 47.5% are accidental or rare.
East Seal Dog is an uninhabited islet of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean. It is located in a smaller sub-group of islands referred to as the Dog Islands, or more commonly, "The Dogs". Other islets in The Dogs include Little Seal Dog Island, West Dog Island and George Dog Island, all of which are to the northwest of Virgin Gorda.
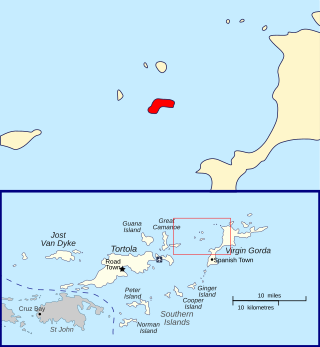
Great Dog Island is an uninhabited islet of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean. It is located in a smaller sub-group of islands referred to as the Dog Islands, or more commonly, "The Dogs". Other islets in The Dogs include Little Seal Dog Island, East Seal Dog Island, West Dog Island and George Dog Island, all of which are to the northwest of Virgin Gorda.

Great Thatch is an uninhabited island of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean. It is one of the westernmost islands in the territory. It is believed to take its name from the famous pirate, Edward Teach, although there is little evidence Blackbeard ever sailed in the Virgin Islands.
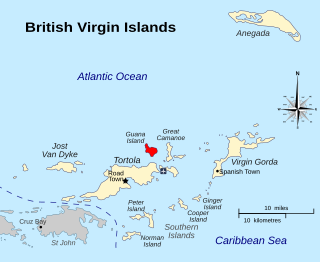
Guana Island is an island of the British Virgin Islands (BVI) in the Caribbean. One of the few remaining privately owned islands in its part of the world, Guana has seven white powder-sand beaches and 850 acres (3.4 km2) of tropical forest, mountains, hills, and valleys. The island is mostly natural preserve and has a small resort.

Little Camanoe is an uninhabited island of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean.

West Dog Island is an uninhabited islet of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean. It is located in a smaller sub-group of islands referred to as the Dog Islands, or more commonly, "The Dogs". Other islets in The Dogs include Little Seal Dog Island, East Seal Dog Island and George Dog Island, all of which are to the northwest of Virgin Gorda.

Little Thatch is a privately owned island of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean, upon which a resort has been built. The island is located less than 500 yards (460 m) from the western end of Tortola, and is less than 1 mile (1.6 km) away from Saint John, United States Virgin Islands. The island was sold by John and Jill Maynard in December 2014 to the owners of OtterBox, Curt and Nancy Richardson.

Sandy Cay is an uninhabited island of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean. It is located between Tortola and Jost Van Dyke. The island was owned by the Laurance Rockefeller Estate. On 1 May 2008, ownership of the island was transferred to the National Parks Trust of the Virgin Islands. In 2002, International NGO, Island Resources Foundation led a project to eradicate invasive black rats from the island.

Prickly Pear is an uninhabited island of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean. Even though the island doesn't have permanent residents, it has a beach bar and recreational water sports facility on it. It is located on the north side of North Sound, opposite Virgin Gorda.

Sandy Spit is an uninhabited islet of the British Virgin Islands in the Caribbean, sitting midway between Sandy Cay and Green Cay. It measures less than half an acre in size, and consists entirely of a ring of sandy beach surrounding light foliage. It has the appearance of a classic paradise "desert island" and has been photographed for use in print medium in a number of advertising campaigns. Sandy Spit is a popular stop for day and term boat charters from Tortola, St. Thomas, and St. John. There are no moorings, but the sandy bottom is suitable for anchoring.

Round Rock is an uninhabited island in the British Virgin Islands, to the south of Virgin Gorda, east of Ginger Island and close to Fallen Jerusalem Island.

Anolis cristatellus is a small species of anole, belonging to the Dactyloidae family of reptiles. The species is native to Puerto Rico and the U.S. and British Virgin Islands, with introduced populations in locations around the Caribbean. The males of A. cristatellus are easily recognizable by the fin running down the top of the tail, which is known as a "caudal crest". The females also have this crest, but it is smaller than that of the males. The species is often quite common in many areas on Puerto Rico, where it can be seen during the day passing the time on the lower parts of tree trunks, or on fences and the walls of buildings in urban areas, sometimes venturing down onto the ground in order to lay eggs, have a snack, or do other cursorial activities. Like many anoles, this species displays the characteristic behaviour of doing push-ups as well as inflating a pizza-like flap of coloured skin on its throat, known as a dewlap, in order to show others how dominant it is, and thus attract mates or intimidate rivals.

The British Virgin Islands dwarf sphaero, Virgin Gorda least gecko, or Virgin Islands dwarf gecko is a species of gecko and also one of the smallest terrestrial vertebrates. It has only been found on three of the British Virgin Islands: Virgin Gorda, Tortola, and Moskito Island. It was discovered in 1964 and is suspected to be a close relative of Sphaerodactylus nicholsi, a dwarf sphaero from the nearby island of Puerto Rico. It shares its range with the big-scaled least gecko (S. macrolepis), which is found in leaf litter. Unlike this larger gecko, the Virgin Islands dwarf sphaero lives on drier hillsides, yet prefers moist microhabitats found under rocks because it lacks the adaptations necessary for preventing water loss, which is a significant problem due to its small body size.

Sphaerodactylus macrolepis, also known as the big-scaled dwarf gecko or the big-scaled least gecko, is a lizard of the Sphaerodactylus genus. It was first documented in 1859 in the US Virgin Islands, specifically, St. Croix. This diurnal species has since been spotted in other locations such as Puerto Rico with major populations in Culebra.






















