
The spotted-winged fruit bat, is the smallest megabat in the world, and the only species in the genus Balionycteris. It inhabits forests in Indonesia and Malaysia.

The velvety myotis, is a species of vesper bat from South America.

The black-winged little yellow bat is a species of vesper bat native to Central America.

The dwarf bonneted bat, or Peters' mastiff bat,, is a bat species from South and Central America.

The dwarf dog-faced bat is a species of free-tailed bat from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Paraguay and Uruguay, typically at lower elevations. It is one of two species in the genus Molossops, the other being the rufous dog-faced bat. Three subspecies are often recognized, though mammalogist Judith Eger considers it monotypic with no subspecies. It is a small free-tailed bat, with a forearm length of 28.9–32.5 mm (1.14–1.28 in) and a weight of 5–8 g (0.18–0.28 oz); males are larger than females. It is brown, with paler belly fur and darker back fur. Its wings are unusual for a free-tailed bat, with exceptionally broad wingtips. Additionally, it has low wing loading, meaning that it has a large wing surface area relative to its body weight. Therefore, it flies more similarly to a vesper bat than to other species in its own family. As it forages at night for its insect prey, including moths, beetles, and others, it uses two kinds of frequency-modulated echolocation calls: one type is to navigate in open areas and to search for prey, while the other type is used for navigating in cluttered areas or while approaching a prey item.

The dwarf little fruit bat is a species of leaf-nosed bat from South America.

Genoways's yellow bat is a species of vesper bat found only in Mexico. It is threatened by habitat loss. Due to its imperiled status, it is identified by the Alliance for Zero Extinction as a species in danger of imminent extinction.

The Chilean myotis is a species of vesper bat found in southern South America.

Findley's myotis is a species of vesper bat. It is found only on the Tres Marías Islands off the west coast of Mexico.

The hairy-legged myotis is a species of mouse-eared bat. It is found from southern Tamaulipas in Mexico, through much of Central America and across northern South America as far east as Trinidad. Further south, it is found along the foothills of the Andes as far south as northern Argentina.

The fraternal fruit-eating bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae that is found in drier habitats in Ecuador and Peru. It was formerly considered to be a subspecies of the Jamaican fruit bat, but was raised to species level in 1978. The smallest species in the group of large Artibeus, it has a forearm length of 52–59 mm (2.0–2.3 in), a total length of 64–76 mm (2.5–3.0 in), and a weight of 30–55 g (1.1–1.9 oz).

The flat-faced fruit-eating bat is a South American species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is sometimes considered a subspecies of the Jamaican fruit bat, but can be distinguished by its larger size, the presence of faint stripes on the face, and of a third molar tooth on each side of the upper jaw. Genetic analysis has also shown that the two species may not be closely related.

The gray short-tailed bat, or Hahn's short-tailed bat, is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae native to Mexico and Central America.
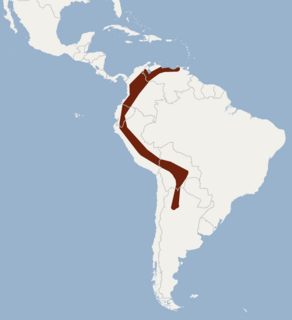
The hairy yellow-shouldered bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae native to South America. There are no recognised subspecies.

The blunt-eared bat or Peruvian crevice-dwelling bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. It is monotypic within the genus Tomopeas and subfamily Tomopeatinae. It is endemic to Peru, where it is considered critically endangered. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Rhogeessa is a genus of bats within the vesper bats family, Vespertilionidae.

The Christmas Island pipistrelle was a species of vesper bat found only on Christmas Island, Australia. The species is now extinct, with the last individual bat seen in August 2009 with no further sightings despite intensive efforts to locate it.

Husson's yellow bat is a species of vesper bat found in Suriname and southern Brazil.
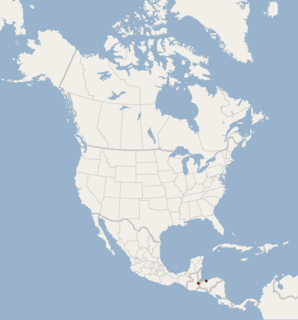
Menchu's little yellow bat is a species of vesper bat found in Central America. It was described as a new species in 2012.
Rhogeessa velilla, also called the Ecuadorian little yellow bat, is a species of vesper bat in the genus Rhogeessa. It is found in Northwestern Peru and parts of Ecuador. The species was previously included in R. io, but is now recognized as a separate species. Very little is known about this species, though it is generally considered to be insectivorous.





















