
The big brown bat is a species of vesper bat distributed widely throughout North America, the Caribbean, and the northern portion of South America. It was first described as a species in 1796. Compared to other microbats, the big brown bat is relatively large, weighing 15–26 g (0.53–0.92 oz) and possessing a wingspan of 32.5–35 cm (12.8–13.8 in).

The serotine bat, also known as the common serotine bat, big brown bat, or silky bat, is a fairly large Eurasian bat with quite large ears. It has a wingspan of around 37 cm (15 in) and often hunts in woodland. It sometimes roosts in buildings, hanging upside down, in small groups or individually. The name serotine is derived from the Latin serotinus, which means 'evening', while the generic name derives from Greek ἔπιεν and οίκος, which means 'house flyer'.

The northern bat is the most abundant species of bat in northern Eurasia occurring from France to Hokkaidō and south to Kazakhstan.
Botta's serotine is a species of vesper bat, one of 25 in the genus Eptesicus. It is found in rocky areas and temperate desert.
The Guadeloupe big brown bat is a species of vesper bat. It is found only on the island of Guadeloupe. It is one of the eleven species of bat found on Guadeloupe, and one of three that are endemic.

Schlieffen's serotine, also known as Schlieffen's bat or Schlieffen's twilight bat, is a species of vesper bat found in Africa. It has been placed in numerous genera since its first description in 1859, but morphological and genetic studies have confirmed it as the only species in the genus Nycticeinops. It is named for the collector of the original specimen, Wilhelm von Schlieffen-Schlieffiennburg.

The Cape serotine is a species of vesper bat occurring in Sub-Saharan Africa. 'Serotine' is from Latin 'serotinus' meaning ‘of the evening'.

The Agreement on the Conservation of Populations of European Bats, or EUROBATS, is an international treaty that binds its States Parties on the conservation of bats in their territories. It was signed in 1991 under the auspices of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), with the Agreement entering into force in 1994. In August 2021, the Agreement applied to 38 of 63 range states.

The Vespertilioninae are a subfamily of vesper bats from the family Vespertilionidae.

The meridional serotine is a species of bat native to the Iberian Peninsula, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya.
Eptesicus lobatus is a species of bat of genus Eptesicus and family Vespertilionidae.
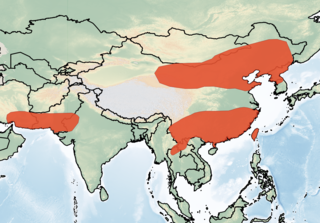
The Oriental serotine is a species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is widespread and found throughout Asia.

Eptescini is a tribe of bats in the family Vespertilionidae. This tribe has a cosmopolitan distribution.
Ognev's serotine is a species of vesper bat found in western and central Asia.










