
The Felsenthal National Wildlife Refuge is a 64,902 acre (262.65 km2) wildlife refuge located in south-central Arkansas in Ashley, Bradley, and Union counties. It is the world's largest green tree reservoir.

The Billy Frank Jr. Nisqually National Wildlife Refuge is a wildlife preserve operated by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service on the Nisqually River Delta near Puget Sound in northeastern Thurston County, Washington and northwestern Pierce County, Washington. The refuge is located just off Interstate 5, between the cities of Tacoma and Olympia.

The Cahaba River National Wildlife Refuge is a 3,689.63 acres (15 km2) National Wildlife Refuge located in central Alabama, along the Cahaba River downstream from Birmingham, Alabama. The refuge was established on September 25, 2002. Additional purchases were approved that will potentially increase the size of the refuge to 7,300 acres (29.5 km²). Additional negotiations propose an expansion to a potential 280,000 acres (1,100 km2), most of which currently belongs to private landowners. The facility is unstaffed, but is administered by the Mountain Longleaf National Wildlife Refuge in Anniston, Alabama.

Hatchie National Wildlife Refuge is an area of swampy bottomland consisting of a portion of the floodplain of the Hatchie River in West Tennessee, covering 11,556 acres in southern Haywood County and central Hardeman County. It is a rich environment for aquatic life and waterfowl. The refuge is bisected by both Interstate 40 and U.S. Route 70 and hence passed through by almost all motor vehicle traffic between Nashville and Memphis. Wildlife includes Fish, Snakes, and Mammals.

The Kenai National Wildlife Refuge is a 1.92-million-acre (7,770 km2) wildlife habitat preserve located on the Kenai Peninsula of Alaska, United States. It is adjacent to Kenai Fjords National Park. This refuge was created in 1941 as the Kenai National Moose Range, but in 1980 it was changed to its present status by the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act. The refuge is administered from offices in Soldotna.

Waccamaw National Wildlife Refuge, established in 1997, is a recent addition to the United States National Wildlife Refuge system. It is located in parts of northeastern Georgetown County, South Carolina, southern Horry, and southeastern Marion counties, and contains lands adjacent to the Pee Dee River, the Little Pee Dee River, and the Waccamaw River near their confluence. Currently the size of the refuge is 22,931 acres (92.80 km2) but plans call for the total refuge to be over 50,000 acres (200 km2).

Nestucca Bay National Wildlife Refuge is a U.S. National Wildlife Refuge on Oregon's coast. It lies in southern Tillamook County, on the state's northern coast. It is one of six National Wildlife Refuges comprising the Oregon Coast National Wildlife Refuge Complex and supports one tenth of the world's dusky Canada goose population. The refuge contains at least seven types of habitat, including tidal marsh, tidal mudflats, grassland, woodland, pasture, forested lagg—a transition between raised peat bog and mineral soil—and freshwater bogs, including the southernmost coastal Sphagnum bog habitat on the Pacific Coast.

The Bill Williams River is a 46.3-mile-long (74.5 km) river in west-central Arizona where it, along with its tributary, the Santa Maria River, form the boundary between Mohave County to the north and La Paz County to the south. It is a major drainage westwards into the Colorado River of the Lower Colorado River Valley south of Hoover Dam and Lake Mead, and the drainage basin covers portions of northwest, and west-central Arizona. The equivalent drainage system paralleling the east–west lower reaches of the Bill Williams is the Gila River, which flows east-to-west across central Arizona, joining the Colorado River in the southwest at Yuma. The confluence of the Bill Williams River with the Colorado is north of Parker, and south of Lake Havasu City.

D'Arbonne National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge of the United States located north of West Monroe, Louisiana. It is in Ouachita and Union Parishes on either side of Bayou D'Arbonne near its confluence with the Ouachita River. It lies on the western edge of the Mississippi River alluvial valley. It was established in 1975 to protect bottomland hardwoods and provide wintering habitat for migratory waterfowl. D'Arbonne is one of four refuges managed in the North Louisiana Refuges Complex.

The Yukon Flats National Wildlife Refuge is a protected wetland area in the U.S. state of Alaska. It encompasses most of the Yukon Flats, a vast wetland area centered on the confluence of the Yukon River, Porcupine River, and Chandalar River. The area is a major waterfowl breeding ground, and after a proposal to flood the Yukon Flats via a dam on the Yukon River was turned down, the Yukon Flats were deemed worthy of protection. The Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act established the refuge in 1980. It is the third-largest National Wildlife Refuge in the United States, although it is less than one-half the size of either of the two largest, the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, or the Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is administered from offices in Fairbanks.

The Two Rivers National Wildlife Refuge is located on the Illinois River and the Mississippi River in parts of Calhoun, Jersey, and Greene counties in Illinois, and St. Charles County, Missouri. It is managed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as part of the Mark Twain National Wildlife Refuge Complex.

Silvio O. Conte National Fish and Wildlife Refuge was established in 1997 to conserve, protect and enhance the abundance and diversity of native plant, fish and wildlife species and the ecosystems on which they depend throughout the 7,200,000-acre (29,000 km2) Connecticut River watershed. The watershed covers large areas of Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts and Connecticut. It contains a great diversity of habitats, notably: northern forest valuable as nesting habitat for migrant thrushes, warblers and other birds; rivers and streams used by shad, salmon, herring and other migratory fishes; and an internationally significant complex of high-quality tidal fresh, brackish and salt marshes.

Swan Lake National Wildlife Refuge is a 10,795-acre (43.69 km2) National Wildlife Refuge established in 1937 and located in Chariton County, Missouri, 2 miles (3.2 km) south of the town of Sumner. It is located near the confluence of the Grand and Missouri Rivers.

McNary National Wildlife Refuge is a wildlife preserve, one of the national wildlife refuges operated by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Extending along the east bank of the Columbia River in southeastern Washington, from the confluence of the Snake River to the mouth of the Walla Walla River, and downstream into Oregon, McNary NWR is located in rural Burbank, but very close to the rapid development of the Tri-Cities. In fact, the refuge meets the definition of an "urban refuge." Few areas in North America support waterfowl populations in the extraordinary numbers found here. Visitors enjoy spectacular concentrations of Canada geese, mallards, and other waterfowl. More than half the mallards in the Pacific Flyway overwinter at some time in this portion of the Columbia River Basin.

Salinas River National Wildlife Refuge is located approximately 11 miles north of Monterey, California, and 3 miles south of Castroville, California, at the point where the Salinas River empties into Monterey Bay. The 367-acre (1.49 km2) refuge encompasses several habitat types including sand dunes, pickleweed salt marsh, river lagoon, riverine habitat, and a saline pond. The refuge was established in 1974 because of its "particular value in carrying out the national migratory bird management program."

Sacramento River National Wildlife Refuge is located along the Sacramento River in the Sacramento Valley of California. Landscape is very flat, bordered by the Sierra and Coast ranges, with intensive agriculture. This riparian community is one of the most important wildlife habitats in California and North America.
West Tennessee National Wildlife Refuge Complex is a National Wildlife Refuge complex in the state of Tennessee.
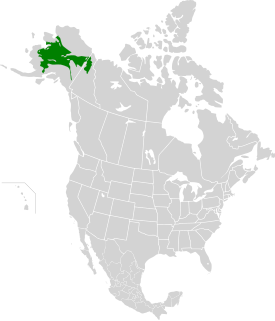
The Interior Alaska-Yukon lowland taiga ecoregion, in the Taiga and Boreal forests Biome, of far northern North America.




















