
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture that administers the nation's 154 national forests and 20 national grasslands. The Forest Service manages 193 million acres (780,000 km2) of land. Major divisions of the agency include the Chief's Office, National Forest System, State and Private Forestry, Business Operations, and Research and Development. The agency manages about 25% of federal lands and is the only major national land management agency not part of the U.S. Department of the Interior, which manages the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and the Bureau of Land Management.

The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior responsible for administering federal lands. With oversight over 247.3 million acres (1,001,000 km2), it governs one eighth of the country's landmass.

The Tongass National Forest in Southeast Alaska is the largest national forest in the United States at 16.7 million acres. Most of its area is temperate rain forest, and is remote enough to be home to many species of endangered and rare flora and fauna. The Tongass, which is managed by the United States Forest Service, encompasses islands of the Alexander Archipelago, fjords and glaciers, and peaks of the Coast Mountains. An international border with Canada runs along the crest of the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The forest is administered from Forest Service offices in Ketchikan. There are local ranger district offices located in Craig, Hoonah, Juneau, Ketchikan, Petersburg, Sitka, Thorne Bay, Wrangell, and Yakutat.

National Grassland is a classification of protected and managed federal lands in the United States authorized by Title III of the Bankhead–Jones Farm Tenant Act of 1937. For administrative purposes, they are essentially identical to United States National Forests, except that grasslands are areas primarily consisting of prairie. Like National Forests, National Grasslands may be open for hunting, grazing, mineral extraction, recreation and other uses. Various National Grasslands are typically administered in conjunction with nearby National Forests.
In all modern states, a portion of land is held by central or local governments. This is called public land, state land, or Crown land. The system of tenure of public land, and the terminology used, varies between countries. The following examples illustrate some of the range.

The Allegheny National Forest is a National Forest in northwestern Pennsylvania, about 100 miles northeast of Pittsburgh. The forest covers 513,175 acres of land. Within the forest is Kinzua Dam, which impounds the Allegheny River to form Allegheny Reservoir. The administrative headquarters for the Allegheny National Forest is in Warren. The Allegheny National Forest has two ranger stations, one in Marienville, Forest County, and the other in Bradford, McKean County.
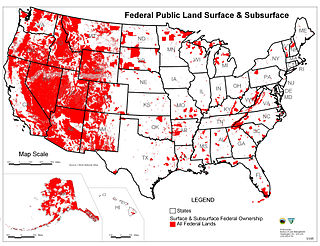
Federal lands are lands in the United States owned by the federal government. Pursuant to the Property Clause of the United States Constitution, the Congress has the power to retain, buy, sell, and regulate federal lands, such as by limiting cattle grazing on them. These powers have been recognized in a long line of U.S. Supreme Court decisions.

The Midewin National Tallgrass Prairie (MNTP) is a tallgrass prairie reserve and United States National Grassland operated by the United States Forest Service. The first national tallgrass prairie ever designated in the U.S. and the largest conservation site in the Chicago Wilderness region, it is located on the site of the former Joliet Army Ammunition Plant between the towns of Elwood, Manhattan and Wilmington in northeastern Illinois. Since 2015, it has hosted a conservation herd of American bison to study their interaction with prairie restoration and conservation.

The Finger Lakes National Forest is a United States National Forest that encompasses 16,259 acres (65.80 km2) of Seneca and Schuyler counties, nestled between Seneca Lake and Cayuga Lake in the Finger Lakes Region of the State of New York. It has over 30 miles (50 km) of interconnecting trails that traverse gorges, ravines, pastures, and woodlands.

The Wilderness Act of 1964 was written by Howard Zahniser of The Wilderness Society. It created the legal definition of wilderness in the United States, and protected 9.1 million acres (37,000 km²) of federal land. The result of a long effort to protect federal wilderness and to create a formal mechanism for designating wilderness, the Wilderness Act was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson on September 3, 1964 after over sixty drafts and eight years of work.

The National Wilderness Preservation System (NWPS) of the United States protects federally managed wilderness areas designated for preservation in their natural condition. Activity on formally designated wilderness areas is coordinated by the National Wilderness Preservation System. Wilderness areas are managed by four federal land management agencies: the National Park Service, the U.S. Forest Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and the Bureau of Land Management. The term "wilderness" is defined as "an area where the earth and community of life are untrammeled by man, where man himself is a visitor who does not remain" and "an area of undeveloped Federal land retaining its primeval character and influence, without permanent improvements or human habitation, which is protected and managed so as to preserve its natural conditions." As of 2016, there are 803 designated wilderness areas, totaling 111,368,221 acres (45,069,120 ha), or about 4.5% of the area of the United States.

National Conservation Lands, formally known as the National Landscape Conservation System, is a 35-million-acre (140,000 km2) collection of lands in 873 federally recognized areas considered to be the crown jewels of the American West. These lands represent 10% of the 258 million acres (1,040,000 km2) managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM). The BLM is the largest federal public land manager and is responsible for over 40% of all the federal public land in the nation. The other major federal public land managers include the US Forest Service (USFS), National Park Service (NPS), and the US Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS).

The National Forest Management Act (NFMA) of 1976 is a United States federal law that is the primary statute governing the administration of national forests and was an amendment to the Forest and Rangeland Renewable Resources Planning Act of 1974, which called for the management of renewable resources on national forest lands. The law was a response to lawsuits involving various practices in the national forest, including timber harvesting., Zieske v Butz was the lawsuit brought by members of the Pt Baker Association on Prince of Wales Island against the US Forest Service's first environmental impact statement. The suit halted logging on the NW tip of the island which consisted of 400,000 acres and resulted in a call by the timber industry for Congressional action to undo the lawsuit.

The Forest Reserve Act of 1891 is a law that gives the President of the United States the authority to unilaterally set aside forest reserves from land in the public domain. After newspapers began to publicize the fraud and speculation under the previous Timber Culture Act of 1873 that granted additional land to homesteaders agreeing to plant trees, scientists of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) joined with the American Forestry Association to advocate for stronger laws for the management of the nation's forest land. The resulting act, passed by the 51st United States Congress and signed into law by President Benjamin Harrison on March 3, 1891, set out to both protect local watersheds from flooding and erosion as well as to prevent over-exploitation of the country's timber supply.
The San Gabriel Timberland Reserve was the first federal reserve in the state of California. It was established on December 20, 1892 by proclamation order of President Benjamin Harrison and consisted of 555,520 acres (2,248.1 km2) extending from Pacoima Canyon at Sylmar to Cajon Pass in Southern California. The San Gabriel Timberland Reserve became the Angeles National Forest in December 1908.

Lincoln National Forest is a unit of the U.S. Forest Service located in southern New Mexico. Established by Presidential Proclamation in 1902 as the Lincoln Forest Reserve, the 1,103,897 acres (4,467.31 km2) forest begins near the Texas border and contains lands in parts of Chaves, Eddy, Lincoln, and Otero counties. The three Ranger Districts within the forest contain all or part of four mountain ranges, and include a variety of different environmental areas, from desert to heavily forested mountains and sub-alpine grasslands. Established to balance conservation, resource management, and recreation, the lands of the Lincoln National Forest include important local timber resources, protected wilderness areas, and popular recreation and winter sports areas. The forest headquarters is located in Alamogordo, N.M. with local offices in Carlsbad, Cloudcroft, and Ruidoso.

Roadless area conservation is a conservation policy limiting road construction and the resulting environmental impact on designated areas of public land. In the United States, roadless area conservation has centered on U.S. Forest Service areas known as inventoried roadless areas. The most significant effort to support the conservation of these efforts was the Forest Service 2001 Roadless Area Conservation Rule.

Logging in the Sierra Nevada arose from the desire for economic growth throughout California. The California Gold Rush created a high demand for timber in housing construction, mining procedures, and building railroads. In the early days, harvesting of forests were unregulated and within the first 20 years after the gold rush, a third of the timber in the Sierra Nevada was logged. Concern for the forests rose and created a movement towards conservation at the turn of the 19th century, leading to the creation of state and national parks and forest reserves, bringing forest land under regulation. Between 1900 and 1940, agencies like the U.S. Forest Service and National Park Service regulated the use of the Sierra Nevada’s resources. The economy boom after World War II dramatically increased timber production in the Sierras using clear-cutting as the dominant form of logging. In addition, the California Forest Practice Act, or the Z'Berg-Nejedly Forest Practice Act was enacted in 1973 to regulate private timberland holdings.
Private landowner assistance program (PLAP) is a class of government assistance program available throughout the U.S. for landowners interested in maintaining, developing, improving and protecting wildlife on their property. Each state provides various programs that assist landowners in agriculture, forestry and conserving wildlife habitat. This helps landowners in the practice of good land stewardship and provides multiple benefits to the environment. Some states offer technical assistance which includes:
The Southeast Alaska Conservation Council (SEACC) is a non-profit organization that focusses on protecting the lands and waters of Southeast Alaska. They promote conservation and advocate for sustainable natural resource management. SEACC is located in Alaska's capital: Juneau. The environmental organization focuses specifically on concerns in the Southeast region of Alaska: including the Panhandle, the Tongass National Forest and the Inside Passage.


















