Related Research Articles

The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems.
The following is a glossary of diabetes which explains terms connected with diabetes.

Beta cells (β-cells), are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes.
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even higher values such as 13.9–16.7 mmol/L (~250–300 mg/dL). A subject with a consistent fasting blood glucose range between ~5.6 and ~7 mmol/L is considered slightly hyperglycemic, and above 7 mmol/L is generally held to have diabetes. For diabetics, glucose levels that are considered to be too hyperglycemic can vary from person to person, mainly due to the person's renal threshold of glucose and overall glucose tolerance. On average, however, chronic levels above 10–12 mmol/L (180–216 mg/dL) can produce noticeable organ damage over time.
Glucokinase is an enzyme that facilitates phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates. In each of these organs it plays an important role in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism by acting as a glucose sensor, triggering shifts in metabolism or cell function in response to rising or falling levels of glucose, such as occur after a meal or when fasting. Mutations of the gene for this enzyme can cause unusual forms of diabetes or hypoglycemia.
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) refers to any of several hereditary forms of diabetes mellitus caused by mutations in an autosomal dominant gene disrupting insulin production. Along with neonatal diabetes, MODY is a form of the conditions known as monogenic diabetes. While the more common types of diabetes involve more complex combinations of causes involving multiple genes and environmental factors, each forms of MODY are caused by changes to a single gene (monogenic). GCK-MODY and HNF1A-MODY are the most common forms.
Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia describes the condition and effects of low blood glucose caused by excessive insulin. Hypoglycemia due to excess insulin is the most common type of serious hypoglycemia. It can be due to endogenous or injected insulin.
Hyperinsulinism refers to an above normal level of insulin in the blood of a person or animal. Normal insulin secretion and blood levels are closely related to the level of glucose in the blood, so that a given level of insulin can be normal for one blood glucose level but low or high for another. Hyperinsulinism can be associated with several types of medical problems, which can be roughly divided into two broad and largely non-overlapping categories: those tending toward reduced sensitivity to insulin and high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia), and those tending toward excessive insulin secretion and low glucose levels (hypoglycemia).

Congenital hyperinsulinism (HI or CHI) is a rare condition causing severe hypoglycemia in newborns due to the overproduction of insulin. There are various causes of HI, some of which are known to be the result of a genetic mutation. Sometimes HI occurs on its own (isolated) and more rarely associated with other medical conditions.
The glucokinase regulatory protein (GKRP) also known as glucokinase regulator (GCKR) is a protein produced in hepatocytes. GKRP binds and moves glucokinase (GK), thereby controlling both activity and intracellular location of this key enzyme of glucose metabolism.

Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for energy and it helps regulate glucose levels in the bloodstream. Before treatment this results in high blood sugar levels in the body. The common symptoms of this elevated blood sugar are frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other serious complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing. Symptoms typically develop over a short period of time, often a matter of weeks if not months.
Many types of glucose tests exist and they can be used to estimate blood sugar levels at a given time or, over a longer period of time, to obtain average levels or to see how fast body is able to normalize changed glucose levels. Eating food for example leads to elevated blood sugar levels. In healthy people, these levels quickly return to normal via increased cellular glucose uptake which is primarily mediated by increase in blood insulin levels.

For pregnant women with diabetes, some particular challenges exist for both mother and fetus. If the pregnant woman has diabetes as a pre-existing disorder, it can cause early labor, birth defects, and larger than average infants. Therefore, experts advise diabetics to maintain blood sugar level close to normal range about 3 months before planning for pregnancy.

Aceruloplasminemia is a rare autosomal recessive disorder in which the liver can not synthesize the protein ceruloplasmin properly, which is needed to transport copper around the blood. Copper deficiency in the brain results in neurological problems that generally appear in adulthood and worsen over time. .
Rabson–Mendenhall syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe insulin resistance. The disorder is caused by mutations in the insulin receptor gene. Symptoms include growth abnormalities of the head, face and nails, along with the development of acanthosis nigricans. Treatment involves controlling blood glucose levels by using insulin and incorporating a strategically planned, controlled diet. Also, direct actions against other symptoms may be taken This syndrome usually affects children and has a prognosis of 1–2 years.

Wolcott–Rallison syndrome,WRS, is a rare, autosomal recessive disorder with infancy-onset diabetes mellitus, multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, osteopenia, mental retardation or developmental delay, and hepatic and renal dysfunction as main clinical findings. Patients with WRS have mutations in the EIF2AK3 gene, which encodes the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3. Other disease names include multiple epiphyseal dysplasia and early-onset diabetes mellitus. Most patients with this disease do not survive to adulthood. The majority of WRS patients die from fulminant hepatitis during childhood. There are few reported cases for this disease. Of the 54 families worldwide with reported WRS cases, 22.2% of them are from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Of the 23 WRS patients in Saudi Arabia, all but one is the result of consanguineous marriages. Another country where WRS cases have been found is Kosovo. Here, the Albanian population is also known for consanguineous marriages, but there were some cases involving patients from non-consanguineous parents that were carriers for the same mutant allele.
MODY 4 or PDX1-MODY is a form of maturity onset diabetes of the young.

Renal cysts and diabetes syndrome (RCAD), also known as MODY 5 or HNF1B-MODY, is a form of maturity onset diabetes of the young.

Neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) is a disease that affects an infant and their body's ability to produce or use insulin.NDM is a kind of diabetes that is monogenic and arises in the first 6 months of life. Infants do not produce enough insulin, leading to an increase in glucose accumulation. It is a rare disease, occurring in only one in 100,000 to 500,000 live births. NDM can be mistaken for the much more common type 1 diabetes, but type 1 diabetes usually occurs later than the first 6 months of life. There are two types of NDM: permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM), a lifelong condition, and transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM), a form of diabetes that disappears during the infant stage but may reappear later in life.
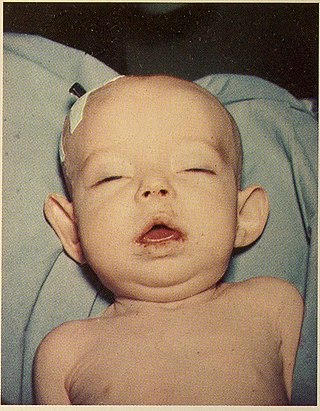
Donohue syndrome is an extremely rare and severe genetic disorder. Leprechaunism derives its name from the hallmark elvish features exhibited by the affected individuals. The disease is caused by a mutation in the INSR gene, which contains the genetic information for the formation of insulin receptors. As a result, affected individuals have either a decreased number of insulin receptors, or insulin receptor with greatly impaired functionality. The lack and impairment of insulin receptor functionality leads to an inability to regulate blood glucose levels through severe insulin resistance. This will ultimately lead to affected development of tissues and organs throughout the body. In addition to the physical abnormalities, leprechaunism is also characterized by endocrine system abnormalities that can lead to conditions such as hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, hyperinsulemia, and the enlargement of certain sex organs such as the penis in males, and the clitoris in females.
References
- ↑ George, Doss C. Priya; Chakraborty, Chiranjib; Haneef, SA Syed; NagaSundaram, Nagarajan; Chen, Luonan; Zhu, Hailong (2014-01-29). "Evolution- and Structure-Based Computational Strategy Reveals the Impact of Deleterious Missense Mutations on MODY 2 (Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young, Type 2)". Theranostics. 4 (4): 366–385. doi:10.7150/thno.7473. ISSN 1838-7640. PMC 3936290 . PMID 24578721.
- ↑ Song, Yuning; Sui, Tingting; Zhang, Yuxin; Wang, Yong; Chen, Mao; Deng, Jichao; Chai, Zhonglin; Lai, Liangxue; Li, Zhanjun (August 2020). "Genetic deletion of a short fragment of glucokinase in rabbit by CRISPR/Cas9 leading to hyperglycemia and other typical features seen in MODY-2". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 77 (16): 3265–3277. doi:10.1007/s00018-019-03354-4. ISSN 1420-682X.