Related Research Articles
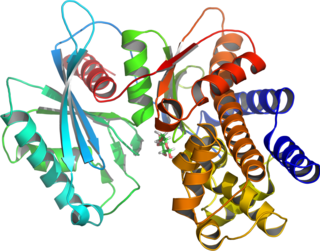
Glucokinase is an enzyme that facilitates phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates. In each of these organs it plays an important role in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism by acting as a glucose sensor, triggering shifts in metabolism or cell function in response to rising or falling levels of glucose, such as occur after a meal or when fasting. Mutations of the gene for this enzyme can cause unusual forms of diabetes or hypoglycemia.
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) refers to any of several hereditary forms of diabetes mellitus caused by mutations in an autosomal dominant gene disrupting insulin production. Along with neonatal diabetes, MODY is a form of the conditions known as monogenic diabetes. While the more common types of diabetes involve more complex combinations of causes involving multiple genes and environmental factors, each forms of MODY are caused by changes to a single gene (monogenic). GCK-MODY and HNF1A-MODY are the most common forms.
Hepatocyte nuclear factors (HNFs) are a group of phylogenetically unrelated transcription factors that regulate the transcription of a diverse group of genes into proteins. These proteins include blood clotting factors and in addition, enzymes and transporters involved with glucose, cholesterol, and fatty acid transport and metabolism.
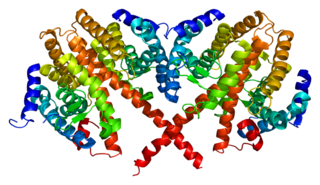
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4A) also known as NR2A1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the HNF4A gene.

HNF1 homeobox A, also known as HNF1A, is a human gene on chromosome 12. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor that is highly expressed in the liver and is involved in the regulation of the expression of several liver-specific genes. Mutations in the HNF1A gene have been known to cause diabetes. The HNF1A gene also contains a SNP associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.

PDX1, also known as insulin promoter factor 1, is a transcription factor in the ParaHox gene cluster. In vertebrates, Pdx1 is necessary for pancreatic development, including β-cell maturation, and duodenal differentiation. In humans this protein is encoded by the PDX1 gene, which was formerly known as IPF1. The gene was originally identified in the clawed frog Xenopus laevis and is present widely across the evolutionary diversity of bilaterian animals, although it has been lost in evolution in arthropods and nematodes. Despite the gene name being Pdx1, there is no Pdx2 gene in most animals; single-copy Pdx1 orthologs have been identified in all mammals. Coelacanth and cartilaginous fish are, so far, the only vertebrates shown to have two Pdx genes, Pdx1 and Pdx2.

HNF1 homeobox B, also known as HNF1B or transcription factor 2 (TCF2), is a human gene.

Neurogenic differentiation 1 (Neurod1), also called β2, is a transcription factor of the NeuroD-type. It is encoded by the human gene NEUROD1.

Paired box gene 4, also known as PAX4, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PAX4 gene.

MODY 1 or HNF4A-MODY is a form of maturity onset diabetes of the young.
MODY 2 or GCK-MODY is a form of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. It is due to any of several mutations in the GCK gene on human chromosome 7 for glucokinase. Glucokinase serves as the glucose sensor for the pancreatic beta cell. Normal glucokinase triggers insulin secretion as the glucose exceeds about 90 mg/dl. These loss-of-function mutations result in a glucokinase molecule that is less sensitive or less responsive to rising levels of glucose. The beta cells in MODY 2 have a normal ability to make and secrete insulin, but do so only above an abnormally high threshold. This produces a chronic, mild increase in blood sugar, which is usually asymptomatic. It is usually detected by accidental discovery of mildly elevated blood sugar. An oral glucose tolerance test is much less abnormal than would be expected from the impaired (elevated) fasting blood sugar, since insulin secretion is usually normal once the glucose has exceeded the threshold for that specific variant of the glucokinase enzyme.
MODY 3 or HNF1A-MODY is a form of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. It is caused by mutations of the HNF1-alpha gene, a homeobox gene on human chromosome 12. This is the most common type of MODY in populations with European ancestry, accounting for about 70% of all cases in Europe. HNF1α is a transcription factor that is thought to control a regulatory network important for differentiation of beta cells. Mutations of this gene lead to reduced beta cell mass or impaired function. MODY 1 and MODY 3 diabetes are clinically similar. About 70% of people develop this type of diabetes by age 25 years, but it occurs at much later ages in a few. This type of diabetes can often be treated with sulfonylureas with excellent results for decades. However, the loss of insulin secretory capacity is slowly progressive and most eventually need insulin.
MODY 4 or PDX1-MODY is a form of maturity onset diabetes of the young.

Renal cysts and diabetes syndrome (RCAD), also known as MODY 5 or HNF1B-MODY, is a form of maturity onset diabetes of the young.
Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM) is a newly identified and potentially treatable form of monogenic diabetes. This type of neonatal diabetes is caused by activating mutations of the KCNJ11 gene, which codes for the Kir6.2 subunit of the beta cell KATP channel. This disease is considered to be a type of maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY).

Transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM) is a form of neonatal diabetes presenting at birth that is not permanent. This disease is considered to be a type of maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY).

Neonatal diabetes mellitus (NDM) is a disease that affects an infant and their body's ability to produce or use insulin.NDM is a kind of diabetes that is monogenic and arises in the first 6 months of life. Infants do not produce enough insulin, leading to an increase in glucose accumulation. It is a rare disease, occurring in only one in 100,000 to 500,000 live births. NDM can be mistaken for the much more common type 1 diabetes, but type 1 diabetes usually occurs later than the first 6 months of life. There are two types of NDM: permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM), a lifelong condition, and transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM), a form of diabetes that disappears during the infant stage but may reappear later in life.
Most cases of type 2 diabetes involved many genes contributing small amount to the overall condition. As of 2011 more than 36 genes have been found that contribute to the risk of type 2 diabetes. All of these genes together still only account for 10% of the total genetic component of the disease.
In recent years it has become apparent that the environment and underlying mechanisms affect gene expression and the genome outside of the central dogma of biology. It has been found that many epigenetic mechanisms are involved in the regulation and expression of genes such as DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling. These epigenetic mechanisms are believed to be a contributing factor to pathological diseases such as type 2 diabetes. An understanding of the epigenome of Diabetes patients may help to elucidate otherwise hidden causes of this disease.
Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) is a genetic heterogenouse autoimmune disorder, which is triggered by genetic predisposition and environmental factors. The prevalence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) among children and young adult from Europe is approximately 0.4%. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) is characterized by acute onset and insulin deficiency. Patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) are found with gradual loss of the pancreatic islet beta cells and therefore not able to produce insulin. As a result, they usually need exogenous insulin to maintain their life.
References
- ↑ Copeman JB, Cucca F, Hearne CM, et al. (January 1995). "Linkage disequilibrium mapping of a type 1 diabetes susceptibility gene (IDDM7) to chromosome 2q31-q33". Nat. Genet. 9 (1): 80–5. doi:10.1038/ng0195-80. PMID 7704030.