
The Amiiformes order of fish has only two extant species, the bowfins: Amia calva and Amia ocellicauda, the latter recognized as a separate species in 2022. These Amiiformes are found in the freshwater systems of North America, in the United States and parts of southern Canada. They live in freshwater streams, rivers, and swamps. The order first appeared in the Triassic, and the extinct members include both marine and freshwater species, many of which are morphologically disparate from bowfins, such as the caturids.

Semionotiformes is an order of ray-finned fish known from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) to the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian). Their closest living relatives are gars (Lepisosteidae), with both groups belonging to the clade Ginglymodi within the Holostei. The group includes both freshwater (Semionotidae) and marine adapted forms. Many members of the family Macrosemiidae, had elongated dorsal fins, often associated with an adjacent area of skin which was free of scales. These fins were likely undulated for use in precision swimming. The body morphology of macrosemiids suggests that they were slow swimmers who were capable of maneuvering around complex topography, such as reef environments.

Neopterygii is a subclass of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii). Neopterygii includes the Holostei and the Teleostei, of which the latter comprise the vast majority of extant fishes, and over half of all living vertebrate species. While living holosteans include only freshwater taxa, teleosts are diverse in both freshwater and marine environments. Many new species of teleosts are scientifically described each year.

Lepisosteiformes is an order of ray-finned fish and the only living members of the clade Ginglymodi. Its only extant representatives are the gar, and it is defined as all members of Ginglymodi that are more closely related to gar than to the extinct Semionotiformes, the other major grouping of ginglymodians. They are one of two extant orders in the infraclass Holostei alongside the Amiiformes.

Lepidotes is an extinct genus of Mesozoic ray-finned fish. It has long been considered a wastebasket taxon, characterised by "general features, such as thick rhomboid scales and, for most of the species, by semi-tritorial or strongly tritorial dentition". with dozens of species assigned to it. Fossils attributed to Lepidotes have been found in Jurassic and Cretaceous rocks worldwide. It has been argued that Lepidotes should be restricted to species closely related to the type species L. gigas, which are only known from the Early Jurassic of Western and Central Europe, with most other species being not closely related, with other species transferred to new genera such as Scheenstia.Lepidotes belongs to Ginglymodi, a clade of fish whose only living representatives are the gars (Lepisosteidae). The type species L. gigas and close relatives are thought to be members of the family Lepidotidae, part of the order Lepisosteiformes within Ginglymodi, with other species occupying various other positions within Ginglymodi.

Belonostomus is a genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish that was described by Louis Agassiz in 1844. It is a member of the order Aspidorhynchiformes, a group of fish known for their distinctive elongated rostrums.

Cosmolepis is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived during the Early Jurassic epoch. It contains a single species, C. ornatus from the Blue Lias in what is now England. It is the only member of the family Cosmolepididae.

Coccolepis is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish in the family Coccolepididae. Originally including most species within the family, it is now restricted to two species from the Late Jurassic Solnhofen Limestone of Germany. The holotype of C. bucklandi, designated and described by Louis Agassiz, was thought to be lost but was later rediscovered in Neuchâtel.

Ptycholepiformes are an extinct order of prehistoric ray-finned fish that existed during the Triassic period and the Early Jurassic epoch. The order includes the genera Acrorhabdus, Ardoreosomus, Boreosomus, Chungkingichthys, Ptycholepis, and Yuchoulepis. Although several families have been proposed, some studies place all these genera in the same family, Ptycholepididae.

Scheenstia is an extinct genus of neopterygian ray-finned fish from the Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous of Europe. Fossils have been found in both marine and freshwater environments.

Callipurbeckia is an extinct genus of marine semionotiform ray-finned fish from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found in Germany, Tanzania, and England.

Halecomorphi is a taxon of ray-finned bony fish in the clade Neopterygii. The only extant Halecomorph species are the bowfin and eyespot bowfin, but the group contains many extinct species in several families in the order Amiiformes, as well as the extinct orders Ionoscopiformes, Panxianichthyiformes, and Parasemionotiformes. The fossil record of halecomorphs goes back at least to the Early Triassic epoch.
This list of fossil fishes described in 2016 is a list of new taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, acanthodians, fossil cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes and other fishes of every kind that have been described during the year 2016, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of fishes that occurred in the year 2016. The list only includes taxa at the level of genus or species.
This list of fossil fishes described in 2019 is a list of new taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, acanthodians, fossil cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes of every kind that were described during the year 2019, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2019.
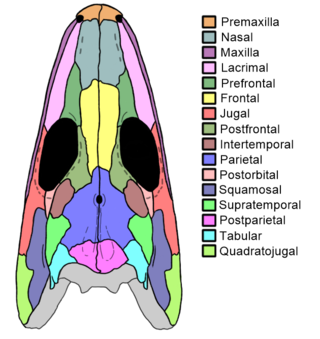
The intertemporal bone is a paired cranial bone present in certain sarcopterygians and extinct amphibian-grade tetrapods. It lies in the rear part of the skull, behind the eyes.
The Besano Formation is a geological formation in the southern Alps of northwestern Italy and southern Switzerland. This formation, a thin but fossiliferous succession of dolomite and black shale, is famous for its preservation of Middle Triassic (Anisian–Ladinian) marine life including fish and aquatic reptiles. It is exposed in the Monte San Giorgio and Besano area. It is among the formations responsible for the area being designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In Switzerland, it is also known as the Grenzbitumenzone. The Anisian-Ladinian boundary lies in the upper part of the Besano Formation.

Ginglymodi is a clade of ray-finned fish containing modern-day gars (Lepisosteidae) and their extinct relatives in the order Lepisosteiformes, the extinct orders Semionotiformes and Kyphosichthyiformes, and various other extinct taxa. Ginglymodi is one of the two major subgroups of the infraclass Holostei, the other one being Halecomorphi, which contains the bowfin and eyespot bowfin and their fossil relatives.

Dapediidae is an extinct family of neopterygian ray-finned fish that lived from the Middle Triassic to Late Jurassic. It is the only family of the order Dapediiformes. Its members were historically placed within the ginglymodian family Semionotidae, but were moved to their own family in 1966.

The San Salvatore Dolomite, sometimes known as the Salvatore Dolomite or San Salvatore Formation, is a Middle Triassic geological formation in Switzerland and Italy. The primarily lithology is micritic dolomite with a high proportion of algal mounds (stromatolites). It corresponds to a thick warm-water carbonate platform on the northern edge of an island in what is now the Po Plain. This formation and its local equivalents are common in the hills around Lake Maggiore, Varese, and Lugano, preserving fossils of marine invertebrates such as ammonoids, gastropods, and bivalves. At its southernmost extent on Monte San Giorgio, only the lower part of the San Salvatore Dolomite is preserved. The middle and upper parts are replaced by the Besano Formation, San Giorgio Dolomite, and Meride Limestone, which were deposited in a deeper and more anoxic basin between carbonate platforms.

Coccolepididae is an extinct family of ray-finned fish, known from the Early Jurassic to Early Cretaceous, most of which were originally referred to the type genus Coccolepis. They had a widespread distribution, being found in North and South America, Australia, Asia and Europe. They are mostly known from freshwater environments, though several species have been found in marine environments. They are morphologically conservative, and have poorly ossified endo and exoskeletons, which usually results in poor preservation. This makes it difficult to distinguish species. They are generally small fish, with the largest known specimens reaching a length of 210 mm. Historically, they have been classified as members of “Palaeonisciformes”, a paraphyletic grouping of non-neopterygian fish, due to their plesiomorphic conservative morphology closely resembling those of many other groups of primitive fish. Some recent authors have suggested that they may belong to the order Chondrostei as relatives of the Acipenseriformes.




















