
The Marantaceae are a family, the arrowroot family, or the prayer plant family, of flowering plants consisting of 31 genera and around 530 species, defining it as one of the most species-rich families in its order. Species of this family are found in lowland tropical forests of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. The majority (80%) of the species are found in the American tropics, followed by Asian (11%) and African (9%) tropics. They are commonly called the prayer-plant family and are also known for their unique secondary pollination presentation.
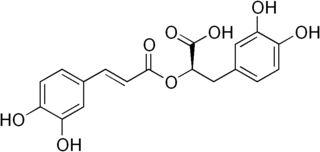
Rosmarinic acid, named after rosemary, is a polyphenol constituent of many culinary herbs, including rosemary, perilla, sage, mint, and basil.

Renealmia is a plant genus in the family Zingiberaceae. Its members are native to tropical Africa and tropical America. In Peru, fruits and tubers are sources of indigenous dyes. and indigenous medical treatments for leishmania and malaria In Colombia, it is used to treat snakebite. Bracts and leaves can serve as phytotelmata, retaining small quantities of water that offer habitat for other organisms.

Sarcophrynium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Marantaceae indigenous to tropical Africa. It was described as a genus in 1902.

Goeppertia insignis, the rattlesnake plant, is a species of flowering plant in the Marantaceae family, native to Rio de Janeiro state in Brazil.
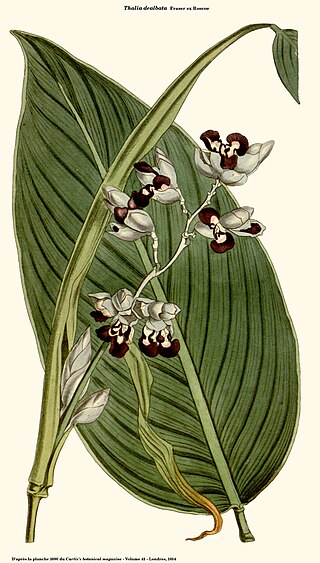
Thalia is a genus of flowering plants in the Marantaceae family found mainly in aquatic, marshy and riparian zones in Eastern, Central and Western Africa—as far south as Zimbabwe—and the Americas, from Illinois in the north, through northern Argentina in the southern part of its range. These plants can grow with their roots and rhizomes fully submerged and their foliage growing emersed from the water's surface. They thrive in floodplains, vernal pools and other seasonally-inundated areas, as well. Alligator-flag is a common name for plants in this genus. The generic name is in honor of Johannes Thal (1542–1583), a German doctor who wrote A Flora of the Harz Mountains.

Goeppertia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Marantaceae, native to the New World Tropics. It contains 243 accepted species, many of which were until recently assigned to Calathea. It was first described by Nees von Esenbeck in 1831, who erroneously erected another genus Goeppertia in 1836, which has now been synonymized with Endlicheria. In 1862 August Grisebach described another genus Goeppertia; this has now been synonymized with Bisgoeppertia.

Maranta leuconeura, widely known as the prayer plant due to its daily sunlight-dependent movements, is a species of flowering plant in the family Marantaceae native to the Brazilian tropical forests. It is a variable, rhizomatous perennial, growing to 30 cm (12 in) tall and broad, with crowded clumps of evergreen, strikingly-marked oval leaves, each up to 12 cm (5 in) long. The plant spreads itself horizontally, carpeting an entire small area of forest floor, sending roots into the substrate at each leaf node.

Halopegia is a genus of plants native to tropical Africa, Madagascar, and tropical southeast Asia. Three species are recognized as of April 2014:
Monophyllanthe is a genus of plants native to Brazil, Colombia, French Guinea and Suriname. It contains 2 recognized species:

Boesenbergia is a genus of plants in the ginger family. It contains more than 90 species, native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.

Globba is a genus of plants in the ginger family. It contains about 104 species, native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, the Bismarck Archipelago and Queensland.
Aframomum alpinum is a monocotyledonous plant species that was first described by François Gagnepain, and given its current name by Karl Moritz Schumann. Aframomum alpinum is part of the genus Aframomum and the family Zingiberaceae.
Aframomum cereum is a monocotyledonous plant species in the family Zingiberaceae that was first described by Joseph Dalton Hooker, and got its current name from Karl Moritz Schumann.

Aframomum citratum is a monocotyledonous plant species in the family Zingiberaceae that was first described by C. Pereira, and given its current name by Karl Moritz Schumann.
Aframomum kayserianum is a species of plant in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It was first described by Karl Moritz Schumann.
Aframomum luteoalbum is a species of plant in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It was first described by Karl Moritz Schumann.
Aframomum subsericeum is a species of plant in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It was first described by Daniel Oliver and Daniel Hanbury and renamed by Karl Moritz Schumann.
Aframomum mala is a species of flowering plant in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It was first described by Karl Moritz Schumann and Adolf Engler, and was given its current name by Karl Moritz Schumann. It is a rhizomatous geophyte native to Tanzania.
Harmsia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Malvaceae.











