Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
MALDI is an ionization technique where laser energy is absorbed by a matrix to create ions from large molecules without fragmentation. The matrix, typically in excess, is mixed with the analyte molecule and deposited on a target. A table of matrix compounds, their structures, laser wavelengths typically used, and typical application is shown below.
| Compound | Abbreviation | Structure | Wavelength (nm) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9-aminoacridine [1] | 9AA |  | 337 | lipids, metabolites |
| α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid [2] | CHCA | 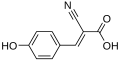 | 337, 355 | peptides, lipids, nucleotides |
| ferulic acid [3] [4] | FA |  | 337, 355, 266 | proteins |
| 2,5-dihydroxy benzoic acid| [5] | DHB |  | 337, 355 | peptides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, oligosaccharides |
| 3-hydroxy picolinic acid [6] | HPA | 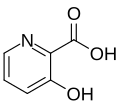 | 337, 355 | oligonucleotides |
| picolinic acid [7] | PA |  | 266 | oligonucleotides |
| sinapinic acid [3] [4] | SA |  | 337, 355, 266 | peptides, proteins, lipids |




