Giambologna, also known as Jean de Boulogne (French), Jehan Boulongne (Flemish) and Giovanni da Bologna (Italian), was the last significant Italian Renaissance sculptor, with a large workshop producing large and small works in bronze and marble in a late Mannerist style.

Cosimo I de' Medici was the second Duke of Florence from 1537 until 1569, when he became the first Grand Duke of Tuscany, a title he held until his death.

A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became small farming compounds, which were increasingly fortified in Late Antiquity, sometimes transferred to the Church for reuse as a monastery. Then they gradually re-evolved through the Middle Ages into elegant upper-class country homes. In the Early Modern period, any comfortable detached house with a garden near a city or town was likely to be described as a villa; most survivals have now been engulfed by suburbia. In modern parlance, "villa" can refer to various types and sizes of residences, ranging from the suburban semi-detached double villa to, in some countries, especially around the Mediterranean, residences of above average size in the countryside.
Villa del Poggio Imperiale is a predominantly neoclassical former grand ducal villa in Arcetri, just to the south of Florence in Tuscany, central Italy. Beginning as a villa of the Baroncelli of Florence, it was seized by the Medici, became the home of a homicidal and unfaithful husband, and a lavish retreat for a Grand Duchess with imperial pretensions. Later given to Napoleon's sister, it was reclaimed by the hereditary rulers of Tuscany before being finally converted to a prestigious girls' school. During its long history, it has often been at the centre of Italy's turbulent history, and has been rebuilt and redesigned many times.

Niccolò di Raffaello di Niccolò dei Pericoli, called "Il Tribolo" was an Italian Mannerist artist in the service of Cosimo I de' Medici in his natal city of Florence.

The Villa Medici is a Mannerist villa and an architectural complex with a garden contiguous with the larger Borghese gardens, on the Pincian Hill next to Trinità dei Monti in Rome, Italy. The Villa Medici, founded by Ferdinando I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany and now property of the French State, has housed the French Academy in Rome since 1803. A musical evocation of its garden fountains features in Ottorino Respighi's Fountains of Rome.

Poggio a Caiano is a town and comune in the province of Prato, Tuscany region Italy. The town, birthplace of Philip Mazzei, lies 9 kilometres (6 mi) south of the provincial capital of Prato.

The Villa Medici at Careggi is a patrician villa in the hills near Florence, Tuscany, central Italy.

Vittoria della Rovere was Grand Duchess of Tuscany as the wife of Grand Duke Ferdinando II. She had four children with her husband, two of whom would survive infancy: the future Cosimo III, Tuscany's longest-reigning monarch, and Francesco Maria, a prince of the Church. At the death of her grandfather Francesco Maria della Rovere, she inherited the Duchies of Rovere and Montefeltro, which reverted to her second son, Francesco Maria, at her death. She was later entrusted with the care of her three grandchildren. Her marriage brought a wealth of treasures to the House of Medici, which can today be seen in the Palazzo Pitti and the Uffizi Gallery in Florence.
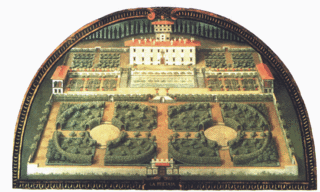
Giusto Utens or Justus Utens was a Flemish painter who is remembered for the series of Medicean villas in lunette form that he painted for the third Grand Duke of Tuscany, Ferdinando I, in 1599–1602.

The Villa Medicea di Cafaggiolo is a villa situated near the Tuscan town of Barberino di Mugello in the valley of the River Sieve, some 25 kilometres north of Florence, central Italy. It was one of the oldest and most favoured of the Medici family estates, having been in the possession of the family since the 14th century, when it was owned by Averardo de' Medici. Averardo's son, Giovanni di Bicci de' Medici, is considered to be the founder of the Medici dynasty.
Alfonso Parigi the Younger (1606–1656) was an Italian architect and scenographer, the son of Giulio Parigi, and grandson of Alfonso Parigi the Elder.

The Villa di Castello, near the hills bordering Florence, Tuscany, central Italy, was the country residence of Cosimo I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany (1519-1574). The gardens, filled with fountains, statuary, and a grotto, became famous throughout Europe. The villa also housed some of the great art treasures of Florence, including Sandro Botticelli's Renaissance masterpieces The Birth of Venus and Primavera. The gardens of the Villa had a profound influence upon the design of the Italian Renaissance garden and the later French formal garden.

The Villa del Trebbio is a Medici villa in Tuscany, Italy.

The Italian Renaissance garden was a new style of garden which emerged in the late 15th century at villas in Rome and Florence, inspired by classical ideals of order and beauty, and intended for the pleasure of the view of the garden and the landscape beyond, for contemplation, and for the enjoyment of the sights, sounds and smells of the garden itself.

The Medici Villa of Poggio a Caiano, also called Ambra, is one of the most famous Medici villas and is located in Poggio a Caiano (Prato). Today it is state owned and it houses two museums: one of the historic apartments and the Museum of Still Life.

Portrait of Cosimo the Elder is an oil on panel painting by Pontormo, executed c. 1519–1520, now in the Uffizi, Florence.

Nano Morgante was an Italian dwarf who was a famed buffoon and court jester in the court of Cosimo I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany. Morgante was ironically nicknamed after the giant from the poem of the same name by Luigi Pulci. He was the most celebrated of the five dwarves of the Medici court at the Palazzo Pitti.