
The geography of Egypt relates to two regions: North Africa and Southwest Asia.

The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. The longest river in Africa, it has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer, the Nile is amongst the smallest in the world by measure of cubic metres flowing annually. About 6,650 km (4,130 mi) long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Republic of the Sudan, and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt and Sudan.

The Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, Libya to the northwest, Chad to the west, the Central African Republic to the southwest, South Sudan to the south, Ethiopia to the southeast, Eritrea to the east, and the Red Sea to the northeast. Sudan has a population of 44.91 million people as of 2021 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres, making it Africa's third-largest country by area and also the third-largest by area in the Arab league. It was also the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab league until the secession of South Sudan in 2011, since which both titles have been held by Algeria.

A swamp is a forested wetland. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in creating this environment. Swamps vary in size and are located all around the world. The water of a swamp may be fresh water, brackish water, or seawater. Freshwater swamps form along large rivers or lakes where they are critically dependent upon rainwater and seasonal flooding to maintain natural water level fluctuations. Saltwater swamps are found along tropical and subtropical coastlines. Some swamps have hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates periodic inundation or soil saturation. The two main types of swamp are "true" or swamp forests and "transitional" or shrub swamps. In the boreal regions of Canada, the word swamp is colloquially used for what is more correctly termed a bog, fen, or muskeg. Some of the world's largest swamps are found along major rivers such as the Amazon, the Mississippi, and the Congo.

The White Nile is a river in Africa, one of the two main tributaries of the Nile, the other being the Blue Nile. The name comes from colouring due to clay carried in the water.

The Sudd is a vast swamp in South Sudan, formed by the White Nile's Baḥr al-Jabal section. The Arabic word sudd is derived from sadd (سد), meaning "barrier" or "obstruction". The term "the sudd" has come to refer to any large solid floating vegetation island or mat. The area which the swamp covers is one of the world's largest wetlands and the largest freshwater wetland in the Nile basin.

The Eastern Desert is the part of the Sahara desert that is located east of the Nile river. It spans 223,000 square kilometres (86,000 sq mi) of North-Eastern Africa and is bordered by the Nile river to the west and the Red Sea and Gulf of Suez to the east. It extends through Egypt, Eritrea, Sudan and Ethiopia. The Eastern Desert is also known as the Red Sea Hills. The Desert consists of a mountain range which runs parallel to the coast, wide sedimentary plateaus extending from either side of the mountains and the Red Sea coast. The rainfall, climate, vegetation and animal life sustained in the desert varies between these different regions.The Desert has been a mining site for building materials, and precious and semi-precious metals throughout history. It has historically contained many trade routes leading to and from the Red Sea, including the Suez Canal.

Bor is the capital of Jonglei State in South Sudan. Since 2016, it has also served as the headquarters of Bor Municipality. The city is situated on the east side of the White Nile at the southern extent of the sudd, South Sudan's vast central wetlands.

Malakal is a city in South Sudan and the second largest city after the national capital Juba. And it is the capital of Upper Nile State, South Sudan, near the White Nile River. It also serves as the headquarters of makal county.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Sudan:

The flag of South Sudan was adopted following the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement that ended the Second Sudanese Civil War. A similar version of the flag was previously used as the flag of the Sudan People's Liberation Movement. The flag of South Sudan is older than the country itself, as the flag was adopted in 2005, while the country became independent in 2011.

The Yabus River rises in the far west of Ethiopia, in Asosa Zone, flows west into Sudan past the town of Yabus, then enters South Sudan. At the town of Bunj it turns south west and enters the Machar Marshes, where it loses its identity.
The South Branch Marsh River is a 3.0-mile-long (4.8 km) tidal river in the towns of Prospect and Frankfort in Waldo County, Maine. It joins the North Branch Marsh River to form Marsh Bay, a short arm of the tidal Penobscot River.

The Sonny Bono Salton Sea National Wildlife Refuge is at the southern end of the Salton Sea in Imperial Valley, California, 40 miles (64 km) north of the Mexican border. Situated along the Pacific Flyway, the Refuge is the only one of its kind, located 227 feet (69 m) below sea level. Because of its southern latitude, elevation and location in the Colorado Desert, the Refuge experiences some of the highest temperatures in the nation. Daily temperatures from May to October generally exceed 100 °F with temperatures of 116°–120 °F recorded yearly.
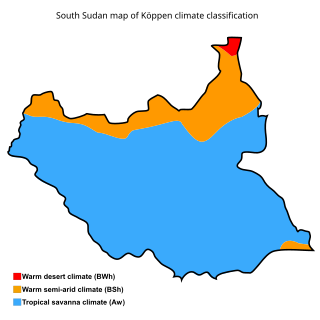
The geography of South Sudan describes the physical features of South Sudan, a country in East Africa. South Sudan is a landlocked country and borders – clockwise – Sudan from the north, Ethiopia from the east, Kenya, Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo from the south and the Central African Republic from the west.

The Lotilla River is a river in South Sudan. It rises in marshes on the borders of the erstwhile Eastern Equatoria and Jonglei states and flows north to join the Pibor River near Pibor, at a junction with the Kangen River. The marshes are fed by the Medikiret River, which has its origins in marshes further south.

The Daga River is a river in South Sudan. It rises in the mountains of the Mirab Welega Zone in Ethiopia, just east of the South Sudan - Ethiopia border, where it is known as the Deqe Sonka Shet. It flows west past the town of Daga Post and enters the Machar Marshes, where it loses its identity.

The Adar River, known to the Dinka as the Yal, is a tributary of the White Nile in the state of Upper Nile, South Sudan. It flows north west from the Machar Marshes and enters the White Nile just upstream of the town of Melut.

The Adar oilfield, also known as the Adar Yale, Adar Yeil or Adaril field, is an oilfield situated in the Mabaan in South Sudan estimated to contain about 276 million barrels (43,900,000 m3) of oil. The Chevron Corporation discovered the Adar Yale field in 1981, shortly before the start of the Second Sudanese Civil War (1983–2005). Soon after Chevron had suspended operations in 1984, Sudanese government troops began attacking civilian settlements in the area, burning the houses and driving the people away, and in the late 1990s, Nuer militias from Nasir helped the army in clearing away the people to make way for the roads and infrastructure of the oilfield.
















