
Psora is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Psoraceae. Members of the genus are commonly called fishscale lichens. Lichens in the genus Psora generally have a squamulose thallus and anthraquinones in the hymenium. Photobiont partners of Psora lichens include members of the green algal genera Asterochloris, Chloroidium, Myrmecia, and Trebouxia.

Aspicilia is a genus of mostly crustose areolate lichens that grow on rock. Most members have black apothecia discs that are slightly immersed in the areolas, hence the common name"Given the same reason, the naming of Aspicilia is derived from the Greek word for "shield concave".
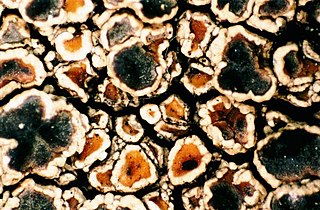
Megasporaceae are a family of fungi belonging to the order Pertusariales. Taxa are lichenized with green algae, and grow on rocks, often in maritime climates close to fresh water. Phylogenetic analysis has shown that this family is related to the Pertusariaceae, another family of lichens. The genus Aspicilia was moved here from the Hymeneliaceae.

The Pertusariales are an order of fungi in the class Lecanoromycetes, comprising 8 families, 31 genera, and over 600 species, many of which form lichens. This diverse group is characterized by complex taxonomic history and ongoing phylogenetic revisions. Originally proposed by Maurice Choisy in 1949 and later formally published by the lichenologists David L. Hawksworth and Ove Eriksson in 1986, Pertusariales has undergone significant reclassification due to molecular phylogenetics studies. The order includes well-known genera such as Pertusaria and Ochrolechia, as well as families like Megasporaceae and Icmadophilaceae.

Acarospora is a genus of mostly lichen-forming fungi in the family Acarosporaceae. Most species in the genus are crustose lichens that grow on rocks in open and arid places all over the world. They may look like a cobblestone road or cracked up old paint, and are commonly called cobblestone lichens or cracked lichens. They usually grow on rock, but some grow on soil (terricolous) or on other lichens. Some species in the genus are fungi that live as parasites on other lichens. Acarospora is a widely distributed genus, with about 128 species according to a 2008 estimate.

Diploschistes is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Graphidaceae. Commonly known as crater lichens, members of the genus are crustose lichens with a thick, cracked (areolate) body (thallus) with worldwide distribution. The fruiting part (apothecia) are immersed in the thick thallus so as to have the appearance of being small "craters". The widespread genus contains about 43 species.

Phaeophyscia is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Physciaceae.

Placopyrenium is a genus of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), crustose lichens in the family Verrucariaceae.

Fuscideaceae is a family of lichen-forming fungi in the order Umbilicariales. It contains five genera and about 55 species of crustose lichens.
Aderkomyces thailandicus is a species of corticolous (bark-dwelling), crustose lichen in the family Gomphillaceae. Found in the lower montane rainforests of Thailand, it was described as new to science in 2011.

Lobothallia is a genus of lichens in the family Megasporaceae. Species in the genus have foliose thalli that become crustose areolate in the center with age, and grow on calcareous to siliceous rocks. The crustose part of the body may keep its lower cortex, though not always. Dark brown to black apothecia may be sunken into the surface of the thallus, as indicated in the common name puffed sunken disk lichen. Members grow to 3–5 cm (1.2–2.0 in) or more radiating lobes (placodioid). The photobiont is green alga from the genus Trebouxia. The genus is represented in Eurasia, Asia, North Africa, Central America, western North America, and Australia.
Teuvoa is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Megasporaceae. It was first classified by lichenologists Mohammad Sohrabi and Steven Leavitt in 2013, with Teuvoa uxoris assigned as the type species. This genus was delineated from the larger genus, Aspicilia, following a molecular phylogenetic analysis which revealed that the Aspicilia uxoris species group constituted a distinct lineage in the Megasporaceae. Initially containing three species, two additional species native to China were added in 2018. Teuvoa is characterised by its small ascospores and conidia, and the absence of secondary metabolites.
Halospora is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi in the family Verrucariaceae. Species in the genus parasitise calcicolous crustose lichens, i.e., those that prefer lime-rich substrates.

Piccolia is a small genus of crustose lichens in the class Lecanoromycetes. First circumscribed by Italian lichenologist Abramo Bartolommeo Massalongo in 1864, it contains ten species. Due to a lack of molecular data, it has not been assigned to an order or family.
Aspiciliopsis is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Trapeliaceae. It has two species, both of which occur in the Southern Hemisphere.
Calogaya orientalis is a species of corticolous (bark-dwelling) and muscicolous lichen (moss-dwelling), crustose lichen in the family Teloschistaceae. It is found in arid steppe and desert habitats in Northwestern China, Iran, and Turkey. The thallus of this lichen is reduced, similar to species in the genus Athallia.

Coniocarpon is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Arthoniaceae. It has eight species of corticolous (bark-dwelling) lichens. This genus is distinct for its crystalline orange, red, and purple quinoid pigments in the ascomata that turn purple in potassium hydroxide solution, its colourless, transversely septate ascospores with large apical cells, and its rounded to lirellate ascomata.

Puttea is a genus of lichen-forming fungi with uncertain familial placement in the order Lecanorales. The genus comprises four species. Finnish lichenologists Soili Stenroos and Seppo Huhtinen established the genus Puttea in 2009 for the lichen species formerly known as Lecidea margaritella, which has undergone various reclassifications. Molecular phylogenetics analyses have shown that Puttea margaritella does not align closely with genera like Fellhanera or Micarea, but its precise familial placement remains uncertain. Puttea is characterized by an indistinct, lichenized thallus composed of delicate fungal filaments and small algal cells. Its minute, round, whitish apothecia lack a distinct margin, and the asci, or spore-producing cells, are thick-walled, club-shaped, and contain eight spores, showing specific reactions with iodine-based stains. The type species of the genus, Puttea margaritella, typically inhabits boreal forests, growing on the liverwort species Ptilidium pulcherrimum and sometimes on decaying wood or bark. Initially thought to be confined to Europe, it has since been found in North America, particularly in Alaska and Québec, extending its known range. The species is parasitic, damaging its host, and is considered rare within its distribution.

Aspiciliella is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Megasporaceae. It has four species. The genus is characterised by its crustose, rimose-areolate thallus that is partially continuous and has a K+ (red) reaction. The epihymenium is typically green to olive-green and turns light green when treated with N. Aspiciliella has eight-spored asci of the Aspicilia-type, containing ellipsoid, colourless, and simple ascospores.

Aspilidea is a fungal genus of uncertain familial placement in the subclass Ostropomycetidae. It contains the single species Aspilidea myrinii, a saxicolous (rock-dwelling) crustose lichen with a circumpolar distribution.















