
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV). The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the syndrome caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. In the 2010s, Chinese scientists traced the virus through the intermediary of Asian palm civets to cave-dwelling horseshoe bats in Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township, Yunnan.
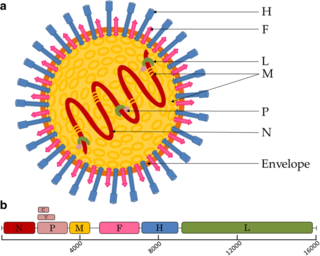
Paramyxoviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include measles, mumps, and respiratory tract infections. The family has four subfamilies, 17 genera, and 78 species, three genera of which are unassigned to a subfamily.

Reoviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses have a wide host range, including vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, protists and fungi. They lack lipid envelopes and package their segmented genome within multi-layered capsids. Lack of a lipid envelope has allowed three-dimensional structures of these large complex viruses to be obtained, revealing a structural and likely evolutionary relationship to the cystovirus family of bacteriophage. There are currently 97 species in this family, divided among 15 genera in two subfamilies. Reoviruses can affect the gastrointestinal system and respiratory tract. The name "reo-" is an acronym for "respiratory enteric orphan" viruses. The term "orphan virus" refers to the fact that some of these viruses have been observed not associated with any known disease. Even though viruses in the family Reoviridae have more recently been identified with various diseases, the original name is still used.

Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), also called human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) and human orthopneumovirus, is a common, contagious airborne virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. Its name is derived from the large cells known as syncytia that form when infected cells fuse.
A syncytium or symplasm is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells, in contrast to a coenocyte, which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without accompanying cytokinesis. The muscle cell that makes up animal skeletal muscle is a classic example of a syncytium cell. The term may also refer to cells interconnected by specialized membranes with gap junctions, as seen in the heart muscle cells and certain smooth muscle cells, which are synchronized electrically in an action potential.
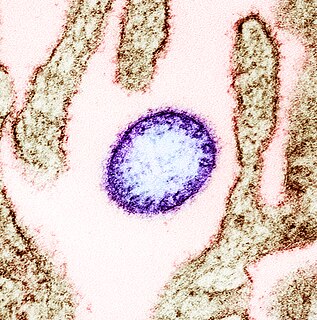
Nipah virus, scientific name Nipah henipavirus, is a bat-borne virus that causes Nipah virus infection in humans and other animals, a disease with a high mortality rate. Numerous disease outbreaks caused by Nipah virus have occurred in South and Southeast Asia. Nipah virus belongs to the genus Henipavirus along with the Hendra virus, which has also caused disease outbreaks.

Coronaviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect amphibians, birds, and mammals. The group includes the subfamilies Letovirinae and Orthocoronavirinae; the members of the latter are known as coronaviruses.
Tioman virus is a paramyxovirus first isolated from the urine of island fruit bats on Tioman Island, Malaysia in 2000. The virus was discovered during efforts to identify the natural host of Nipah virus which was responsible for a large outbreak of encephalitic illness in humans and pigs in Malaysia and Singapore in 1998–99.

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illness responsible for the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which infects the epithelial cells within the lungs. The virus enters the host cell by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. It infects humans, bats, and palm civets.

Human coronavirus NL63 (HCoV-NL63) is a species of coronavirus, specifically a Setracovirus from among the Alphacoronavirus genus. It was identified in late 2004 in patients in the Netherlands. The virus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to ACE2. Infection with the virus has been confirmed worldwide, and has an association with many common symptoms and diseases. Associated diseases include mild to moderate upper respiratory tract infections, severe lower respiratory tract infection, croup and bronchiolitis.

Orthoreovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Reoviridae, in the subfamily Spinareovirinae. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. There are ten species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include mild upper respiratory tract disease, gastroenteritis, and biliary atresia. Mammalian orthoreovirus 3 induces cell death preferentially in transformed cells and therefore displays inherent oncolytic properties.
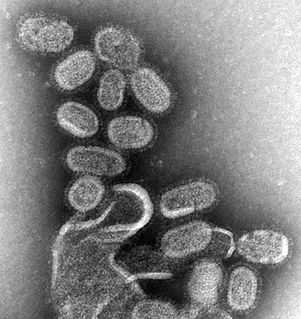
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin from one to four days after exposure to the virus and last for about 2–8 days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia, which can be caused by the virus or by a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications of infection include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease.
Bocaparvovirus is a genus of viruses in the subfamily Parvovirinae of the virus family Parvoviridae. Humans, cattle, and dogs serve as natural hosts. There are 28 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include, in humans, acute respiratory illness, and in cattle, diarrhea and mild respiratory symptoms.

Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (MERS-CoV), or EMC/2012 (HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, bats, and camels. The infecting virus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the DPP4 receptor. The species is a member of the genus Betacoronavirus and subgenus Merbecovirus.

The bat virome is the group of viruses associated with bats. Bats host a diverse array of viruses, including all seven types described by the Baltimore classification system: (I) double-stranded DNA viruses; (II) single-stranded DNA viruses; (III) double-stranded RNA viruses; (IV) positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses; (V) negative-sense single-stranded RNA viruses; (VI) positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate; and (VII) double-stranded DNA viruses that replicate through a single-stranded RNA intermediate. The greatest share of bat-associated viruses identified as of 2020 are of type IV, in the family Coronaviridae.
Nelson Bay orthoreovirus, often called Nelson Bay virus (NBV) is a novel double-stranded RNA orthoreovirus species first isolated from a flying fox near Nelson Bay in New South Wales, Australia.

Bourbon virus is an RNA virus in the genus Thogotovirus of the family Orthomyxoviridae, which is similar to Dhori virus and Batken virus. It was first identified in 2014 in a man from Bourbon County, Kansas, United States, who died after being bitten by ticks. The case is the eighth report of human disease associated with a thogotovirus globally, and the first in the Western hemisphere. As of May 2015, a case was discovered in Stillwater, Oklahoma and relatively little is known about the virus. No specific treatment or vaccine is available. The virus is suspected to be transmitted by ticks or insects, and avoidance of bites is recommended to reduce risk of infection. In June 2017 a 58-year-old female Missouri State Park employee died from an infection of the Bourbon virus after it had been misdiagnosed for a significant period of time.
The Punta Toro virus is a member of the genus Phlebovirus of the order Bunyavirales. It was initially isolated from patients in Colombia and two key patients in Panama. Two individual serotypes of PTV were isolated from these patients, PTV-Adames (A) and PTV-Balliet (B), with PTV-A appearing to be more virulent. PTV is considered to be relatively contained to the Americas with no cases being reported outside of this region. Along with a few other human pathogenic Phleboviruses, PTV is considered to be a significant virus in terms of public health as little information is known about its clinical effects and with further research underway, PTV could have unforeseen impacts on health and virology.
Mammalian orthoreovirus (MRV) is a double-stranded RNA virus. It is a part of the family Reoviridae, as well as the subfamily Spinareovirinae. As seen in the name, the Mammalian Ortheoreovirus infects numerous mammalian species and vertebrates which serve as natural hosts. Some diseases that occur as a result of this virus or are associated with this virus include mild upper respiratory illness, and gastrointestinal illness. Examples of these are: upper respiratory tract syndromes, gastroenteritis, biliary atresia, obstructive hydrocephalus, jaundice, alopecia, conjunctivitis, and ‘oily hair’ associated with steatorrhea.
Civet SARS-CoV is a coronavirus associated with Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), which infected humans and caused SARS events from 2002 to 2003. It infected the masked palm civet. The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) is highly similar, with a genome sequence similarity of about 99.8%. Because several patients infected at the early stage of the epidemic had contact with fruit-eating Japanese Raccoon Dog in the market, fruit-eating Tanuki may be a direct source of human SARS coronavirus. At the end of 2003, four more people in Guangzhou, China were infected with the disease. Sequence analysis found that the similarity with the Tanuki virus reached 99.9%, and the SARS coronavirus was also caused by cases of Tanuki transmission.











