
Monterey is a city in Monterey County on the southern edge of Monterey Bay on the U.S. state of California's Central Coast. Founded on June 3, 1770, Monterey was the second permanent settlement established by Spanish explorers in what is now California. It functioned as the capital of Alta California under both Spain (1804–1821) and Mexico (1822–1846). During this period, Monterey hosted California's first theater, public building, public library, publicly funded school, printing press, and newspaper. It was originally the only port of entry for all taxable goods in California. In 1846, during the Mexican–American War of 1846–1848, the United States Flag was raised over the Customs House. After Mexico ceded California to the U.S. at the end of the war, Monterey hosted California's first constitutional convention in 1849.

Monterey Bay Aquarium is a nonprofit public aquarium in Monterey, California. Known for its regional focus on the marine habitats of Monterey Bay, it was the first to exhibit a living kelp forest when it opened in October 1984. Its biologists have pioneered the animal husbandry of jellyfish and it was the first to successfully care for and display a great white shark. The organization's research and conservation efforts also focus on sea otters, various birds, and tunas. Seafood Watch, a sustainable seafood advisory list published by the aquarium beginning in 1999, has influenced the discussion surrounding sustainable seafood. The aquarium was home to Otter 841 prior to her release into the wild as well as Rosa, the oldest living sea otter at the time of her death.

Monterey Bay is a bay of the Pacific Ocean located on the coast of the U.S. state of California, south of the San Francisco Bay Area. San Francisco itself is further north along the coast, by about 75 miles, accessible via CA 1 and US 101.

The red-headed woodpecker is a mid-sized woodpecker found in temperate North America. Its breeding habitat is open country across southern Canada and the east-central United States. It is rated as least concern on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)'s Red List of Endangered species, having been down-listed from near threatened in 2018.

Hesperocyparis macrocarpa also known as Cupressus macrocarpa, or the Monterey cypress is a coniferous tree, and is one of several species of cypress trees endemic to California.

Stellamedusa is a genus of jellyfish. The genus is monotypic with a single species recognized, Stellamedusa ventana.

Zmudowski State Beach is located on Monterey Bay, in Moss Landing, Monterey County, northern California.

Opisthoteuthis californiana, also known as the flapjack octopus, or flapjack devilfish is a species of umbrella octopus.

Larvaceans or appendicularians, class Appendicularia, are solitary, free-swimming tunicates found throughout the world's oceans. While larvaceans are filter feeders like most other tunicates, they keep their tadpole-like shape as adults, with the notochord running through the tail. They can be found in the pelagic zone, specifically in the photic zone, or sometimes deeper. They are transparent planktonic animals, usually ranging from 2 mm (0.079 in) to 8 mm (0.31 in) in body length including the tail, although giant larvaceans can reach up to 10 cm (3.9 in) in length.

The Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary (MBNMS) is a federally protected marine area offshore of California's Big Sur and central coast in the United States. It is the largest US national marine sanctuary and has a shoreline length of 276 miles (444 km) stretching from just north of the Golden Gate Bridge at San Francisco to Cambria in San Luis Obispo County. Supporting one of the world's most diverse marine ecosystems, it is home to numerous mammals, seabirds, fishes, invertebrates and plants in a remarkably productive coastal environment. The MBNMS was established on September 18, 1992, for the purpose of resource protection, research, education, and public use.
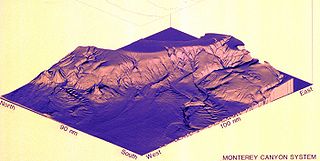
Monterey Canyon, or Monterey Submarine Canyon, is a submarine canyon in Monterey Bay, California with steep canyon walls measuring a full 1 mile (1.6 km) in height from bottom to top, which height/depth rivals the depth of the Grand Canyon itself. It is the largest such submarine canyon along the West coast of the North American continent, and was formed by the underwater erosion process known as turbidity current erosion. Many questions remain unresolved regarding the exact nature of its origins, and as such it is the subject of several ongoing geological and marine life studies being carried out by scientists stationed at the nearby Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute, the Moss Landing Marine Laboratories, and other oceanographic institutions.

The Monterey Clipper is a fishing boat common to the San Francisco Bay Area, the Monterey Bay Area and east to the Sacramento delta.

Davidson Seamount is a seamount located off the coast of Central California, 80 mi (129 km) southwest of Monterey and 75 mi (121 km) west of San Simeon. At 26 mi (42 km) long and 8 mi (13 km) wide, it is one of the largest known seamounts in the world. From base to crest, the seamount is 7,480 ft (2,280 m) tall, yet its summit is still 4,101 ft (1,250 m) below the sea surface. The seamount is biologically diverse, with 237 species and 27 types of deep-sea coral having been identified.
Polistes erythrocephalus is a species of paper wasp in the subfamily Polistinae of family Vespidae found in Central and South America. P. erythrocephalus is a eusocial wasp, meaning that it possesses both reproductive and non-reproductive castes. The cooperation between the two castes to raise young demonstrates the altruistic nature of these wasps. P. erythrocephalus exhibits a four-stage colony cycle, as do many other Polistes wasps. This species generally feeds on larvae, occasionally their own, and is preyed upon by species such as army ants.
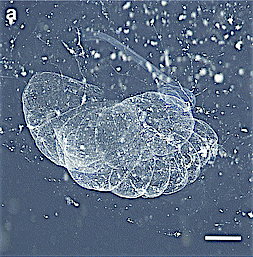
Bathochordaeus charon is a species of giant larvacean, a solitary, free-swimming tunicate that filter feeds in surface waters. The species was named after Charon, the mythical Greek ferryman who carried the souls of the dead across the rivers dividing the world of the living from the world of the dead.

Bathochordaeus, the giant larvaceans, is a genus of larvacean tunicates in the family Oikopleuridae. They are free-swimming filter-feeding marine animals that build mucus bubbles. They eat tiny particles of dead or drifting organic material that float through the water column, which contribute to the oceanic carbon cycle and the accelerated transfer of carbon to the deep sea.
The defunct Boy Scout councils are those which have been closed and merged with other councils.
Bathochordaeus mcnutti, the blue-tailed giant larvacean, is a species of larvacean in the genus Bathochordaeus within the family Oikopleuridae. It's found in the North Pacific Ocean, it is comparatively large and reaching up to 10 centimeters in length including the tail. It can be distinguished from other giant larvaceans by its bright blue tail margin.
Bathochordaeus stygius is a species of larvacean in the genus Bathochordaeus within the family Oikopleuridae.
Fritillaria is a genus of larvacean tunicates belonging to the family Fritillariidae.














