
The hourglass dolphin is a small dolphin in the family Delphinidae that inhabits offshore Antarctic and sub-Antarctic waters. It is commonly seen from ships crossing the Drake Passage but has a circumpolar distribution.

Stylocheilus is a genus of sea slugs, specifically sea hares, marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusks in the family Aplysiidae, the sea hares.

Jean René Constant Quoy was a French naval surgeon, zoologist and anatomist.

Thaliacea is a class of marine chordates within the subphylum Tunicata, comprising the salps, pyrosomes and doliolids. Unlike their benthic relatives the ascidians, from which they are believed to have emerged, thaliaceans are free-floating (pelagic) for their entire lifespan. The group includes species with complex life cycles, with both solitary and colonial forms.

Pyura is a large genus of sessile ascidians that live in coastal waters at depths of up to 80 m (260 feet). Like all ascidians, Pyura are filter feeders. A few species, including Pyura chilensis are commercially fished.

A salp or salpa is a barrel-shaped, planktonic tunicate in the family Salpidae. It moves by contracting, thereby pumping water through its gelatinous body; it is one of the most efficient examples of jet propulsion in the animal kingdom. The salp strains the pumped water through its internal feeding filters, feeding on phytoplankton.

Botryllus is a genus of colonial ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.

Siphonaria is a genus of air-breathing sea snails or false limpets, marine pulmonate gastropod molluscs in the family Siphonariidae, the false limpets.

Chiton is a genus of chitons, a polyplacophoran mollusk in the family Chitonidae.

Clavelina is genus of sea squirts, containing the following species:

Echinolittorina is a genus of small sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Littorinidae, the winkles.

The Abylidae are a family of marine invertebrates in the order Siphonophorae. They are colonial, but the colonies can superficially resemble jellyfish; although they appear to be a single organism, each specimen is actually a colony of Siphonophora.

Scyllaea is a genus of nudibranchs. They are marine gastropod molluscs in the family Scyllaeidae.

Actinodendron arboreum, commonly known as tree anemone or hell's fire anemone, is a species of sea anemone in the family Actinodendronidae. It is native to the Indo-Pacific where it grows at depths of down to 28 metres (92 ft). Most sea anemone species are harmless to humans, but A. arboreum is highly venomous and its sting can cause severe skin ulcers.

Asterocarpa is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.
Chorizocarpa is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.

Distomus is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.

Boltenia is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Pyuridae.
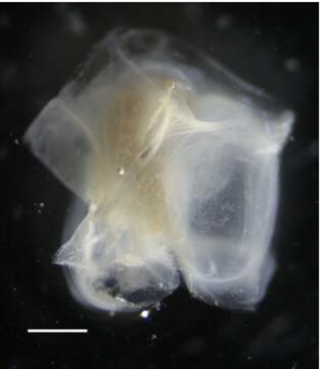
Abyla is a genus of colonial siphonophore in the subfamily Abylidae and the suborder Calycophorae. The genus contains three species and was established by Quoy and Gaimard in 1827.

Sycozoa cerebriformis, is a sea squirt in the family Holozoidae, first described by Jean René Constant Quoy and Joseph Paul Gaimard in 1834 as Aplidie cerebriforme. The taxonomic decision which determined the name, Sycozoa cerebriformis, and the species' synonymy was given by Patricia Kott in 1990.



















