
Ascidia is a genus of tunicates in the family Ascidiidae.

Pyura is a large genus of sessile ascidians that live in coastal waters at depths of up to 80 m (260 feet). Like all ascidians, Pyura are filter feeders. A few species, including Pyura chilensis are commercially fished.

Microcosmus is a genus of tunicates in the family Pyuridae, containing the following species:

Didemnum is a genus of colonial tunicates in the family Didemnidae. It is the most speciose genus in the didemnid family. Species in this genus often have small calcareous spicules embedded in the tunic and form irregular or lobed colonies. Some Didemnum species, including Didemnum vexillum and Didemnum perlucidem are considered invasive species. In early 2006, Didemnum vexillum was found covering a 230 km2 area of cobble habitat in Georges Bank off the coast of New England, and is classified as an invasive species of greatest concern in coastal areas throughout Europe, New Zealand, and North America. Didemnum sp. invasions have also been recorded in Canada, the Mediterranean, and the Netherlands.

Styela is a genus of tunicates. Styela clava, an edible species, is known as an invasive species in some areas.

Clavelina is genus of sea squirts, containing the following species:

Phlebobranchia is an order of sea squirts in the class Ascidiacea, first described by Fernando Lahille in 1886.

Halocynthia is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Pyuridae. Species such as H. roretzi are eaten in parts of Asia as a delicacy.

Stolidobranchia is an order of tunicates in the class Ascidiacea. The group includes both colonial and solitary animals. They are distinguished from other tunicates by the presence of folded pharyngeal baskets. This provides the etymology of their name: in ancient Greek, στολίς, ίδος means the "fold" of a cloth. Stolidobranchian sea squirts are also characterized by the complete absence of an abdomen. The abdominal organs of other tunicates are instead located to one side of the pharyngeal basket in this group.

Aplousobranchia is an order of sea squirts in the class Ascidiacea, first described by Fernando Lahille in 1886. They are colonial animals, and are distinguished from other sea squirts by the presence of relatively simple pharyngeal baskets. This provides the etymology of their name: in ancient greek, ἁ.πλοος-ους (ha.ploos-ous) means "simple". The posterior part of the abdomen contains the heart and gonads, and is typically larger than in other sea squirts.

Aplidium is a genus of colonial sea squirts, tunicates in the family Polyclinidae. There are about 188 species in the genus found in shallow waters around the world.

Polycarpa is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.

Styelidae is a family of ascidian tunicates.

Polyclinum is a genus of colonial sea squirts, tunicates in the family Polyclinidae.
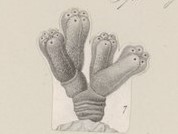
Synoicum is a genus of colonial sea squirts, tunicates in the family Polyclinidae.
Eugyra are marine tunicates.
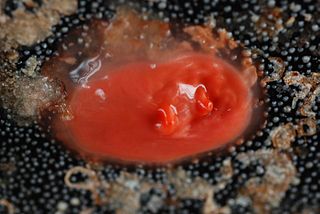
Cnemidocarpa is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.
Stolonica is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.

Symplegma is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.

Trididemnum is a genus of tunicates belonging to the family Didemnidae.
















