
Genus is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

The Portuguese man o' war, also known as the man-of-war or bluebottle, is a marine hydrozoan found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Indian Ocean. It is considered to be the same species as the Pacific man o' war or bluebottle, which is found mainly in the Pacific Ocean. The Portuguese man o' war is the only species in the genus Physalia, which in turn is the only genus in the family Physaliidae.

Krill(Euphausiids) are small and exclusively marine crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word krill, meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish.
Stenolaemata are a class of exclusively marine bryozoans. Stenolaemates originated and diversified in the Ordovician, and more than 600 species are still alive today. All extant (living) species are in the order Cyclostomatida, the third-largest order of living bryozoans.

Thaliacea is a class of marine chordates within the subphylum Tunicata, comprising the salps, pyrosomes and doliolids. Unlike their benthic relatives the ascidians, from which they are believed to have emerged, thaliaceans are free-floating (pelagic) for their entire lifespan. The group includes species with complex life cycles, with both solitary and colonial forms.
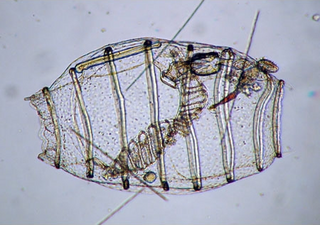
The Doliolida are an order of small marine chordates of the subphylum Tunicata. They are in the class Thaliacea, which also includes the salps and pyrosomes. The doliolid body is small, typically 1–2 mm long, and barrel-shaped; it features two wide siphons, one at the front and the other at the back end, and eight or nine circular muscle strands reminiscent of barrel bands.

A salp or salpa is a barrel-shaped, planktonic tunicate in the family Salpidae. It moves by contracting, thereby pumping water through its gelatinous body; it is one of the most efficient examples of jet propulsion in the animal kingdom. The salp strains the pumped water through its internal feeding filters, feeding on phytoplankton.

Pyrosomes are free-floating colonial tunicates in family Pyrosomatidae. There are three genera, Pyrosoma, Pyrosomella and Pyrostremma, and eight species. They usually live in the upper layers of the open ocean in warm seas, although some may be found at greater depths.

Zoanthids are an order of cnidarians commonly found in coral reefs, the deep sea and many other marine environments around the world. These animals come in a variety of different colonizing formations and in numerous different colors. They can be found as individual polyps, attached by a fleshy stolon or a mat that can be created from small pieces of sediment, sand and rock. The term "zoanthid" refers to all animals within this order Zoantharia, and should not be confused with "Zoanthus", which is one genus within Zoantharia.

Corallimorpharia is an order of marine cnidarians closely related to stony or reef building corals (Scleractinia). They occur in both temperate and tropical climates, although they are mostly tropical. Temperate forms tend to be very robust, with wide and long columns, whereas tropical forms tend to have very short columns with a wide oral disc and very short tentacles. The tentacles are usually arranged in rows radiating from the mouth. Many species occur together in large groups, although there are recorded instances of individuals. In many respects, they resemble the stony corals, except for the absence of a stony skeleton. Morphological and molecular evidence suggests that they are very closely related to stony corals.

Rhipicephalus is a genus of ticks in the family Ixodidae, the hard ticks, consisting of about 74 or 75 species. Most are native to tropical Africa.

Lucerapex is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Turridae, the turrids.

Euthria is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the whelk family Tudiclidae.

Aesopus is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Columbellidae, the dove snails.

Doliolum is a genus of tunicates, the members of which move via jet propulsion. A detailed description can be found in the article, "On the anatomical structure of the trophozooid of Doliolum denticulatum."

Pyrosoma atlanticum is a pelagic species of marine colonial tunicate in the class Thaliacea found in temperate waters worldwide. The name of the genus comes from the Greek words pyros meaning 'fire' and soma meaning 'body', referring to the bright bioluminescence sometimes emitted. The specific epithet atlanticum refers to the Atlantic Ocean, from where the first specimen of the species was collected for scientific description; it was described in 1804 by François Péron, a French naturalist.

Doliolidae is a family of tunicates in the order Doliolida. Members of the family are pelagic and often found far away from coastlines.
Dolioletta gegenbauri is a species of tunicate in the family Doliolidae. It is small, exists in various forms and is sometimes found in great abundance in the Atlantic and Pacific waters where it lives.
Dolioletta mirabilis is a species of tunicate in the family Doliolidae. It is small, exists in various forms and is sometimes found in great abundance in the Indo-Pacific waters where it lives.

The Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera (IRMNG) is a taxonomic database which attempts to cover published genus names for all domains of life, from 1758 in zoology up to the present, arranged in a single, internally consistent taxonomic hierarchy, for the benefit of Biodiversity Informatics initiatives plus general users of biodiversity (taxonomic) information. In addition to containing just over 500,000 published genus name instances as at May 2023, the database holds over 1.7 million species names, although this component of the data is not maintained in as current or complete state as the genus-level holdings. IRMNG can be queried online for access to the latest version of the dataset and is also made available as periodic snapshots or data dumps for import/upload into other systems as desired. The database was commenced in 2006 at the then CSIRO Division of Marine and Atmospheric Research in Australia and, since 2016, has been hosted at the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) in Belgium.














