A web portal is a specially designed website that brings information from diverse sources, like emails, online forums and search engines, together in a uniform way. Usually, each information source gets its dedicated area on the page for displaying information ; often, the user can configure which ones to display. Variants of portals include mashups and intranet "dashboards" for executives and managers. The extent to which content is displayed in a "uniform way" may depend on the intended user and the intended purpose, as well as the diversity of the content. Very often design emphasis is on a certain "metaphor" for configuring and customizing the presentation of the content and the chosen implementation framework or code libraries. In addition, the role of the user in an organization may determine which content can be added to the portal or deleted from the portal configuration.
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) is a standard way to send messages that include multimedia content to and from a mobile phone over a cellular network. Users and providers may refer to such a message as a PXT, a picture message, or a multimedia message. The MMS standard extends the core SMS capability, allowing the exchange of text messages greater than 160 characters in length. Unlike text-only SMS, MMS can deliver a variety of media, including up to forty seconds of video, one image, a slideshow of multiple images, or audio. The first MMS-capable phones were introduced around 2002 in conjunction with the first GSM network. The Sony Ericsson T68i is widely believed to be the first MMS-capable cell phone, while many more hit North American markets beginning in 2004 and 2005.
Digital display advertising is graphic advertising on Internet websites, apps or social media through banners or other advertising formats made of text, images, flash, video, and audio. The main purpose of display advertising is to deliver general advertisements and brand messages to site visitors.

Direct marketing is a form of communicating an offer, where organizations communicate directly to a pre-selected customer and supply a method for a direct response. Among practitioners, it is also known as direct response marketing. By contrast, advertising is of a mass-message nature.

Parental controls are features which may be included in digital television services, computer and video games, mobile devices and software that allow parents to restrict the access of content to their children. These controls were created to assist parents in their ability to restrict certain content viewable by their children. This may be content they deem inappropriate for their age, maturity level or feel is aimed more at an adult audience. Parental controls fall into roughly four categories: content filters, which limit access to age inappropriate content; usage controls, which constrain the usage of these devices such as placing time-limits on usage or forbidding certain types of usage; computer usage management tools, which enforces the use of certain software; and monitoring, which can track location and activity when using the devices.
Online advertising, also known as online marketing, Internet advertising, digital advertising or web advertising, is a form of marketing and advertising which uses the Internet to deliver promotional marketing messages to consumers. Many consumers find online advertising disruptive and have increasingly turned to ad blocking for a variety of reasons.
Local search is the use of specialized Internet search engines that allow users to submit geographically constrained searches against a structured database of local business listings. Typical local search queries include not only information about "what" the site visitor is searching for but also "where" information, such as a street address, city name, postal code, or geographic coordinates like latitude and longitude. Examples of local searches include "Hong Kong hotels", "Manhattan restaurants", and "Dublin car rental". Local searches exhibit explicit or implicit local intent. A search that includes a location modifier, such as "Bellevue, WA" or "14th arrondissement", is an explicit local search. A search that references a product or service that is typically consumed locally, such as "restaurant" or "nail salon", is an implicit local search.
A scraper site is a website that copies content from other websites using web scraping. The content is then mirrored with the goal of creating revenue, usually through advertising and sometimes by selling user data. Scraper sites come in various forms. Some provide little, if any material or information, and are intended to obtain user information such as e-mail addresses, to be targeted for spam e-mail. Price aggregation and shopping sites access multiple listings of a product and allow a user to rapidly compare the prices.

A search engine is a software system that is designed to carry out web searches, which means to search the World Wide Web in a systematic way for particular information specified in a textual web search query. The search results are generally presented in a line of results, often referred to as search engine results pages (SERPs). The information may be a mix of links to web pages, images, videos, infographics, articles, research papers, and other types of files. Some search engines also mine data available in databases or open directories. Unlike web directories, which are maintained only by human editors, search engines also maintain real-time information by running an algorithm on a web crawler. Internet content that is not capable of being searched by a web search engine is generally described as the deep web.

The mobile web refers to browser-based World Wide Web services accessed from handheld mobile devices, such as smartphones or feature phones, through a mobile or other wireless network.
Voice portals are the voice equivalent of web portals, giving access to information through spoken commands and voice responses. Ideally a voice portal could be an access point for any type of information, services, or transactions found on the Internet. Common uses include movie time listings and stock trading. In telecommunications circles, voice portals may be referred to as interactive voice response (IVR) systems, but this term also includes DTMF services. With the emergence of conversational assistants such as Apple's Siri, Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, Microsoft Cortana, and Samsung's Bixby, Voice Portals can now be accessed through mobile devices and Far Field voice smart speakers such as the Amazon Echo and Google Home.

Mobile social networking (MSN) is social networking where individuals with similar interests converse and connect with one another through their mobile phone and/or tablet. Much like web-based social networking, mobile social networking occurs in virtual communities.
Digital marketing is the component of marketing that utilizes internet and online based digital technologies such as desktop computers, mobile phones and other digital media and platforms to promote products and services. Its development during the 1990s and 2000s, changed the way brands and businesses use technology for marketing. As digital platforms became increasingly incorporated into marketing plans and everyday life, and as people increasingly use digital devices instead of visiting physical shops, digital marketing campaigns have become prevalent, employing combinations of search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), content marketing, influencer marketing, content automation, campaign marketing, data-driven marketing, e-commerce marketing, social media marketing, social media optimization, e-mail direct marketing, display advertising, e–books, and optical disks and games have become commonplace. Digital marketing extends to non-Internet channels that provide digital media, such as television, mobile phones, callback, and on-hold mobile ring tones. The extension to non-Internet channels differentiates digital marketing from online marketing.
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a technical standard for accessing information over a mobile wireless network. A WAP browser is a web browser for mobile devices such as mobile phones that use the protocol. Introduced in 1999, WAP achieved some popularity in the early 2000s, but by the 2010s it had been largely superseded by more modern standards. Most modern handset internet browsers now fully support HTML, so they do not need to use WAP markup for web page compatibility, and therefore, most are no longer able to render and display pages written in WML, WAP's markup language.
Location-based advertising (LBA) is a form of advertising that integrates mobile advertising with location-based services. The technology is used to pinpoint consumers location and provide location-specific advertisements on their mobile devices.
On-Device Portals (ODPs) allow mobile phone users to easily browse, purchase and use mobile content and services. An ODP platform enables operators to provide a consistent and branded on-device experience across their broadening portfolio of services and typically provides on-device catalogs of content for purchase, deep links to WAP portals, customer care functionality and rich media services such as full track music, TV and video.
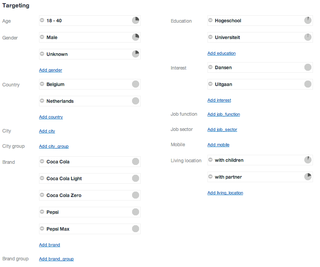
Targeted advertising is a form of advertising, including online advertising, that is directed towards an audience with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting. These traits can either be demographic with a focus on race, economic status, sex, age, generation, level of education, income level, and employment, or there can be a psychographic focus which is based on the consumer values, personality, attitude, opinion, lifestyle and interest. This focus can also entail behavioral variables, such as browser history, purchase history, and other recent online activities. Targeted advertising is focused on certain traits and consumers who are likely to have a strong preference. These individuals will receive messages instead of those who have no interest and whose preferences do not match a particular product's attributes. This eliminates waste.
Social media marketing is the use of social media platforms and websites to promote a product or service. Although the terms e-marketing and digital marketing are still dominant in academia, social media marketing is becoming more popular for both practitioners and researchers. Most social media platforms have built-in data analytics tools, enabling companies to track the progress, success, and engagement of ad campaigns. Companies address a range of stakeholders through social media marketing, including current and potential customers, current and potential employees, journalists, bloggers, and the general public. On a strategic level, social media marketing includes the management of a marketing campaign, governance, setting the scope and the establishment of a firm's desired social media "culture" and "tone."
Call tracking software records information about incoming telephone calls, and in some regions even the conversation. Call tracking is a technology which can enable the pay per call, pay per minute or pay per lead business model, allowing the tracking of phone calls to be associated with performance-based advertising such as Google AdWords, SEO Services, Display and Electronic Direct Marketing, and supplying additional analytic information about the phone calls themselves. Call tracking is a method of performance review for advertising and/or staff. It is based on the technological possibility of measuring the behavior of callers and is thus the equivalent in telephony to the conversion tracking used on the internet. Via different channels, both procedures offer the opportunity of clearly assigning a customer response to a specific advertising medium.
Contextual search is a form of optimizing web-based search results based on context provided by the user and the computer being used to enter the query. Contextual search services differ from current search engines based on traditional information retrieval that return lists of documents based on their relevance to the query. Rather, contextual search attempts to increase the precision of results based on how valuable they are to individual users.





