This article needs additional citations for verification .(August 2007) |

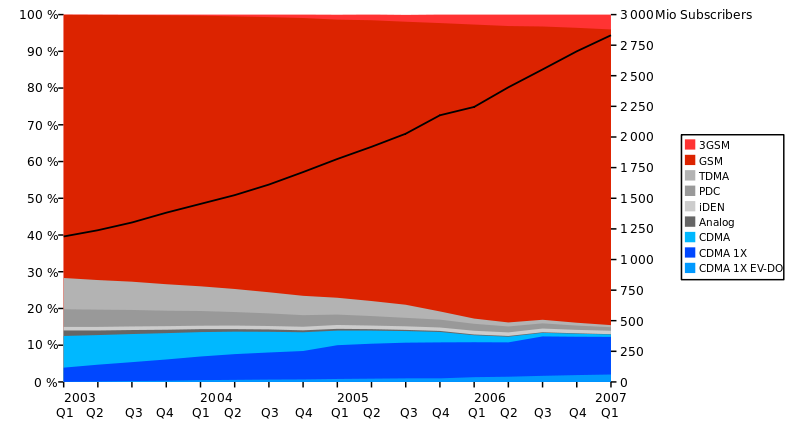
This is a comparison of standards of wireless networking technologies for devices such as mobile phones. A new generation of cellular standards has appeared approximately every tenth year since 1G systems were introduced in 1979 and the early to mid-1980s.