
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. GSM is also a trade mark owned by the GSM Association. GSM may also refer to the Full Rate voice codec.
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a 3G mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP, UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators.

3G is the third generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology. It is the upgrade to 2G, 2.5G, GPRS and 2.75G Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution networks, offering faster data transfer, and better voice quality. This network was superseded by 4G, and later by 5G. This network is based on a set of standards used for mobile devices and mobile telecommunications services and networks that comply with the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) specifications set by the International Telecommunication Union. 3G is used in wireless voice telephony, mobile Internet access, fixed wireless Internet access, video calls and mobile TV.

NTT Docomo, Inc., also known as Docomo, is a Japanese mobile phone operator owned by the Nippon Telegraph and Telephone (NTT). The name is officially an abbreviation of the phrase, "do communications over the mobile network", and is also from a compound word dokomo, meaning "everywhere" in Japanese. The company is headquartered in Sanno Park Tower, Nagatachō, Chiyoda, Tokyo. Docomo provides phone, video phone, i-mode (internet), and mail services. It is the largest wireless carrier in Japan, with 82.632 million subscribers as of March 2021.

CDMA2000 is a family of 3G mobile technology standards for sending voice, data, and signaling data between mobile phones and cell sites. It is developed by 3GPP2 as a backwards-compatible successor to second-generation cdmaOne (IS-95) set of standards and used especially in North America and South Korea.

SK Telecom Co., Ltd., abbreviated as SKT is a South Korean wireless telecommunications operator and former film distributor and is part of the SK Group, one of the country's largest chaebols. It leads the local market with 50.5 percent share as of 2008. SK Telecom is the largest wireless carrier in South Korea, with 23 million subscribers as of Q4 2023.
4G is the fourth generation of broadband cellular network technology, succeeding 3G and preceding 5G. A 4G system must provide capabilities defined by ITU in IMT Advanced. Potential and current applications include amended mobile web access, IP telephony, gaming services, high-definition mobile TV, video conferencing, and 3D television.
Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) was a 2G mobile telecommunications standard used exclusively in Japan.

A cellular network or mobile network is a telecommunications network where the link to and from end nodes is wireless and the network is distributed over land areas called cells, each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver. These base stations provide the cell with the network coverage which can be used for transmission of voice, data, and other types of content. A cell typically uses a different set of frequencies from neighboring cells, to avoid interference and provide guaranteed service quality within each cell.

The history of mobile phones covers mobile communication devices that connect wirelessly to the public switched telephone network.
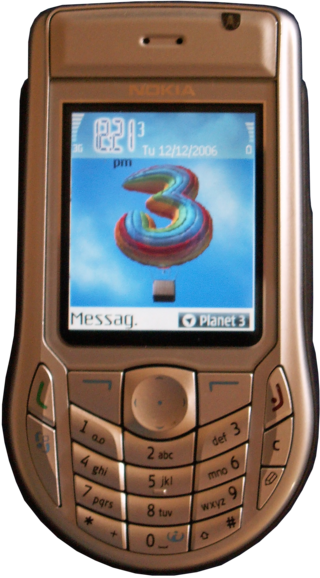
The Nokia 6630 is a 3G mobile phone announced by Nokia on 14 June 2004 and released in November. It runs on Symbian OS 8.0a. Codenamed Charlie during development, it is an evolution of the 6600 and 6620 smartphones, supporting tri-band GSM.
The Personal Handy-phone System (PHS), also marketed as the Personal Communication Telephone (PCT) in Thailand, and the Personal Access System (PAS) and commercially branded as Xiaolingtong in Mainland China, was a mobile network system operating in the 1880–1930 MHz frequency band, used mainly in Japan, China, Taiwan, and some other Asian countries and regions.
The UMTS frequency bands are radio frequencies used by third generation (3G) wireless Universal Mobile Telecommunications System networks. They were allocated by delegates to the World Administrative Radio Conference (WARC-92) held in Málaga-Torremolinos, Spain between 3 February 1992 and 3 March 1992. Resolution 212 (Rev.WRC-97), adopted at the World Radiocommunication Conference held in Geneva, Switzerland in 1997, endorsed the bands specifically for the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) specification by referring to S5.388, which states "The bands 1,885-2,025 MHz and 2,110-2,200 MHz are intended for use, on a worldwide basis, by administrations wishing to implement International Mobile Telecommunications 2000 (IMT-2000). Such use does not preclude the use of these bands by other services to which they are allocated. The bands should be made available for IMT-2000 in accordance with Resolution 212 ." To accommodate the reality that these initially defined bands were already in use in various regions of the world, the initial allocation has been amended multiple times to include other radio frequency bands.

Hutchison 3G Enterprises S.A.R.L., trading as 3 (Three) and Hutchison 3G, is the owner of several originally UMTS-based mobile phone networks and broadband Internet providers, which operate in Hong Kong, Macau, Austria, Denmark, Indonesia, Ireland, Italy, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by using a different radio interface and core network improvements. LTE is the upgrade path for carriers with both GSM/UMTS networks and CDMA2000 networks. Because LTE frequencies and bands differ from country to country, only multi-band phones can use LTE in all countries where it is supported.

The XT Network was a brand name for a UMTS and LTE mobile network run by Spark New Zealand . The network was initially built nationwide on WCDMA/UMTS 850 MHz, with 2100 MHz infill in major urban areas. The UMTS network is HSPA+ enabled, with a maximum downlink transmission rate of 21.1 Mbit/s and an uplink rate of 5.2 Mbit/s attainable for capable hardware. HSPA+ has a theoretical maximum of 56 Mbit/s download speed and 22 Mbit/s upload speed. Then under Spark 4G LTE is being built out. The network is not 2G capable, Telecom never operated a public GSM network.

FOMA SH906i is a mobile phone developed by Sharp for NTT DoCoMo using the FOMA(HSDPA) 3G network.

Tata Docomo was an Indian mobile network operator, a wholly owned subsidiary of Tata Teleservices deriving its name from NTT Docomo who invested in the company in 2008. In October 2017, Bharti Airtel announced a merger deal with Tata Teleservices and the acquisition of Tata Docomo. As of 7 July 2019, all Tata Docomo users are merged with Airtel network and provided with all the Airtel services.

The Japanese mobile phone industry is one of the most advanced in the world. As of March, 2022 there were 199.99 million mobile contracts in Japan according to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. This is 158 percent of Japan's total population.













