
Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE), also known as 2.75G, Enhanced GPRS (EGPRS), IMT Single Carrier (IMT-SC), and Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution, is a 2G digital mobile phone technology for data transmission. It is a subset of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) on the GSM network and improves upon it offering speeds close to 3G technology, hence the name 2.75G. It is also recognized as part of the International Mobile Telecommunications - 2000 (IMT-2000) standard.

The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. GSM is also a trade mark owned by the GSM Association. "GSM" may also refer to the voice codec initially used in GSM.
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a 3G mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP, UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators.

4G is the fourth generation of cellular network technology, succeeding 3G and designed to support all-IP communications and broadband services, enabling a variety of data-intensive applications. A 4G system must meet the performance requirements defined by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in IMT Advanced. 4G supports a range of applications, including enhanced mobile internet access, high-definition streaming, IP telephony, video conferencing, and the expansion of Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) was a 2G mobile telecommunications standard used exclusively in Japan.
The GPRS core network is the central part of the general packet radio service (GPRS) which allows 2G, 3G and WCDMA mobile networks to transmit Internet Protocol (IP) packets to external networks such as the Internet. The GPRS system is an integrated part of the GSM network switching subsystem.
Network switching subsystem (NSS) is the component of a GSM system that carries out call out and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations. It is owned and deployed by mobile phone operators and allows mobile devices to communicate with each other and telephones in the wider public switched telephone network (PSTN). The architecture contains specific features and functions which are needed because the phones are not fixed in one location.

The base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, transmission and reception over the air interface and many other tasks related to the radio network.
In communications, Circuit Switched Data (CSD) is the original form of data transmission developed for the time-division multiple access (TDMA)-based mobile phone systems like Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM). After 2010 many telecommunication carriers dropped support for CSD, and CSD has been superseded by GPRS and EDGE (E-GPRS).
The IP Multimedia Subsystem or IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) is a standardised architectural framework for delivering IP multimedia services. Historically, mobile phones have provided voice call services over a circuit-switched-style network, rather than strictly over an IP packet-switched network. Various voice over IP technologies are available on smartphones; IMS provides a standard protocol across vendors.
The Mobile Application Part (MAP) is an SS7 protocol that provides an application layer for the various nodes in GSM and UMTS mobile core networks and GPRS core networks to communicate with each other in order to provide services to users. The Mobile Application Part is the application-layer protocol used to access the Home Location Register, Visitor Location Register, Mobile Switching Center, Equipment Identity Register, Authentication Centre, Short message service center and Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN).
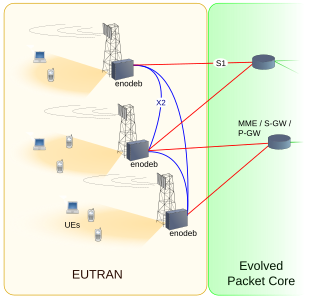
E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access, also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and a Node B.

BSSGP is a protocol used in the GPRS mobile packet data system. It denotes Base Station System GPRS Protocol. It transfers information between two GPRS entities SGSN and BSS over a BSSGP Virtual Connection (BVC). This protocol provides radio-related quality of service and routing information that is required to transmit user data between a BSS and an SGSN. It does not carry out any form of error correction.

High Speed Packet Access (HSPA) is an amalgamation of two mobile protocols—High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) and High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA)—that extends and improves the performance of existing 3G mobile telecommunication networks using the WCDMA protocols. A further-improved 3GPP standard called Evolved High Speed Packet Access was released late in 2008, with subsequent worldwide adoption beginning in 2010. The newer standard allows bit rates to reach as high as 337 Mbit/s in the downlink and 34 Mbit/s in the uplink; however, these speeds are rarely achieved in practice.
Dual Transfer Mode (DTM) is a protocol based on the GSM standard that makes simultaneous transfer of Circuit switched (CS) voice and Packet switched (PS) data over the same radio channel (ARFCN) simpler. Without DTM, the mobile device must be capable of reception and transmission simultaneously (full-duplex) requiring complex and expensive circuitry in the mobile terminal. With DTM this requirement doesn't exist and makes the device implementation simpler and cheaper. DTM is a 3GPP feature introduced in R4 of the specification series.
System Architecture Evolution (SAE) is the core network architecture of mobile communications protocol group 3GPP's LTE wireless communication standard.
The Um interface is the air interface for the GSM mobile telephone standard. It is the interface between the mobile station (MS) and the Base transceiver station (BTS). It is called Um because it is the mobile analog to the U interface of ISDN. Um is defined in the GSM 04.xx and 05.xx series of specifications. Um can also support GPRS packet-oriented communication.

A mobile broadband modem, also known as wireless modem or cellular modem, is a type of modem that allows a personal computer or a router to receive wireless Internet access via a mobile broadband connection instead of using telephone or cable television lines. A mobile Internet user can connect using a wireless modem to a wireless Internet Service Provider (ISP) to get Internet access.
In mobile telephony a bearer service is a link between two points, which is defined by a certain set of characteristics. Whenever user equipment (UE) is being provided with any service, the service has to be associated with a Radio Bearer specifying the configuration for layer 2 and physical layer in order to have its QoS clearly defined. Radio bearers are channels offered by Layer 2 to higher layers for the transfer of either user or control data. In other words, Layer 2 offers to the upper layers the service of information transmission between the UE and the UTRAN by means of the Radio Bearers (RBs) and Signaling Radio Bearers (SRBs). Therefore, the service access points between Layer 2 and upper layers are RBs.











