Related Research Articles

Herbicides, also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds. Selective herbicides control specific weed species while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides kill plants indiscriminately. The combined effects of herbicides, nitrogen fertilizer, and improved cultivars has increased yields of major crops by 3x to 6x from 1900 to 2000.

Pesticide resistance describes the decreased susceptibility of a pest population to a pesticide that was previously effective at controlling the pest. Pest species evolve pesticide resistance via natural selection: the most resistant specimens survive and pass on their acquired heritable changes traits to their offspring. If a pest has resistance then that will reduce the pesticide's efficacy – efficacy and resistance are inversely related.
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality, and profit. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward. Most fungicides that can be bought retail are sold in liquid form, the active ingredient being present at 0.08% in weaker concentrates, and as high as 0.5% for more potent fungicides. Fungicides in powdered form are usually around 90% sulfur.

Paraquat (trivial name; ), or N,N′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride (systematic name), also known as methyl viologen, is an organic compound with the chemical formula [(C6H7N)2]Cl2. It is classified as a viologen, a family of redox-active heterocycles of similar structure. This salt is one of the most widely used herbicides. It is quick-acting and non-selective, killing green plant tissue on contact. It is also toxic (lethal) to human beings and animals due to its redox activity, which produces superoxide anions. It has been linked to the development of Parkinson's disease and is banned in 58 countries.

Diquat is the ISO common name for an organic dication that, as a salt with counterions such as bromide or chloride is used as a contact herbicide that produces desiccation and defoliation. Diquat is no longer approved for use in the European Union, although its registration in many other countries including the USA is still valid.

Glufosinate is a naturally occurring broad-spectrum herbicide produced by several species of Streptomyces soil bacteria. Glufosinate is a non-selective, contact herbicide, with some systemic action. Plants may also metabolize bialaphos and phosalacine, other naturally occurring herbicides, directly into glufosinate. The compound irreversibly inhibits glutamine synthetase, an enzyme necessary for the production of glutamine and for ammonia detoxification, giving it antibacterial, antifungal and herbicidal properties. Application of glufosinate to plants leads to reduced glutamine and elevated ammonia levels in tissues, halting photosynthesis and resulting in plant death.

Pendimethalin is an herbicide of the dinitroaniline class used in premergence and postemergence applications to control annual grasses and certain broadleaf weeds. It inhibits cell division and cell elongation. Pendimethalin is listed in the K1-group according to the Herbicide Resistance Action Committee (HRAC) classification and is approved in Europe, North America, South America, Africa, Asia and Oceania for different crops including cereals, corn, soybeans, rice, potato, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts as well as lawns and ornamental plants.
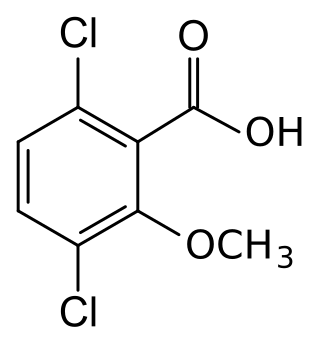
Dicamba is a selective systemic herbicide first registered in 1967. Brand names for formulations of this herbicide include Dianat, Banvel, Diablo, Oracle and Vanquish. This chemical compound is a chlorinated derivative of o-anisic acid. It has been described as a "widely used, low-cost, environmentally friendly herbicide that does not persist in soils and shows little or no toxicity to wildlife and humans."
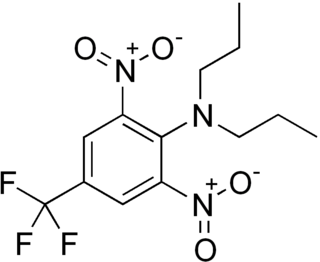
Trifluralin is a commonly used pre-emergence selective herbicide. With about 14 million pounds (6,400 t) used in the United States in 2001, and 3–7 million pounds (1,400–3,200 t) in 2012, it is one of the most widely used herbicides. Trifluralin is also used in Australia. Introduced in 1964, Trifluralin was the first organofluorine compound used as an agrochemical.
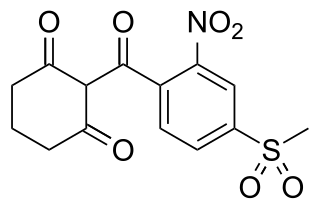
Mesotrione is a selective herbicide used mainly in maize crops. It is a synthetic compound inspired by the natural substance leptospermone found in the bottlebrush tree Callistemon citrinus. It inhibits the enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) and is sold under brand names including Callisto and Tenacity. It was first marketed by Syngenta in 2001.
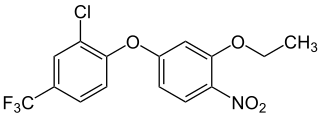
Oxyfluorfen is a chemical compound used as an herbicide. It is manufactured by Dow AgroSciences and Adama Agricultural Solutions under the trade names Goal and Galigan. Oxyfluorfen is used to control broadleaf and grassy weeds in a variety of nut, tree fruit, vine, and field crops, especially wine grapes and almonds. It is also used for residential weed control.

Fluazifop is the common name used by the ISO for an organic compound that is used as a selective herbicide. The active ingredient is the 2R enantiomer at its chiral centre and this material is known as fluazifop-P when used in that form. More commonly, it is sold as its butyl ester, fluazifop-P butyl with the brand name Fusilade.

Indaziflam is a preemergent herbicide especially for grass control in tree and bush crops.

Butafenacil is the ISO common name for an organic compound of the pyrimidinedione chemical class used as an herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase to control broadleaf and some grass weeds in crops including cereals and canola.

Aclonifen is a diphenyl ether herbicide which has been used in agriculture since the 1980s. Its mode of action has been uncertain, with evidence suggesting it might interfere with carotenoid biosynthesis or inhibit the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PPO). Both mechanisms could result in the observed whole-plant effect of bleaching and the compound includes chemical features that are known to result in PPO effects, as seen with acifluorfen, for example. In 2020, further research revealed that aclonifen has a different and novel mode of action, targeting solanesyl diphosphate synthase which would also cause bleaching.

Sethoxydim is a postemergent herbicide for control of grass weeds in a wide variety of horticultural crops.

Tribenuron in the form of tribenuron-methyl is a sulfonylurea herbicide. Its mode of action is the inhibition of acetolactate synthase, group 2 of the Herbicide Resistance Action Committee's classification scheme.

Chlorsulfuron is an ALS inhibitor herbicide, and is a sulfonylurea compound. It was discovered by George Levitt in February 1976 while working at DuPont, which was the patent assignee.
Prosulfocarb is a pre-emergent herbicide used agriculturally in Australia, the EU, Morocco and Iran, for control of annual ryegrass and toad rush in wheat and barley crops. It was introduced to the EU in 1988 and is rapidly growing in use, with sales increasing by over 500% in France since 2008.
References
- 1 2 Grant RL, Combs AB, Acosta D (2010). "Experimental Models for the Investigation of Toxicological Mechanisms". In McQueen CA (ed.). Comprehensive Toxicology (2nd ed.). Oxford: Elsevier. p. 204. ISBN 978-0-08-046884-6.
- ↑ "Mechanisms and mode of dioxin action" (PDF). US EPA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 February 2015. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ↑ Ng, Wai-Leung; Krystyna M. Kazmierczak; Gregory T. Robertson; Raymond Gilmour; Malcolm E. Winkler (Jan 2003). "Transcriptional Regulation and Signature Patterns Revealed by Microarray Analyses of Streptococcus Pneumoniae R6 Challenged with Sublethal Concentrations of Translation Inhibitors". Journal of Bacteriology. 185 (1): 359–70. doi:10.1128/JB.185.1.359-370.2003. PMC 141824 . PMID 12486074.
- ↑ "Herbicide Group Classification by Mode of Action". Alberta Agriculture and Rural Development. Archived from the original on 2019-01-23. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ↑ FRAC (Fungicide Resistance Action Committee) (March 2021). "FRAC Code List ©*2021: Fungal control agents sorted by cross resistance pattern and mode of action (including coding for FRAC Groups on product labels)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-11-05. Retrieved 2021-04-02.
- ↑ Weed Science Society of America. "Summary of Herbicide Mechanism of Action According to the Weed Science Society of America (WSSA)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-08. Retrieved 2021-04-02.
- ↑ Heap, Ian. "HERBICIDE MODE OF ACTION TABLE". Archived from the original on 2022-07-05. Retrieved 2021-04-02.
- ↑ "HRAC MOA 2020 Revision Description and Master Herbicide List". Herbicide Resistance Action Committee . 2020-09-14. Archived from the original on 2023-01-15. Retrieved 2021-04-01.
- ↑ "Interactive MoA Classification". Insecticide Resistance Action Committee . 2020-09-16. Archived from the original on 2022-08-08. Retrieved 2021-04-01.
- ↑ United States Environmental Protection Agency. "PESTICIDE REGISTRATION NOTICE (PRN) 2017-1 NOTICE TO MANUFACTURERS, PRODUCERS, PRODUCERS AND REGISTRANTS OF PESTICIDE PRODUCTS AND DEVICES" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-03-23. Retrieved 2021-04-02.
- ↑ "PROTECTING CROP YIELDS AND QUALITY WORLDWIDE". Herbicide Resistance Action Committee.