
The Sillaginidae, commonly known as the smelt-whitings, whitings, sillaginids, sand borers and sand-smelts, are a family of benthic coastal marine fish historically classified in the order Perciformes, although the 5th edition of Fishes of the World places the family in the Spariformes. The smelt-whitings inhabit a wide region covering much of the Indo-Pacific, from the west coast of Africa east to Japan and south to Australia. The family comprises only five genera and 35 species, of which a number are dubious, with the last major revision of the family in 1992 unable to confirm the validity of a number of species. They are elongated, slightly compressed fish, often light brown to silver in colour, with a variety of markings and patterns on their upper bodies. The Sillaginidae are not related to a number of fishes commonly called 'whiting' in the Northern Hemisphere, including the fish originally called whiting, Merlangius merlangus.

The oriental trumpeter whiting is a widely distributed species of benthic inshore fish in the smelt-whiting family. The species ranges from east Africa to Japan, inhabiting much if the southern Asian and Indonesian coastlines. Its morphology is very similar to other species within the genus Sillago, with a long, compressed body and silvery overall colour. It can be distinguished from its relatives by colour patterns and particularly swim bladder morphology, which helps define most species of Sillago. S aeolus is a benthic predator, consuming a variety of crustaceans and polychaetes. As with most members of the smelt whiting family, it is important to small coastal fisheries in various areas of its range.

The shortnose whiting is a poorly known species, described in 1989, of inshore marine fish of the smelt whiting family Sillaginidae that inhabits only the Persian Gulf. S. arabica is similar in morphology to other sillaginids, although has a distinctive shortened snout which gives the species its common name. This species is of no current interest to local fisheries, although beach seines may take minor amounts of this species.

The Asian whiting is a species inshore marine fish in the smelt whiting family, Sillaginidae, distributed along the Asian coastline from the Gulf of Thailand to Taiwan. The Asian whiting's appearance is very similar to other closely related species in the genus Sillago, with swim bladder morphology and ray counts of fins the most reliable identifying features. The species inhabits slightly deeper water than many of the sillaginid species its distribution overlaps, forming an important part of the whiting fishery in the countries within its range.

The slender whiting is a poorly known species of inshore marine fish of the smelt whiting family, Sillaginidae that has a distribution limited to the Persian Gulf only. The Slender whiting, like most sillaginids requires careful study to determine its identity, with ray and vertebrae counts as well as swim bladder morphology distinguishing features. This inshore species of fish is commonly taken by fishermen using beach seines and is sold fresh in local markets.

Boutan's whiting is a poorly understood species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae that inhabits the waters of the Gulf of Tonkin and south eastern China. Like most sillaginids, the species inhabits areas populated with a number of other whiting species of similar appearance, causing the species to often be misidentified as the well known Sillago sihama, and for this reason its biology is poorly known. The species is taken by seine net in Vietnam and is often exported to Japan.

The western trumpeter whiting is a species of marine fish of the smelt whiting family Sillaginidae that is commonly found along the northern coast of Australia and in southern Indonesia and New Guinea. As its name suggests, it is closely related to and resembles the trumpeter whiting which inhabits the east coast of Australia and is distinguishable by swim bladder morphology alone. The species inhabits a variety of sandy, silty and muddy substrates in depths from 0 to 15 m deep, with older fish inhabiting deeper waters. Western trumpeter whiting are benthic carnivores which take predominantly crustaceans and polychaetes as prey. The species reaches sexual maturity at the end of its first year of age, spawning in batches between December and February. The species is taken as bycatch with other species of whiting and shrimps in Australia.
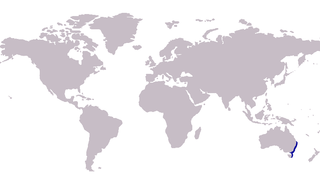
The eastern school whiting, also known as the redspot whiting, Bass Strait whiting, Flinders' sillago, silver whiting or spotted whiting, is a species of benthic marine fish of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The eastern school whiting is endemic to Australia, distributed along the east coast from southern Queensland down to Tasmania and South Australia, where it inhabits sandy substrates from shallow tidal flats to depths of 180 m on the continental shelf. Eastern school whiting prey on various crustaceans and polychaete worms, with the diet varying seasonally and throughout the range of the species. Eastern school whiting reproduce in the deeper waters twice a year, releasing up to 110,000 eggs during a season.

The Indian whiting is a poorly known species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The species was named in 1985, having previously being misidentified as another species of Sillago, S. parvisquamis. The Indian whiting inhabits the east and west coasts of the Indian subcontinent, apparently not extending to the southern tip of India. Like all sillaginids, it is benthic in nature, living in depths to 30 m where it is caught by fishermen alongside other species of Sillago.

The bay whiting is a species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. The bay whiting's range extends throughout the west Indian Ocean, including northern Australia, Thailand, India and Taiwan, where it inhabits protected waters. It is benthic in nature, preying on shrimps, polychaetes and molluscs, however little else is known of its biology. Bay whiting are an important part of some inshore fisheries around Australia and Asia, where subsistence and commercial fishermen regularly take the species.

The Intermediate whiting, is a species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The intermediate whiting ranges from the west coast of India to the Gulf of Thailand in the east, inhabiting silty substrates in shallow waters. First identified in 1977 from a specimen found in a fish market, the species has had little research performed on its biology, and is frequently misidentified as Sillago sihama or Sillago maculata intermediate whiting are commonly caught by fishermen throughout their range and are marketed fresh locally.

The large-scale whiting the only member of the genus Sillaginops, is a poorly understood species of coastal marine fish of the smelt- whiting family Sillaginidae. First described in 1859, the large-scale whiting is known to inhabit shallow waters along the coasts of a number of Indo-Pacific countries including Japan, Indonesia, Philippines and the Solomon Islands. Little is known of the species biology, even though it is of minor importance to fisheries throughout its range.
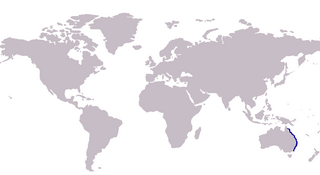
The trumpeter whiting, also known as the winter whiting or diver whiting, is a common species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. The trumpeter whiting is endemic to Australia, inhabiting the eastern seaboard from southern New South Wales to northern Queensland. The species is found in bays, estuaries, coastal lakes and mangrove creeks on silty and muddy substrates in waters ranging from 0 to 30 m deep, occasionally inhabiting sandy and seagrass beds.

The large-headed whiting is a dubious species of coastal marine fish in the smelt-whiting family that has only been recorded from one specimen captured off the coast of China in 1933. Although very similar to Sillago sihama, the species is characterised by an unusually large head which accounts for 33% of the total body length.

The small-eyed whiting is a poorly known species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The species is known from only two specimens; the holotype collected by Roland McKay in 1985 from a Taipei market, both specimens of which were taken from the waters of Taiwan. Apart from a relatively small eye size, the species is hard to distinguish from other common species of sillaginid taken in the area, and may be a minor part of local fisheries.

The rough whiting is a dubious species of coastal marine fish in the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The species is known only from the holotype which was collected in 1941 on the south coast of Papua New Guinea, but is thought to be lost. S. nierstraszi is currently a valid species, although during his revision of the sillaginids, Roland McKay suggested the species to be a senior synonym of Sillago analis.

The northern whiting, also known as the silver whiting and sand smelt, is a marine fish, the most widespread and abundant member of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The northern whiting was the first species of sillaginid scientifically described and is therefore the type species of both the family Sillaginidae and the genus Sillago. The species is distributed in the Indo-Pacific region from South Africa in the west to Japan and Indonesia in the east. The northern whiting inhabits coastal areas to 60 m, but is most often found in shallow water around bays and estuaries, often entering freshwater. It is a carnivore, taking a variety of polychaetes and crustaceans. The species is of major economic importance throughout the Indo-Pacific. It is most frequently taken by seine nets and cast nets and marketed fresh.
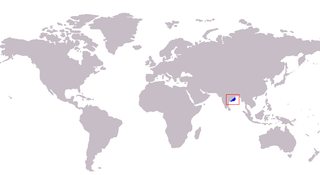
The soringa whiting, also known simply as soringa or soringa sillago, is a poorly known species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. The Soringa whiting is known exclusively from the east coast of India, inhabiting shallow inshore environments, particularly sandy substrates. S. soringa was first described in 1982 by Dutt and Sujatha, with the taxonomic status of the species was questioned by Roland McKay in his review of the Sillaginidae, with similar features to S. asiatica suggesting it is a senior synonym of the latter.

The estuarine whiting, also known as Vincent's whiting, is a species of benthic inshore marine fish of the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. The estuarine whiting is very similar in appearance to the northern whiting, Sillago sihama, and as such was mistaken for the latter until 1980, when R.J. McKay identified the species based primarily on swimbladder morphology. The estuarine whiting is distributed along both the east and west coasts of India, primarily inhabiting the muddy substrates of estuaries. The species is locally important to fisheries in India, and is recognized as having aquaculture potential.

The stout whiting, also known as the yellow-cheek whiting or school whiting, is a species of benthic marine fish in the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. Like other sillaginids, it is an elongate, slightly compressed fish, growing to a maximum known length of 30 cm. The stout whiting is endemic to Australia, with the species divided into western and eastern populations, with the western population ranging from Shark Bay to Fremantle and the eastern population from Bustard Head, Queensland to northern New South Wales. The species inhabits deep, sandy continental shelf regions to a depth of at least 70 m.





















