Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.

Nanoviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 12 species in this family, divided among 2 genera and one unassigned species. Diseases associated with this family include: stunting. Their name is derived from the Greek word νᾶνος, because of their small genome and their stunting effect on infected plants.
Pseudoviridae is a family of viruses, which includes three genera.
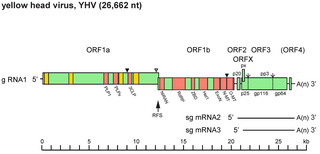
Okavirus is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Roniviridae. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus.
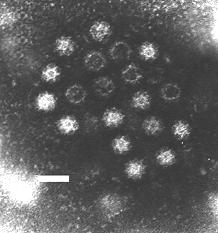
The Caliciviridae are a family of "small round structured" viruses, members of Class IV of the Baltimore scheme. Caliciviridae bear resemblance to enlarged picornavirus and was formerly a separate genus within the picornaviridae. They are positive-sense, single-stranded RNA which is not segmented. Thirteen species are placed in this family, divided among eleven genera. Diseases associated with this family include feline calicivirus, rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus, and Norwalk group of viruses (gastroenteritis). Caliciviruses naturally infect vertebrates, and have been found in a number of organisms such as humans, cattle, pigs, cats, chickens, reptiles, dolphins and amphibians. The caliciviruses have a simple construction and are not enveloped. The capsid appears hexagonal/spherical and has icosahedral symmetry with a diameter of 35–39 nm.

Closteroviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four genera and 59 species in this family, seven of which are unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this family include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem.
Luteoviridae was a family of viruses. The family was abolished in 2020 based on evidence that its three genera and seven species unassigned to a genus belonged to two other, existing families.

Nodaviridae is a family of nonenveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Vertebrates and invertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include: viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in fish. There are nine species in the family, assigned to two genera.

The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus taxon. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as identifying new taxa and delimiting the boundaries of species, genera, families, etc. typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families.
Plasmaviridae is a family of bacteria-infecting viruses. Acholeplasma species serve as natural hosts. There is one genus in the family, Plasmavirus, which contains one species: Acholeplasma virus L2. All viruses known in this family have been isolated from species in the class Mollicutes.
Guttaviridae is a family of viruses. Archaea serve as natural hosts. There are two genera in this family, containing one species each. The name is derived from the Latin gutta, meaning 'droplet'.
Hypovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Hypoviridae. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Infection reduces the virulence of its parasitic host, making it a hyperparasite useful for blight control.

Iflaviridae is a family of positive sense RNA viruses insect-infecting viruses. Some of the insects commonly infected by iflaviruses include aphids, leafhoppers, flies, bees, ants, silkworms and wasps. The name "Ifla" is derived from the name "Infectious flacherie virus", a member species. There is one genus (Iflavirus) and 16 species in this family.

Aspiviridae, formerly Ophioviridae, is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It is a monotypic taxon containing only one genus, Ophiovirus. Aspiviridae is also the only family in the order Serpentovirales, which in turn is the only order in the class Milneviricetes.

Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.

Bottigliavirus is the only genus in the family Ampullaviridae and contains 3 species. Ampullaviridae infect archaea of the genus Acidianus. The name of the family and genus is derived from the Latin word for bottle, ampulla, due to the virions having the shape of a bottle. The family was first described during an investigation of the microbial flora of hot springs in Italy.

Emaravirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. The plant virus group is the sole genus in the family Fimoviridae. The genus has 21 species.
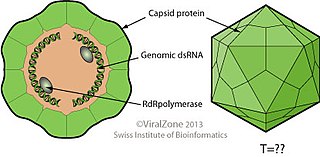
Megabirnaviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses with one genus Megabirnavirus which infects fungi. The group name derives from member's bipartite dsRNA genome and mega that is greater genome size than families Birnaviridae and Picobirnaviridae. There is only one species in this family: Rosellinia necatrix megabirnavirus 1. Diseases associated with this family include: reduced host virulence.

Quadriviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses with a single genus Quadrivirus. The fungi Rosellinia necatrix serves as a natural host. The name of the group derives from the quadripartite genome of its members where in Latin quad means four. There is only one species in this family: Rosellinia necatrix quadrivirus 1.

Peribunyaviridae is a family of viruses in the order Bunyavirales. Its name partially derives from Bunyamwera, Uganda, where the founding species was first isolated.














