
Weasels are mammals of the genus Mustela of the family Mustelidae. The genus Mustela includes the least weasels, polecats, stoats, ferrets, and European mink. Members of this genus are small, active predators, with long and slender bodies and short legs. The family Mustelidae, or mustelids, is often referred to as the "weasel family". In the UK, the term "weasel" usually refers to the smallest species, the least weasel (M. nivalis), the smallest carnivoran species.

Genus is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

Nightjars are medium-sized nocturnal or crepuscular birds in the family Caprimulgidae and order Caprimulgiformes, characterised by long wings, short legs, and very short bills. They are sometimes called bugeaters, their primary source of food being insects. Some New World species are called nighthawks. The English word nightjar originally referred to the European nightjar.

Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among other animals.

The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae and the Ochotonidae (pikas). There are 110 recent species of lagomorph, of which only 109 species in twelve genera are extant, including ten genera of rabbits ; one genus of hare and one genus of pika. The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek lagos + morphē.

Pheasants are birds of several genera within the family Phasianidae in the order Galliformes. Although they can be found all over the world in introduced populations, the pheasant genera's native range is restricted to Eurasia. The classification "pheasant" is paraphyletic, as birds referred to as pheasants are included within both the subfamilies Phasianinae and Pavoninae, and in many cases are more closely related to smaller phasianids, grouse, and turkey than to other pheasants.

Vespertilionidae is a family of microbats, of the order Chiroptera, flying, insect-eating mammals variously described as the common, vesper, or simple nosed bats. The vespertilionid family is the most diverse and widely distributed of bat families, specialised in many forms to occupy a range of habitats and ecological circumstances, and it is frequently observed or the subject of research. The facial features of the species are often simple, as they mainly rely on vocally emitted echolocation. The tails of the species are enclosed by the lower flight membranes between the legs. Over 300 species are distributed all over the world, on every continent except Antarctica. It owes its name to the genus Vespertilio, which takes its name from a word for bat, vespertilio, derived from the Latin term vesper meaning 'evening'; they are termed "evening bats" and were once referred to as "evening birds".

Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae, Anseranatidae, and Anatidae, the largest family, which includes over 170 species of waterfowl, among them the ducks, geese, and swans. Most modern species in the order are highly adapted for an aquatic existence at the water surface. With the exception of screamers, males have penises, a trait that has been lost in the Neoaves, the clade consisting of all other modern birds except the galliformes and paleognaths. Due to their aquatic nature, most species are web-footed.

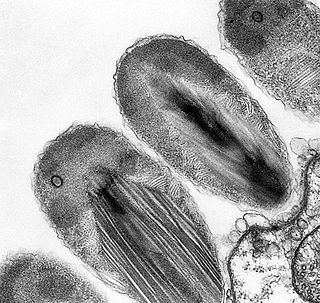
A spirochaete or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota, which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) Gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm.

Eutheria, also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of placentals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.

The Lamniformes are an order of sharks commonly known as mackerel sharks. It includes some of the most familiar species of sharks, such as the great white as well as less familiar ones, such as the goblin shark and megamouth shark.
Verrucomicrobiota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated species have been identified in association with eukaryotic hosts including extrusive explosive ectosymbionts of protists and endosymbionts of nematodes from genus Xiphinema, residing in their gametes. The verrucomicrobial bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila is a human intestinal symbiotic bacterium that is considered as a promising probiotic.

An argus, or argus pheasant, is a member of a clade in the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae, containing two species of bird that are closely related to peafowl.

In biological taxonomy, the type genus is the genus which defines a biological family and the root of the family name.

The Old World rats and mice, part of the subfamily Murinae in the family Muridae, comprise at least 519 species. Members of this subfamily are called murines. In terms of species richness, this subfamily is larger than all mammal families except the Cricetidae and Muridae, and is larger than all mammal orders except the bats and the remainder of the rodents.

Herpesviridae is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are also known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ἕρπειν, referring to spreading cutaneous lesions, usually involving blisters, seen in flares of herpes simplex 1, herpes simplex 2 and herpes zoster (shingles). In 1971, the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) established Herpesvirus as a genus with 23 viruses among four groups. As of 2020, 115 species are recognized, all but one of which are in one of the three subfamilies. Herpesviruses can cause both latent and lytic infections.

Gammaherpesvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the order Herpesvirales and in the family Herpesviridae. Viruses in Gammaherpesvirinae are distinguished by reproducing at a more variable rate than other subfamilies of Herpesviridae. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 43 species in this subfamily, divided among 7 genera with three species unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: HHV-4: infectious mononucleosis. HHV-8: Kaposi's sarcoma.

Pytilia is a genus of small brightly coloured seed-eating birds in the family Estrildidae. They are distributed across Africa.

The Herpesvirales is an order of dsDNA viruses with animal hosts, characterised by a common morphology consisting of an icosahedral capsid enclosed in a glycoprotein-containing lipid envelope. Common infections in humans caused by members of this order include cold sores, genital herpes, chickenpox, shingles, and glandular fever. Herpesvirales is the sole order in the class Herviviricetes, which is the sole class in the phylum Peploviricota.

An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.



















