Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.

Parvoviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family Parvoviridae. They have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes that typically contain two genes encoding for a replication initiator protein, called NS1, and the protein the viral capsid is made of. The coding portion of the genome is flanked by telomeres at each end that form into hairpin loops that are important during replication. Parvovirus virions are small compared to most viruses, at 23–28 nanometers in diameter, and contain the genome enclosed in an icosahedral capsid that has a rugged surface.
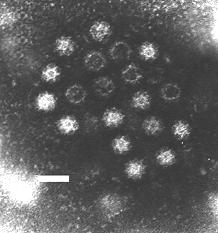
The Caliciviridae are a family of "small round structured" viruses, members of Class IV of the Baltimore scheme. Caliciviridae bear resemblance to enlarged picornavirus and was formerly a separate genus within the picornaviridae. They are positive-sense, single-stranded RNA which is not segmented. Thirteen species are placed in this family, divided among eleven genera. Diseases associated with this family include feline calicivirus, rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus, and Norwalk group of viruses (gastroenteritis). Caliciviruses naturally infect vertebrates, and have been found in a number of organisms such as humans, cattle, pigs, cats, chickens, reptiles, dolphins and amphibians. The caliciviruses have a simple construction and are not enveloped. The capsid appears hexagonal/spherical and has icosahedral symmetry with a diameter of 35–39 nm.

Nodaviridae is a family of nonenveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Vertebrates and invertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include: viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in fish. There are nine species in the family, assigned to two genera.

The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus taxon. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as identifying new taxa and delimiting the boundaries of species, genera, families, etc. typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families.

Benyvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Benyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: BNYVV: rhizomania.
Hypovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Hypoviridae. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Infection reduces the virulence of its parasitic host, making it a hyperparasite useful for blight control.

Aspiviridae, formerly Ophioviridae, is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It is a monotypic taxon containing only one genus, Ophiovirus. Aspiviridae is also the only family in the order Serpentovirales, which in turn is the only order in the class Milneviricetes.
Brazilian hemorrhagic fever (BzHF) is an infectious disease caused by Brazilian mammarenavirus, an arenavirus. Brazilian mammarenavirus is one of the arenaviruses from South America to cause hemorrhagic fever. It shares a common progenitor with Argentinian mammarenavirus, Machupo mammarenavirus, Tacaribe mammarenavirus, and Guanarito mammarenavirus. It is an enveloped RNA virus and is highly infectious and lethal. Very little is known about this disease, but it is thought to be transmitted by the excreta of rodents. This virus has also been implicated as a means for bioterrorism, as it can be spread through aerosols.

Betacoronavirus gravedinis is a species of coronavirus which infects humans and cattle. The infecting virus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus and is a member of the genus Betacoronavirus and subgenus Embecovirus. Like other embecoviruses, it has an additional shorter spike-like surface protein called hemagglutinin esterase (HE) as well as the larger coronavirus spike protein.
Alphasphaerolipovirus is a genus of double stranded DNA viruses that infect Haloarchaea. The genus contains four species.
Yingchengvirus is a genus of double stranded DNA viruses that infect haloarchaea. The genus was previously named Betasphaerolipovirus.
Hukuchivirus is a genus of double-stranded DNA viruses that infect thermophilic bacteria. The genus was previously named Gammasphaerolipovirus.

Peribunyaviridae is a family of viruses in the order Bunyavirales. Its name partially derives from Bunyamwera, Uganda, where the founding species was first isolated.
Testudinid alphaherpesvirus 3 (TeHV-3) is a species of virus in the family Herpesviridae.
Macacine betaherpesvirus 3 (McHV-3) is a species of virus in the genus Cytomegalovirus, subfamily Betaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Papiine betaherpesvirus 3 (PaHV-3) is a species of virus in the genus Cytomegalovirus, subfamily Betaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Suid gammaherpesvirus 3 (SuHV-3) is a species of virus in the genus Macavirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Phocid gammaherpesvirus 3 (PhHV-3) is a species of virus in the family Herpesviridae.
Ateline gammaherpesvirus 3 (AtHV-3) is a species of virus in the genus Rhadinovirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.








