
The NZR WB class was a class of tank locomotives that operated in New Zealand. Built in 1898 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works, the twelve members of the class entered service during the first five months of 1899. Eight were withdrawn by the end of 1935, while four others survived with new boilers until the mid-1950s.

The NZR WD class was a class of tank locomotive built by Baldwin Locomotive Works to operate on New Zealand's national rail network.

The NZR O class consisted of six steam locomotives that operated on New Zealand's national rail network. Ordered from the Baldwin Locomotive Works of Pennsylvania in 1885, three arrived in time to begin work in December 1885, while two more were placed in service in January 1886 and the sixth in February 1886. After almost four decades of service, all six were withdrawn in May 1922. None survived to be preserved, although two engine frames and 5 tenders from O class locomotives are known to exist near Summit on the former Rimutaka Incline.

The N class were 12 steam locomotives that operated on the national rail network of New Zealand. They were built in three batches, including one batch of two engines for the private Wellington and Manawatu Railway Company, the WMR, by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1885, 1891, and 1901. Previously the N class designation had been applied between 1877 and 1879 to Lady Mordaunt, a member of the B class of 1874.
The NZR NA class was a class of two steam locomotives that operated on the privately-owned Wellington and Manawatu Railway (WMR) and then the publicly owned New Zealand Railways (NZR). Ordered by the WMR to operate on its line up the west coast of the North Island north of Wellington, the first was built in 1894 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works and entered service that year as WMR No. 14. In 1896, a second locomotive that was slightly more powerful was ordered from Baldwin, and it entered service in October 1897. The engines were similar to the two members of the N class ordered in 1891, except they were heavier and more powerful. They were Vauclain compound locomotives.

The NZR NC class was a class of two steam locomotives built by Baldwin Locomotive Works built for service on New Zealand's private Wellington and Manawatu Railway (WMR). They did not acquire their NC classification until the publicly owned New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) purchased the WMR and its locomotive fleet.

The OB class was the first class of steam locomotives constructed by the Baldwin Locomotive Works for the Wellington and Manawatu Railway Company (WMR) in New Zealand. The class consisted of two locomotives ordered in 1888, and they entered service in September of that year as WMR No.'s 11 and 12.

The OA class is a solitary steam locomotive built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works for the Wellington and Manawatu Railway (WMR) in New Zealand. Ordered in 1894, it entered service in August of that year as No. 13 and was the first narrow gauge Vauclain compound in the world. In 1908, the WMR and its locomotive fleet were purchased by New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) and incorporated into the national rail network, and, although No. 13 bore a likeness to members of the O class, it was sufficiently different that it warranted separate classification. The designation of OA was created and it was numbered OA 457. It operated for another two decades until it was withdrawn in December 1929 in Auckland. The locomotive was known to WMR staff as "The Lady".

The OC class, built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works for the Wellington and Manawatu Railway (WMR) in New Zealand, consists of a solitary steam locomotive. Ordered in 1896 as an externally similar but more powerful version of the OA class locomotive ordered in 1894, it entered service in June 1897 as No. 16. It was a Vauclain compound locomotive.

The P class was a class of steam locomotives built to haul freight trains on the national rail network of New Zealand. The class consisted of ten individual locomotives ordered from the British company of Nasmyth, Wilson and Company in 1885, but miscommunications about the weight limitations imposed on the locomotives meant they did not start work until 1887. This debacle came at a time when the New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) was suffering from a lack of motive power to work on its rapidly expanding network and was part of what prompted a shift towards American and home-grown manufacturers.

The BC class comprised a single steam locomotive that operated on New Zealand's national rail network. Built for the Wellington and Manawatu Railway (WMR) and classified simply as No.17, it passed into the ownership of the New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) when the government purchased the WMR in December 1908, and it was then that it acquired the BC classification as BC 463.

The NZR LA class was a class of 4-4-0T steam locomotives used by the New Zealand Railways Department and the New Zealand Midland Railway Company. They were built by Nasmyth, Wilson and Company in 1887 for New Zealand Midland Railway Company, and were taken over by NZR in 1900, when the government acquired the incomplete Midland line. The designation also applies to the NZR 4-4-0Trebuilds of the Avonside L class of 1875 which were later reclassified LB after being rebuilt as 4-4-2Ts.

The NZR R class was a class of early 0-6-4T single Fairlie steam locomotives operated by New Zealand's Railways Department (NZR) between 1879 and 1936.

The New Zealand V class steam locomotive was used on New Zealand's railway network from 1885 onwards. They were operated by New Zealand Government Railways and the Wellington and Manawatu Railway Company.

The NZR WJ class was a class of one steam locomotive built by Baldwin Locomotive Works for service on New Zealand's private Wellington and Manawatu Railway (WMR). She acquired the WJ classification when the publicly owned New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) purchased the WMR and its locomotive fleet in 1908.

The NZR U class, the first tender locomotives built in New Zealand, were a class of 4-6-0 Ten Wheeler locomotive designed to the requirements of Mr T. F. Rotherham and built at NZR Addington between 1894 and 1903. They were amongst NZRs' longest lived tender engines.

The NZR UA class were a class of 4-6-0 Ten Wheeler locomotive built by the Scottish firm of Sharp Stewart and Company to ease a motive power shortage. They lived relatively short lives amongst NZR ten wheelers, mostly at the southern end of the country where they were seldom photographed.

The NZR M class were a series of four tank engines built in England for the Otago railways Bluff to Winton section. They were acquired by NZR in the late 1870s and rebuilt in the late 1880s. As rebuilt they were not very successful and were used in shunting duties until retirement in the 1920s.

The NZR UB class were a series of Ten Wheelers built by American manufacturers for New Zealand Railways (NZR) around the start of the twentieth century. Two batches were built by Baldwin in 1898 and 1901. The earlier engines had slide valves and Stephenson motion, the later had piston valves and Walschaerts valve gear, as well as a higher boiler pressure. Two additional locomotives were obtained in 1901 from ALCO, one each from Brooks and Richmond. The Brooks locomotive (#17) was heavier with attendant increase in tractive effort (18340 lbf), and had a larger grate. This locomotive was very popular with crews. This locomotive was dumped on the Oamaru foreshore. The Richmond locomotive had less evaporative heating surface but included a superheater. Boiler pressure was lower and tractive effort was marginally lower. The locomotives were initially assigned to Dunedin to Christchurch expresses and were reassigned as newer power replaced them. The last assignment for the class was on the West Coast Region.
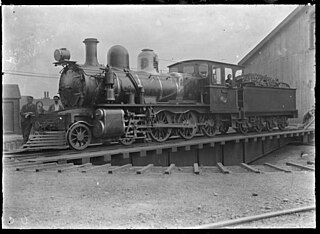
The NZR UC class were a group of ten 4-6-0 steam locomotives obtained from Scottish builders Sharp, Stewart and Company for New Zealand Railways (NZR). Essentially they were developments of the firm's previous batch of 4-6-0s' for NZR.



















