Native Americans or Native American usually refers to Native Americans in the United States.
Contents
Related terms and peoples include:
Native Americans or Native American usually refers to Native Americans in the United States.
Related terms and peoples include:
Indian or Indians may refer to something or someone of, from, or associated with the nation of India or with the indigenous people of the Americas.
Metis or Métis may refer to:
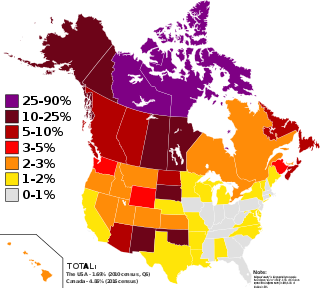
Indigenous peoples in Canada are the indigenous peoples within the boundaries of Canada. They comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although "Indian" is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors "Indian" and "Eskimo" have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider them to be pejorative. "Aboriginal" as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in some legal documents, including the Constitution Act, 1982, though in some circles that word is also falling into disfavour.
First Nations is a term used to identify Indigenous peoples in Canada who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia.
The minister of Crown–Indigenous relations is a minister of the Crown in the Canadian Cabinet, one of two ministers who administer Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada (CIRNAC), the department of the Government of Canada which is responsible for administering the Indian Act and other legislation dealing with "Indians and lands reserved for the Indians" under subsection 91(24) of the Constitution Act, 1867. The minister is also more broadly responsible for overall relations between the federal government and First Nations, Métis, and Inuit.

The Assembly of First Nations is an assembly of Canadian First Nations represented by their chiefs. Established in 1982 and modelled on the United Nations General Assembly, it emerged from the National Indian Brotherhood, which dissolved in the late 1970s.

The Métis are an Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, Northwest Ontario and the northern United States. They have a shared history and culture, deriving from specific mixed European and Indigenous ancestry, which became distinct through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade.
The Native American name controversy is an ongoing discussion about the changing terminology used by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas to describe themselves, as well as how they prefer to be referred to by others. Preferred terms vary primarily by region and age. As Indigenous peoples and communities are diverse, there is no consensus on naming.
In Canada, an Indian band, First Nation band or simply band, is the basic unit of government for those peoples subject to the Indian Act. Bands are typically small groups of people: the largest in the country, the Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation had 22,294 members in September 2005, and many have a membership below 100 people. Each First Nation is typically represented by a band council chaired by an elected chief, and sometimes also a hereditary chief. As of 2013, there were 614 bands in Canada. Membership in a band is controlled in one of two ways: for most bands, membership is obtained by becoming listed on the Indian Register maintained by the government. As of 2013, there were 253 First Nations which had their own membership criteria, so that not all status Indians are members of a band.
Anthony "Tony" Belcourt OC is a Métis rights leader and activist in Canada. He was the first president of the Native Council of Canada (1971-1974). He is best known for his work as the founding President of the Métis Nation of Ontario in 1993 and his leadership through the Powley Case in 2003.

Inuit are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of North America, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, Yukon (traditionally), Alaska, and Chukotsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut.
Indigenism can refer to several different ideologies that seek to promote the interests of indigenous peoples. The term is used differently by various scholars and activists, and can be used purely descriptively or carry political connotations. There are a range of ways to define Indigenous identity, including political, legal, cultural, and geographic distinctions.
Over the course of centuries, many Indigenous Canadians have played a critical role in shaping the history of Canada. From art and music, to law and government, to sports and war; Indigenous customs and culture have had a strong influences on defining Canadian culture. The Indspire Awards are the annual awards presented by Indspire, formerly the National Aboriginal Achievement Foundation. The awards were first established in 1993 in conjunction with the United Nations declaring the 1990s "International Decade of the World's Indigenous peoples". June 21 is Canada's National Aboriginal Day, in recognition of the cultural contributions made by Canada's indigenous population. The day was first celebrated in 1996 following Governor General of Canada Roméo LeBlanc's proclamation.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to Indigenous peoples in Canada, comprising the First Nations, Inuit and Métis peoples.
Métis fiddle is the style that the Métis of Canada and Métis in the northern United States have developed to play the violin, solo and in folk ensembles. It is marked by the percussive use of the bow and percussive accompaniment. The Metis people are a poly-ethnic post-contact Indigenous peoples. Fiddles were "introduced in this area by Scottish and French-Canadian fur traders in the early 1800s", where the Metis community adopted the instrument into their culture.

NunatuKavut is an Inuit territory in Labrador. It is unrecognized by other Indigenous groups in Canada, including the Innu Nation, the Nunatsiavut government, and the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami. The NunatuKavummiut claim to be the direct descendants of the Inuit that lived south of the Churchill or Grand River prior to European contact, with recent European admixture primarily from English settlers. Despite claims of Inuit heritage, according to recent censuses completed by Statistics Canada, the vast majority of individuals living in communities that NunatuKavut claims are within its region continue to identify as Métis as opposed to 'Inuit'.
Indigenous or Aboriginal self-government refers to proposals to give governments representing the Indigenous peoples in Canada greater powers of government. These proposals range from giving Aboriginal governments powers similar to that of local governments in Canada to demands that Indigenous governments be recognized as sovereign, and capable of "nation-to-nation" negotiations as legal equals to the Crown, as well as many other variations.
Indigenous peoples of Canada are culturally diverse. Each group has its own literature, language and culture. The term "Indigenous literature" therefore can be misleading. As writer Jeannette Armstrong states in one interview, "I would stay away from the idea of "Native" literature, there is no such thing. There is Mohawk literature, there is Okanagan literature, but there is no generic Native in Canada".
Pretendian is a pejorative colloquialism used to call out a person who has falsely claimed Indigenous identity by professing to be a citizen of a Native American or Indigenous Canadian tribal nation, or to be descended from Native American or Indigenous Canadian ancestors. As a practice, being a pretendian is considered an extreme form of cultural appropriation, especially if that individual then asserts that they can represent, and speak for, communities from which they do not originate. It is sometimes also referred to as a form of fraud, ethnic fraud or race shifting.
First Nations usually refers to Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.