| Nemegtbaatar | |
|---|---|
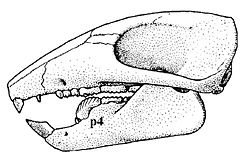 | |
| Reconstructed skull | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | † Multituberculata |
| Superfamily: | † Djadochtatherioidea |
| Genus: | † Nemegtbaatar |
| Species: | †N. gobiensis |
| Binomial name | |
| †Nemegtbaatar gobiensis Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974 | |
Nemegtbaatar is an extinct genus of mammal from the Upper Cretaceous Period of what is now Central Asia. It belonged to the order Multituberculata. Nemegtbaatar is within the suborder Cimolodonta and is a member of the superfamily Djadochtatherioidea.
The genus Nemegtbaatar (Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974) was named after the Nemegt Valley and Ulan Bator, the capital of Mongolia. The type species is Nemegtbaatar gobiensis. It was discovered in Campanian aged strata of the Barun Goyot Formation in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia. [1] Fossils of this species have been found in rocks dated from 76 to 71 million years ago, correlating to the Campanian and early Maastrichtian ages. [2] With several intact skulls having been found, it can be determined that N.gobiensis has a dental formula of 2.0.4.21.0.2.2 with a "roughly triangular" snout. [3] Nemegtbaatar is possibly derived from a Bulganbaatar ancestor, based on a comparison of their dentition. [4]
Nemegtbaatar was a relatively large member of Djadochtatherioidea, with a skull length of up to 4.2 centimetres (1.7 in) and estimated adult body mass of 210 grams (7.4 oz), [5] which is roughly the size of a modern rat. According to detailed reconstructions by Kielan-Jaworowska and Gambaryan, Nemegtbaatar was likely nocturnal due its large eyes, and had live births but relatively undeveloped young due to its pelvic structure. It likely was behaviorially similar to that of the modern gerbil. [6]

Fossil specimens were collected during several Polish-Mongolian expeditions that took place during the 1960s and 1970s, during which this species was discovered. At least one specimen is in the Institute of Paleobiology collection of the Polish Academy of Sciences at Warsaw, (ZPAL MgM-1/76). Fossil remains of Nemegtbaatar are unusually complete, allowing for significant reconstructive analyses to be performed on them. [7] [8] [9]

