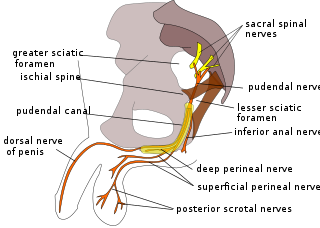
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a mixed nerve and also conveys sympathetic autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter.

The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibres from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.

The cervical plexus is a nerve plexus of the anterior rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves C1-C4. The cervical plexus provides motor innervation to some muscles of the neck, and the diaphragm; it provides sensory innervation to parts of the head, neck, and chest.

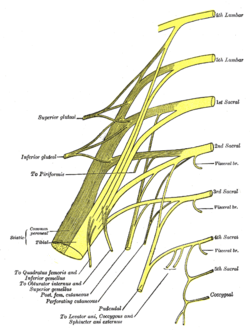
The piriformis muscle is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.

The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis.

The iliopsoas muscle refers to the joined psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name iliopsoas. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest flexor of the hip.

A nerve plexus is a plexus of intersecting nerves. A nerve plexus is composed of afferent and efferent fibers that arise from the merging of the anterior rami of spinal nerves and blood vessels. There are five spinal nerve plexuses, except in the thoracic region, as well as other forms of autonomic plexuses, many of which are a part of the enteric nervous system. The nerves that arise from the plexuses have both sensory and motor functions. These functions include muscle contraction, the maintenance of body coordination and control, and the reaction to sensations such as heat, cold, pain, and pressure. There are several plexuses in the body, including:

In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar vertebrae and sacral vertebrae (L4-S4). A sacral plexopathy is a disorder affecting the nerves of the sacral plexus, usually caused by trauma, nerve compression, vascular disease, or infection. Symptoms may include pain, loss of motor control, and sensory deficits.

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.

The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a sensory nerve of the thigh. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It supplies the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh, leg, buttock, and also the perineum.

The inferior gluteal nerve is the main motor neuron that innervates the gluteus maximus muscle. It is responsible for the movement of the gluteus maximus in activities requiring the hip to extend the thigh, such as climbing stairs. Injury to this nerve is rare but often occurs as a complication of posterior approach to the hip during hip replacement. When damaged, one would develop gluteus maximus lurch, which is a gait abnormality which causes the individual to 'lurch' backwards to compensate lack in hip extension.

The superior gluteal nerve is a mixed nerve of the sacral plexus that originates in the pelvis. It provides motor innervation to the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fasciae latae, and piriformis muscles; it also has a cutaneous branch.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.

The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves in the lumbar plexus; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.

The perforating cutaneous nerve is a cutaneous nerve of the sacral plexus that provides sensory innervation to the skin of the buttocks.

The inferior gluteal artery is a terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. It is distributed chiefly to the buttock and the back of the thigh.
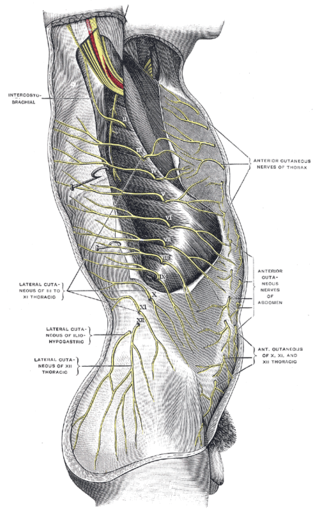
The subcostal nerve is a mixed motor and sensory nerve contributing to the lumbar plexus. It runs along the lower border of the twelfth rib, often gives a communicating branch to the first lumbar nerve, and passes under the lateral lumbocostal arch.

The piriformis nerve, also known as the nerve to piriformis, is the peripheral nerve that provides motor innervation to the piriformis muscle.

The nerve to quadratus femoris is a nerve of the sacral plexus that provides motor innervation to the quadratus femoris muscle and gemellus inferior muscle, and an articular branch to the hip joint. The nerve leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen.

The lumbosacral trunk is nervous tissue that connects the lumbar plexus with the sacral plexus. It is formed by the union of parts of the fourth and fifth lumbar nerves and descends to join the sacral plexus.