Related Research Articles

Substance P (SP) is an undecapeptide member of the tachykinin neuropeptide family. It is a neuropeptide, acting as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. Substance P and its closely related neurokinin A (NKA) are produced from a polyprotein precursor after differential splicing of the preprotachykinin A gene. The deduced amino acid sequence of substance P is as follows:
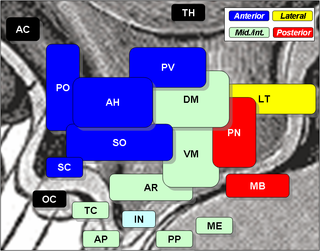
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. The function of the arcuate nucleus relies on its diversity of neurons, but its central role is involved in homeostasis. The arcuate nucleus provides many physiological roles involved in feeding, metabolism, fertility, and cardiovascular regulation.

Neuropeptides are chemical messengers made up of small chains of amino acids that are synthesized and released by neurons. Neuropeptides typically bind to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to modulate neural activity and other tissues like the gut, muscles, and heart.

Gastrin-releasing peptide, also known as GRP, is a neuropeptide, a regulatory molecule that has been implicated in a number of physiological and pathophysiological processes. Most notably, GRP stimulates the release of gastrin from the G cells of the stomach.
Neurogenic inflammation is inflammation arising from the local release by afferent neurons of inflammatory mediators such as Substance P, Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP), neurokinin A (NKA), and endothelin-3 (ET-3). In such neurons, release of these pro-inflammatory mediators is thought to be triggered by the activation of ion channels that are the principal detectors of noxious environmental stimuli. In particular, the heat/capsaicin receptor TRPV1 and the irritant/wasabi receptor TRPA1. TRPA1 channels stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) may also cause acute neurogenic inflammation. Once released, these neuropeptides induce the release of histamine from adjacent mast cells. In turn, histamine evokes the release of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide; thus, a bidirectional link between histamine and neuropeptides in neurogenic inflammation is established.

Tachykinin peptides are one of the largest families of neuropeptides, found from amphibians to mammals. They were so named due to their ability to rapidly induce contraction of gut tissue. The tachykinin family is characterized by a common C-terminal sequence, Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, where X is either an Aromatic or an Aliphatic amino acid. The genes that produce tachykinins encode precursor proteins called preprotachykinins, which are chopped apart into smaller peptides by posttranslational proteolytic processing. The genes also code for multiple splice forms that are made up of different sets of peptides.

Urocortin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UCN gene. Urocortin belongs to the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) family of proteins which includes CRF, urotensin I, sauvagine, urocortin II and urocortin III. Urocortin is involved in the mammalian stress response, and regulates aspects of appetite and stress response.
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a member of the calcitonin family of peptides consisting of calcitonin, amylin, adrenomedullin, adrenomedullin 2 (intermedin) and calcitonin‑receptor‑stimulating peptide. Calcitonin is mainly produced by thyroid C cells whilst CGRP is secreted and stored in the nervous system. This peptide, in humans, exists in two forms: CGRP alpha, and CGRP beta. α-CGRP is a 37-amino acid neuropeptide and is formed by alternative splicing of the calcitonin/CGRP gene located on chromosome 11. β-CGRP is less studied. In humans, β-CGRP differs from α-CGRP by three amino acids and is encoded in a separate, nearby gene. The CGRP family includes calcitonin (CT), adrenomedullin (AM), and amylin (AMY).
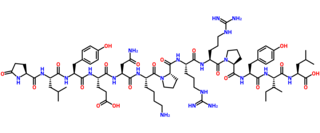
Neurotensin is a 13 amino acid neuropeptide that is implicated in the regulation of luteinizing hormone and prolactin release and has significant interaction with the dopaminergic system. Neurotensin was first isolated from extracts of bovine hypothalamus based on its ability to cause a visible vasodilation in the exposed cutaneous regions of anesthetized rats.

Galanin is a neuropeptide encoded by the GAL gene, that is widely expressed in the brain, spinal cord, and gut of humans as well as other mammals. Galanin signaling occurs through three G protein-coupled receptors.
Preprotachykinins are precursor proteins that are modified into tachykinin peptides. Via alternative splicing and post-translational modifications, preprotachykinins produce multiple peptide neurotransmitters.

Neurokinin A (NKA), formerly known as Substance K, is a neurologically active peptide translated from the pre-protachykinin gene. Neurokinin A has many excitatory effects on mammalian nervous systems and is also influential on the mammalian inflammatory and pain responses.

Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript, also known as CART, is a neuropeptide protein that in humans is encoded by the CARTPT gene. CART appears to have roles in reward, feeding, and stress, and it has the functional properties of an endogenous psychostimulant.
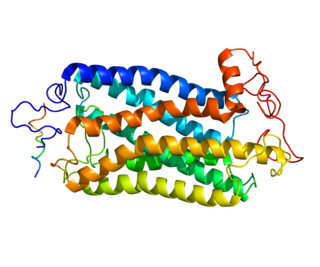
The tachykinin receptor 1 (TACR1) also known as neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) or substance P receptor (SPR) is a G protein coupled receptor found in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The endogenous ligand for this receptor is Substance P, although it has some affinity for other tachykinins. The protein is the product of the TACR1 gene.

Neuropeptide Y receptor type 2 (Y2R) is a member of the neuropeptide Y receptor family of G-protein coupled receptors, that in humans is encoded by the NPY2R gene.

Substance-K receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TACR2 gene.

Tachykinin receptor 3, also known as TACR3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TACR3 gene.

Pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1, also known as Neuropeptide Y receptor type 4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPYR1 gene.

Tachykinin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAC3 gene.

Preprotachykinin-1,, is a precursor protein that in humans is encoded by the TAC1 gene.
References
- ↑ Dornan WA, Vink KL, Malen P, Short K, Struthers W, Barrett C (August 1993). "Site-specific effects of intracerebral injections of three neurokinins (neurokinin A, neurokinin K, and neurokinin gamma) on the expression of male rat sexual behavior". Physiol. Behav. 54 (2): 249–58. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(93)90107-Q. PMID 7690487. S2CID 33412235.
- ↑ Takeda, Y; Krause, JE (Jan 1989). "Neuropeptide K potently stimulates salivary gland secretion and potentiates substance P-induced salivation". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 86 (1): 392–396. Bibcode:1989PNAS...86..392T. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.392 . PMC 286471 . PMID 2463627.
- 1 2 Holzer, P. (1988-03-01). "Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: Involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides". Neuroscience. 24 (3): 739–768. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(88)90064-4. PMID 3288903. S2CID 35325223.
- ↑ Bannon, Michael J.; Poosch, Michael S.; Haverstick, Doris M.; Anita, Mandal; Xue, Iris C. -H.; Shibata, Kazuhiko; Dragovic, Ljubisa J. (1992-01-01). "Preprotachykinin gene expression in the human basal ganglia: characterization of mRNAs and pre-mRNAs produced by alternate RNA splicing". Molecular Brain Research. 12 (1–3): 225–231. doi:10.1016/0169-328X(92)90088-S. PMID 1312203.