
Thomas Mifflin was an American merchant, soldier, and politician from Pennsylvania, who is regarded as a Founding Father of the United States for his roles during and after the American Revolution. Mifflin signed the United States Constitution, was the first governor of Pennsylvania, serving from 1790 to 1799, and was also the state's last president, succeeding Benjamin Franklin in 1788.

1783 (MDCCLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 1783rd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 783rd year of the 2nd millennium, the 83rd year of the 18th century, and the 4th year of the 1780s decade. As of the start of 1783, the Gregorian calendar was 11 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

Alexander Hamilton was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first U.S. secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795 during George Washington's presidency.

Nathaniel Gorham was an American Founding Father, merchant, and politician from Massachusetts. He was a delegate from the Bay Colony to the Continental Congress and for six months served as the presiding officer of that body under the Articles of Confederation. He also attended the Constitutional Convention, served on its Committee of Detail, and signed the United States Constitution.

Marie-Joseph Paul Yves Roch Gilbert du Motier de La Fayette, Marquis de La Fayette, known in the United States as Lafayette, was a French nobleman and military officer who volunteered to join the Continental Army, led by General George Washington, in the American Revolutionary War. Lafayette was ultimately permitted to command Continental Army troops in the decisive Siege of Yorktown in 1781, the Revolutionary War's final major battle that secured American independence. After returning to France, Lafayette became a key figure in the French Revolution of 1789 and the July Revolution of 1830 and continues to be celebrated as a hero in both France and the United States.

New Windsor is a town in Orange County, New York, United States. The population was 27,805 at the 2020 census. It is located on the eastern side of the county and is adjacent to the Hudson River and the City of Newburgh.
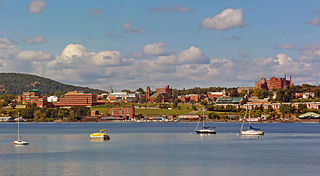
Newburgh is a city in Orange County, New York, United States. With a population of 28,856 as of the 2020 census, it is a principal city of the Kiryas Joel-Poughkeepsie-Newburgh metropolitan area. Located 60 miles (97 km) north of New York City, and 90 miles (140 km) south of Albany on the Hudson River within the Hudson Valley Area, the city of Newburgh is located near Stewart International Airport, one of the primary airports for Downstate New York.

Events from the year 1782 in Canada.

The Newburgh Conspiracy was a failed apparent threat by leaders of the Continental Army in March 1783, at the end of the American Revolutionary War. The Army's commander, George Washington, successfully calmed the soldiers and helped secure back pay. The conspiracy may have been instigated by members in the Congress of the Confederation, which circulated an anonymous letter in the army camp at Newburgh, New York, on March 10, 1783. Soldiers were unhappy that they had not been paid for some time and that pensions that had been promised remained unfunded.

General of the Armies of the United States, more commonly referred to as General of the Armies, is the highest military rank in the United States. The rank has been conferred three times: to John J. Pershing in 1919, as a personal accolade for his command of the American Expeditionary Forces during World War I; to George Washington in 1976, as a posthumous honor during the United States Bicentennial celebrations; and to Ulysses S. Grant in December 2022, when Congress authorized the president to posthumously appoint him to the rank.

Washington's Headquarters State Historic Site, also called Hasbrouck House, is located in Newburgh, New York, United States, overlooking the Hudson River. George Washington and his staff were headquartered in the house while commanding the Continental Army during the final year and a half of the American Revolutionary War; at 16 months and 19 days it was his longest tenure at any of his headquarters during the war.
Lewis Nicola was an Irish-born American military officer, merchant, and writer who held various military and civilian positions throughout his career. Nicola is most notable for authoring the Newburgh letter, which urged George Washington to assume a royal title. Born in Dublin, Ireland, Nicola had been an officer in the British Army, serving in Europe before immigrating to the Thirteen Colonies. Establishing a residence in Philadelphia with his family, Nicola opened a library in 1767 and was active in colonial philosophical organizations. As a result of his work to establish the American Philosophical Society, he was elected as one of its curators. When the American Revolution broke out, Nicola offered his services to the colonial government, which eventually appointed him to various positions with local forces.

General Sir Charles Asgill, 2nd Baronet, was a career soldier in the British Army. At the end of the American Revolutionary War he became the principal of the so-called Asgill Affair of 1782, in which his retaliatory death sentence while a prisoner of war was commuted by the American forces who held him, due to the direct intervention of the government of France. Later in his career, he was involved in the Flanders campaign, the suppression of the Irish Rebellion of 1798 and was Commander of the Eastern Division of Ireland during the Irish rebellion of 1803.

The National Purple Heart Hall of Honor is located along New York State Route 300 in the Town of New Windsor, New York, United States. It is less than two miles south of the Town of Newburgh line and not far from the City of Newburgh. It is a Purple Heart national registry of military personnel that have been injured or killed during combat. In 1782, at Washington's Headquarters State Historic Site, his headquarters in the City of Newburgh, George Washington created the Badge of Military Merit to be given to enlisted men and non-commissioned officers for meritorious action. The museum is located at the New Windsor Cantonment State Historic Site, the last encampment of the Continental Army. It is the first and currently only museum dedicated to a U.S. military medal.
Events from the year 1783 in the United States. The American Revolution officially ended with the Treaty of Paris.
The Prussian scheme refers to the rumor about a supposed suggestion in 1786 by Massachusetts politician Nathaniel Gorham that if the country adopted a constitutional monarchy like England it ought to invite Henry of Prussia, a German prince of the House of Hohenzollern, as the new king.
Monarchism in the United States is the advocacy of a monarchical form of government in the United States of America. During the American Revolution a significant element of the population remained loyal to the British crown. However, aside from a few considerations in the 1780s, since independence there has not been any serious movement for an American monarchy.

George Washington's resignation as commander-in-chief marked the end of Washington's military service in the American Revolutionary War and his return to civilian life at Mount Vernon.

George Washington's political evolution comprised the transformation of a young man from a moderately wealthy family in the British colony of Virginia motivated largely by self-interest, into the first president of the United States and one of the Founding Fathers. Washington was ambitious for the status and influence with which he had been surrounded in a youth spent around his half-brother Lawrence and the influential Fairfax family Lawrence married into. After working as a surveyor, a position he gained with the patronage of the Fairfaxes, Washington sought to emulate his brother's military career with a commission in the Virginia militia, despite his lack of military experience. With the patronage of more influential people, he was appointed major in 1752. The following year, he was appointed special envoy charged with delivering to the French a demand to vacate territory claimed by the British. His successful completion of this task gained him his first measure of renown. Washington was promoted in 1754 and made second-in-command of the Virginia Regiment. He enhanced his reputation with his first military victory in the Battle of Jumonville Glen, a skirmish that ignited the French and Indian War. He was promoted again in 1755 and given command of the regiment, serving until his resignation in 1758. During his military service, Washington grew disillusioned with the British because of his treatment as a second-class citizen and the defensive strategy they adopted during the war. He gained no further opportunity for military honor and failed to achieve his ambition of a royal commission in the British Army.
Samuel Loudon (1727–1813) was a colonial American printer, publisher and merchant who emigrated from Ireland some time prior to 1753. Loudon founded The New-York Packet and The American Advertiser and became the postmaster at New York State's first post office in Fishkill, New York. During the American Revolution he became the official printer of New York State and printed its first Constitution, laws, acts and other official documents, while also taking on some private commissions. Before and during the Revolution Loudon became active through the use of his newspapers promoting the cause for American independence, and for freedom of the press. After the war Loudon printed the Laws of the City of New York, and later promoted ratification of the proposed Constitution by publishing selected essays of The Federalist Papers in his newspaper.














