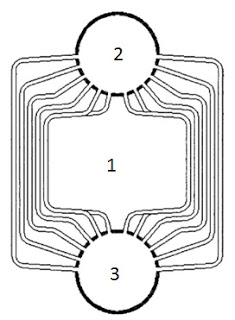
- 1 - Furnace
- 2 - Steam drum
- 3 - Water drum
An O-type boiler is a form of water-tube boiler. It is named, like the D-type and A-type boilers, from the approximate shape of its tubes.
They are characterised by single steam and water drums vertically above each other, with curved vertical water tubes to the sides forming an overall cylindrical volume. There is no grate at the base of this furnace space, so they are fired by liquid burners, oil or gas, rather than a solid fuel furnace producing ash. [1]
O-type boilers first appeared as marine boilers, such as the Johnson boiler, once the switch from coal firing to oil firing began. [1] The large radiant heating area available allows a combustion rate, for a given furnace volume, of around twice that for a contemporary boiler, such as the Yarrow.
Small examples of the O-type are used as some package boilers. [2] Most package boilers are fire-tube boilers, often used for heating or process steam, and generally work at lower pressures than propulsion boilers. If high pressure steam is needed, such as for steam turbines, then a water-tube boiler may be preferred and these are mostly O-type. O-type package boilers appeared post-World War II, with the general shift away from coal and to more automated boilers needing fewer human operators. [3]
O-type boilers are available with or without end water-walls. They may also use tube and refractory cement infill, or else a steel membrane wall between the tubes. [4]