
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses (M☉), possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes, neutron stars are the smallest and densest known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of 10 kilometers (6 mi) and a mass of about 1.4 M☉. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei.

PSR B1620−26 is a binary star system located at a distance of 3,800 parsecs in the globular cluster of Messier 4 in the constellation of Scorpius. The system is composed of a pulsar and a white dwarf star. As of 2000, the system is also confirmed to have an exoplanet orbiting the two stars.

3C 58 or 3C58 is a pulsar and supernova remnant within the Milky Way. The object is listed as No. 58 in the Third Cambridge Catalogue of Radio Sources.

A pulsar is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Earth, and is responsible for the pulsed appearance of emission. Neutron stars are very dense and have short, regular rotational periods. This produces a very precise interval between pulses that ranges from milliseconds to seconds for an individual pulsar. Pulsars are one of the candidates for the source of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays.

A carbon planet is a theoretical type of planet that contains more carbon than oxygen. Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen.

PSR J0737−3039 is the first known double pulsar. It consists of two neutron stars emitting electromagnetic waves in the radio wavelength in a relativistic binary system. The two pulsars are known as PSR J0737−3039A and PSR J0737−3039B. It was discovered in 2003 at Australia's Parkes Observatory by an international team led by the Italian radio astronomer Marta Burgay during a high-latitude pulsar survey.
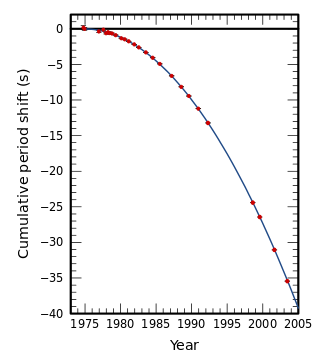
The Hulse–Taylor pulsar is a binary star system composed of a neutron star and a pulsar which orbit around their common center of mass. It is the first binary pulsar ever discovered.

A binary pulsar is a pulsar with a binary companion, often a white dwarf or neutron star. Binary pulsars are one of the few objects which allow physicists to test general relativity because of the strong gravitational fields in their vicinities. Although the binary companion to the pulsar is usually difficult or impossible to observe directly, its presence can be deduced from the timing of the pulses from the pulsar itself, which can be measured with extraordinary accuracy by radio telescopes.

The Vela Pulsar is a radio, optical, X-ray- and gamma-emitting pulsar associated with the Vela Supernova Remnant in the constellation of Vela. Its parent Type II supernova exploded approximately 11,000–12,300 years ago.
The Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff limit is an upper bound to the mass of cold, non-rotating neutron stars, analogous to the Chandrasekhar limit for white dwarf stars. If the mass of a neutron star reaches the limit it will collapse to a denser form, most likely a black hole. The original calculation in 1939, which neglected complications such as nuclear forces between neutrons, placed this limit at approximately 0.7 solar masses (M☉). Later, more refined analyses have resulted in larger values.

PSR J1748−2446ad is the fastest-spinning pulsar known, at 716 Hz, or 43,000 revolutions per minute. This pulsar was discovered by Jason W. T. Hessels of McGill University on November 10, 2004 and confirmed on January 8, 2005.
PSR B0329+54 is a pulsar approximately 3,460 light-years away in the constellation of Camelopardalis. It completes one rotation every 0.71452 seconds and is approximately 5 million years old.

NGC 2060 is a star cluster within the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud, very close to the larger NGC 2070 cluster containing R136. It was discovered by John Herschel in 1836. It is a loose cluster approximately 10 million years old, within one of the Tarantula Nebula's superbubbles formed by the combined stellar winds of the cluster or by old supernovae.
PSR B1828-11 is a pulsar approximately 10,000 light-years away in the constellation of Scutum. The star exhibits variations in the timing and shape of its pulses: this was at one stage interpreted as due to a possible planetary system in orbit around the pulsar, though the model required an anomalously large second period derivative of the pulse times. The planetary model was later discarded in favour of precession effects as the planets could not cause the observed shape variations of the pulses. While the generally accepted model is that the pulsar is a neutron star undergoing free precession, a model has been proposed that interprets the pulsar as a quark star undergoing forced precession due to an orbiting "quark planet". The entry for the pulsar on SIMBAD lists this hypothesis as being controversial.
PSR J0437−4715 is a pulsar. Discovered in the Parkes 70 cm survey, it remains the closest and brightest millisecond pulsar (MSP) known. The pulsar rotates about its axis 173.7 times per second and therefore completes a rotation every 5.75 milliseconds. It emits a searchlight-like radio beam that sweeps past the Earth each time it rotates. Currently the most precisely located object outside of the Solar System, PSR J0437-4715 is 156.3 parsecs or 509.8 light-years distant.

PSR B1937+21 is a pulsar located in the constellation Vulpecula a few degrees in the sky away from the first discovered pulsar, PSR B1919+21. The name PSR B1937+21 is derived from the word "pulsar" and the declination and right ascension at which it is located, with the "B" indicating that the coordinates are for the 1950.0 epoch. PSR B1937+21 was discovered in 1982 by Don Backer, Shri Kulkarni, Carl Heiles, Michael Davis, and Miller Goss.
PSR J0108−1431 is a solitary pulsar located at a distance of about 130 parsecs (424 light-years) in the constellation Cetus. This pulsar was discovered in 1994 during the Parkes Southern Pulsar Survey. It is considered a very old pulsar with an estimated age of 166 million years and a rotation period of 0.8 seconds. The rotational energy being generated by the spin-down of this pulsar is 5.8 × 1023 W and the surface magnetic field is 2.5 × 107 T. As of 2008, it is the second faintest known pulsar.
PSR J1614–2230 is a pulsar in a binary system with a white dwarf in the constellation Scorpius. It was discovered in 2006 with the Parkes telescope in a survey of unidentified gamma ray sources in the Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope catalog. PSR J1614–2230 is a millisecond pulsar, a type of neutron star, that spins on its axis roughly 317 times per second, corresponding to a period of 3.15 milliseconds. Like all pulsars, it emits radiation in a beam, similar to a lighthouse. Emission from PSR J1614–2230 is observed as pulses at the spin period of PSR J1614–2230. The pulsed nature of its emission allows for the arrival of individual pulses to be timed. By measuring the arrival time of pulses, astronomers observed the delay of pulse arrivals from PSR J1614–2230 when it was passing behind its companion from the vantage point of Earth. By measuring this delay, known as the Shapiro delay, astronomers determined the mass of PSR J1614–2230 and its companion. The team performing the observations found that the mass of PSR J1614–2230 is 1.97 ± 0.04 M☉. This mass made PSR J1614–2230 the most massive known neutron star at the time of discovery, and rules out many neutron star equations of state that include exotic matter such as hyperons and kaon condensates.
PSR B0943+10 is a pulsar 2,000 light years from Earth in the direction of the constellation of Leo. It was discovered at Pushchino in December 1968, becoming the first pulsar discovered by Soviet astronomers. The original designation of this pulsar was PP 0943

PSR J0952–0607 is a massive millisecond pulsar in a binary system, located between 3,200–5,700 light-years (970–1,740 pc) away from Earth in the constellation Sextans. It holds the record for being the most massive neutron star known as of 2022, with a mass 2.35±0.17 times as much as the Sun—potentially close to the Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff mass upper limit for neutron stars. The pulsar rotates at a frequency of 707 Hz, making it the second-fastest-spinning pulsar known, and the fastest-spinning pulsar known within the Milky Way.











