
Triacanthidae, the triplespines or tripodfishes, is a family of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Tetraodontiformes, whicj also includes the pufferfishes, boxfishes, filefishes and related groups. The family is made up of four extant genera and three extinct genera which are known from fossils.

The spikefishes are ray-finned fishes related to the pufferfishes and triggerfishes. They live in deep waters; more than 50 m (160 ft), but above the continental shelves. They are found in the Atlantic, Indian Ocean, and the west-central Pacific.
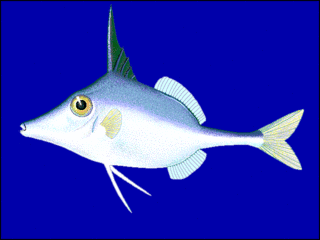
Triacanthus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthidae, the triplespines or tripodfishes. The two species in this genus are found in the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Tripodichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthidae, the triplespines or tripodfishes. The three species in this genus are found in the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean in shallow water over soft substrates.
Bathyphylax is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. The fishes in this genus are found in the deep waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Halimochirurgus is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. The fishes in this genus are found in the deep waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Hollardia is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. These demersal fishes are found in the Western Atlantic Ocean with one species being found in the Pacific Ocean.

Macrorhamphosodes, the trumpetsnouts, is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. The fishes in this genus are found in the deep waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
Mephisto fraserbrunneri, the devil's spikefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. This species is found in the Indian Ocean.
Mephisto is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. These fishes are found in the Indian Ocean.

Parahollardia is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. These demersal fishes are found in the Western Atlantic Ocean.

Triacanthodes is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. These fishes are found found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
Tydemania navigatoris, the fleshy-lipped spikefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. This species is found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans where it occurs at depths of from 50 to 607 metres. This species grows to a length of 12 centimetres (4.7 in) SL. This fish is specialized to feed on the scales of other fishes. This species is the only known member of the genus Tydemania.

Triacanthus biaculeatus, also known as the short-nosed tripod fish, black-finned triple-spine, blacktail tripodfish, hollow-snouted tripodfish or silver tripodfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthidae, the triplespines or tripodfishes. This species is found in the Indo-West Pacific region.

Triacanthodes ethiops, the shortsnout spikefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. This species is found in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.

Paratriacanthodes retrospinis, the sawspine spikefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. This species is found in the Indo-Pacific region.

Triacanthus nieuhofii, the silver tripodfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthidae, the triplespines or tripodfishes. This species is found in the Indo-West Pacific region.

Triacanthodes anomalus, the red spikefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. This species is found in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.

Triacanthoidei is a suborder of ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Tetraodontiformes, which includes the pufferfishes, triggerfishes and related taxa. These benthic fishes are mainly found in the Indian Ocean with some of the spikefishes found in the Western Atlantic Ocean.

Triacanthodinae is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triacanthodidae, the spikefishes. This subfamily comprises nine genera and a total of nineteen species and all, except one species, are found in the tropical and subtropical waters of the Indo-Pacific. The exception is found in the western Atlantic Ocean.











