
The Vercors massif is a mountain range in eastern France consisting of rugged plateaus and mountains straddling the départements of Isère and Drôme in the French Prealps. It lies west of the Dauphiné Alps, from which it is separated by the rivers Drac and Isère. The cliffs at the massif's eastern limit face the city of Grenoble.

The Massif Central is a highland region in south-central France consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France.

The Diablerets are a huge ice-covered mountain massif of the Alps, culminating at the Sommet des Diablerets (VS) at 3,216 metres (10,551 ft) above sea level and almost straddling the border between the Swiss cantons of Vaud (VD) and Valais (VS). The northeastern part of the massif stretches also into the canton of Bern (BE).

The French Alps are the portions of the Alps mountain range that stand within France, located in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur regions. While some of the ranges of the French Alps are entirely in France, others, such as the Mont Blanc massif, are shared with Switzerland and Italy.

The Grand Combin is a mountain massif in the western Pennine Alps in the canton of Valais. At a height of 4,309 metres (14,137 ft) the summit of Combin de Grafeneire is one of the highest peaks in the Alps and the second most prominent of the Pennine Alps. The Grand Combin is also a large glaciated massif consisting of several summits, among which three are above 4000 metres. The highest part of the massif is wholly in Switzerland, although the border with Italy lies a few kilometres south.

The Mont Blanc massif is a mountain range in the Alps, located mostly in France and Italy, but also straddling Switzerland at its northeastern end. It contains eleven major independent summits, each over 4,000 metres (13,123 ft) in height. It is named after Mont Blanc, the highest point in western Europe and the European Union. Because of its considerable overall altitude, a large proportion of the massif is covered by glaciers, which include the Mer de Glace and the Miage Glacier – the longest glaciers in France and Italy, respectively.
Massif des Cerces is a region of the French Alps on the Franco-Italian border. On the French side it lies in the departments of Hautes-Alpes and Savoie.

The Vanoise massif is a mountain range of the Graian Alps, located in the Western Alps. After the Mont Blanc Massif and the Écrins Massif it is the third-highest massif in France, reaching a height of 3,885 m at the summit of Grande Casse. It lies between Tarentaise Valley to the north and the Maurienne Valley in the south. The range is the site of France's first national park, established in 1963, Vanoise National Park. The ski resorts of Tignes and Val-d'Isère and the 2,770-metre-high Col de l'Iseran are located in the eastern part of the range.

Mouxy is a commune in the Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.

Mont Bégo is a mountain in the Mercantour massif of the Maritime Alps, in southern France, with an elevation of 2,872 metres (9,423 ft). It is included in the Vallée des Merveilles.

The Vaucluse Mountains are a mountain range of the French Prealps located in the departement of Vaucluse, between the Luberon Massif and Mont Ventoux.

The Grand Veymont, a mountain in the district of Gresse-en-Vercors, part of the department of Isère, France, is the highest point of the Massif du Vercors, but not the highest of the Vercors Regional Natural Park. It has a prominence of 1165 metres and an isolation of 26.88 kilometres.

Mont Pelat (3,050m), is a mountain of the Maritime Alps located in the chain of mountains between the high valley of Verdon to the west, the high valley of Var to the east and the Bachelard valley in the North. Located in the department of Alpes-de-Haute-Provence, it is the namesake of the Pelat Massif. The summit is located in the central area of the Mercantour National Park. It is known as being one of the easiest of the 3,000m Alpine peaks to climb. It overlooks the magnificent glacial Allos Lake, the largest mountain lake in Europe, which is 2,227 m (7,306 ft) above sea level.

Massif des Trois-Évêchés is a mountain range in the Provence Alps and Prealps in Alpes-de-Haute-Provence, France. Its name comes from the central summit of the massif, the Pic des Trois-Évêchés where there are ridges to the north, west and south. The highest peak is the Tête de l'Estrop, at 2,961 metres (9,715 ft).

The Second Battle of the Alps was a military campaign fought between combined German and Italian Social Republic forces, and the re-established French Republic led by Charles de Gaulle and other Allied forces.

The Mercantour-Argentera massif is a massif in the Maritime Alps located astride the French departments of Alpes-Maritimes and Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and the Italian region of Piedmont. The name of the massif comes respectively from the summit of Mercantour, a secondary central summit, and from Mount Argentera, the highest point of the massif, entirely in Italy.
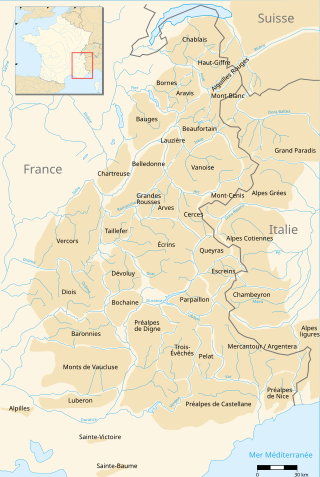
The Nice Prealps are a massif in the southern part of the French Prealps located mainly in the south-east of the French department of Alpes-Maritimes and, for a very small part, in the Italian region of Liguria between the Roya river and the Franco-Italian border.

The Digne Prealps are a massif in the southern part of the French Prealps located in the department of Alpes-de-Haute-Provence.

The Castellane Prealps are a massif of the southern French Prealps located in the departments of Alpes-Maritimes, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and Var. The easternmost part is often called the Préalpes de Grasse.

The Arves massif are a massif in the French Alps located in the departments of Savoie, Isère and Hautes-Alpes. Oisans covers part of the massif.




















