Related Research Articles
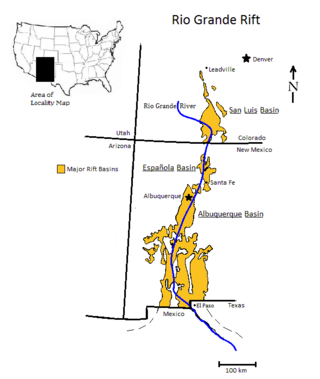
The Rio Grande rift is a north-trending continental rift zone. It separates the Colorado Plateau in the west from the interior of the North American craton on the east. The rift extends from central Colorado in the north to the state of Chihuahua, Mexico, in the south. The rift zone consists of four basins that have an average width of 50 kilometres (31 mi). The rift can be observed on location at Rio Grande National Forest, White Sands National Park, Santa Fe National Forest, and Cibola National Forest, among other locations.

The African Plate, also known as the Nubian Plate, is a major tectonic plate that includes much of the continent of Africa and the adjacent oceanic crust to the west and south. It is bounded by the North American Plate and South American Plate to the west ; the Arabian Plate and Somali Plate to the east; the Eurasian Plate, Aegean Sea Plate and Anatolian Plate to the north; and the Antarctic Plate to the south.

In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben with normal faulting and rift-flank uplifts mainly on one side. Where rifts remain above sea level they form a rift valley, which may be filled by water forming a rift lake. The axis of the rift area may contain volcanic rocks, and active volcanism is a part of many, but not all, active rift systems.
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust.

The Cameroon line is a 1,600 km (1,000 mi) long chain of volcanoes that includes islands in the Gulf of Guinea and mountains on the African mainland, from Mount Cameroon on the coast towards Lake Chad on the northeast. They form a natural border between eastern Nigeria and the West Region of Cameroon. The islands, which span the equator, have tropical climates and are home to many unique plant and bird species. The mainland mountain regions are much cooler than the surrounding lowlands, and also contain unique and ecologically important environments.

The Rio de la Plata Craton (RPC) is a medium-sized continental block found in Uruguay, eastern Argentina and southern Brazil. During its complex and protracted history it interacted with a series other blocks and is therefore considered important for the understanding of the amalgamation of West Gondwana. Two orogenic cycles have been identified in the RPC: a 2000 Ma-old western domain representing the old craton and a 700–500 Ma-old eastern domain assigned to the Brasiliano Cycle. It is one of the five cratons of the South American continent. The other four cratons are: Amazonia, São Francisco, Río Apa and Arequipa–Antofalla.

The Southwest Indian Ridge (SWIR) is a mid-ocean ridge located along the floors of the south-west Indian Ocean and south-east Atlantic Ocean. A divergent tectonic plate boundary separating the Somali Plate to the north from the Antarctic Plate to the south, the SWIR is characterised by ultra-slow spreading rates (only exceeding those of the Gakkel Ridge in the Arctic) combined with a fast lengthening of its axis between the two flanking triple junctions, Rodrigues (20°30′S70°00′E) in the Indian Ocean and Bouvet (54°17′S1°5′W) in the Atlantic Ocean.

The Olympic-Wallowa lineament (OWL) – first reported by cartographer Erwin Raisz in 1945 on a relief map of the continental United States – is a physiographic feature of unknown origin in the state of Washington running approximately from the town of Port Angeles, on the Olympic Peninsula to the Wallowa Mountains of eastern Oregon.

The Brothers Fault Zone (BFZ) is the most notable of a set of northwest-trending fault zones including the Eugene–Denio, McLoughlin, and Vale zones that dominate the geological structure of most of Oregon. These are also representative of a regional pattern of generally northwest-striking geological features ranging from Walker Lane on the California–Nevada border to the Olympic–Wallowa Lineament in Washington; these are generally associated with the regional extension and faulting of the Basin and Range Province, of which the BFZ is considered the northern boundary.

The Puget Sound faults under the heavily populated Puget Sound region of Washington state form a regional complex of interrelated seismogenic (earthquake-causing) geologic faults. These include the:

The Central African Shear Zone (CASZ) is a wrench fault system extending in an ENE direction from the Gulf of Guinea through Cameroon into Sudan. The structure is not well understood. As of 2008, there was still no general agreement about how the individual shears along the lineament link up.

The Benue Trough is a major geological structure underlying a large part of Nigeria and extending about 1,000 km northeast from the Bight of Benin to Lake Chad. It is part of the broader West and Central African Rift System.
The Trans Brazilian Lineament (TBL), or Transbrasiliano Lineament, is a major shear zone that developed in the Precambrian period, and that has been reactivated several times since then, mostly recently during the Mesozoic. Movement along the shear zone helps explain how the South American continent could have fitted tightly to the African continent before the breakup of Gondwana.
The Pharusian Ocean is an ancient ocean that existed from 800 to 635 million years ago, between the break-up of the Rodinia supercontinent and the start of formation of the Gondwana supercontinent.
The Kandi fault zone is a southern extension of the Hoggar fault zone in West Africa, with splays in Benin, Togo and southeastern Ghana. It lies at the southern end of the Trans Saharan belt, a lineament that extends in a southwest direction from Algeria to Benin. The Kandi fault zone is identified with the Sobral fault in northeastern Brazil, considered to be the northern section of the Trans Brazilian Lineament.
The Sobral fault is a major fault in the Borborema geological province of northeastern Brazil, a part of the Transbrasiliano lineament. It is commonly correlated with the Kandi fault in Benin, east of the West African craton. The fault lies in the northwest of Ceará state. It appears to have formed late in the orogeny when the West African craton engaged with the Congo craton, and to have allowed significant dextral strike-slip movement. It was reactivated when South America was breaking away from Africa. In this later phase, a sinistral shear movement of about 100 km seems to have taken place during and after the break-up.
The Foumban Shear Zone, or Central Cameroon Shear Zone (CCSZ), is a fault zone in Cameroon that has been correlated with the Pernambuco fault in northeastern Brazil, which splays from the Trans-Brazilian Lineament. It is part of the Central African Shear Zone (CASZ) and dates to at least 640 million years ago. The zone was rejuvenated several times, usually with a dextral movement, before and during the opening of the South Atlantic in the Cretaceous period.
The Damara orogeny was part of the Pan-African orogeny. The Damara orogeny occurred late in the creation of Gondwana, at the intersection of the Congo and the Kalahari cratons.

The geology of the Czech Republic is very tectonically complex, split between the Western Carpathian Mountains and the Bohemian Massif.
The geology of Brazil includes very ancient craton basement rock from the Precambrian overlain by sedimentary rocks and intruded by igneous activity, as well as impacted by the rifting of the Atlantic Ocean.
References
- 1 2 J D Fairhead, Nasreddine Bournas and M Chaker Raddadi (2007). "The Role of Gravity and Aeromagnetic Data in Mapping Mega Gondwana Crustal Lineaments: the Argentina - Brazil – Algeria (ABA) Lineament" (PDF). SEG. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-11. Retrieved 2011-01-30.
- ↑ Robert J. Pankhurst (2008). West Gondwana: pre-Cenozoic correlations across the South Atlantic Region. Geological Society. p. 91. ISBN 978-1-86239-247-2.
- ↑ Alain Vauchez and Marcos Egydio da Silva (November 1992). "Termination of a continental-scale strike-slip fault in partially melted crust: The West Pernambuco shear zone, northeast Brazil". Geology. 20 (11): 1007–1010. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<1007:TOACSS>2.3.CO;2 . Retrieved 2011-02-03.
7°50′S38°15′W / 7.833°S 38.250°W